Abstract
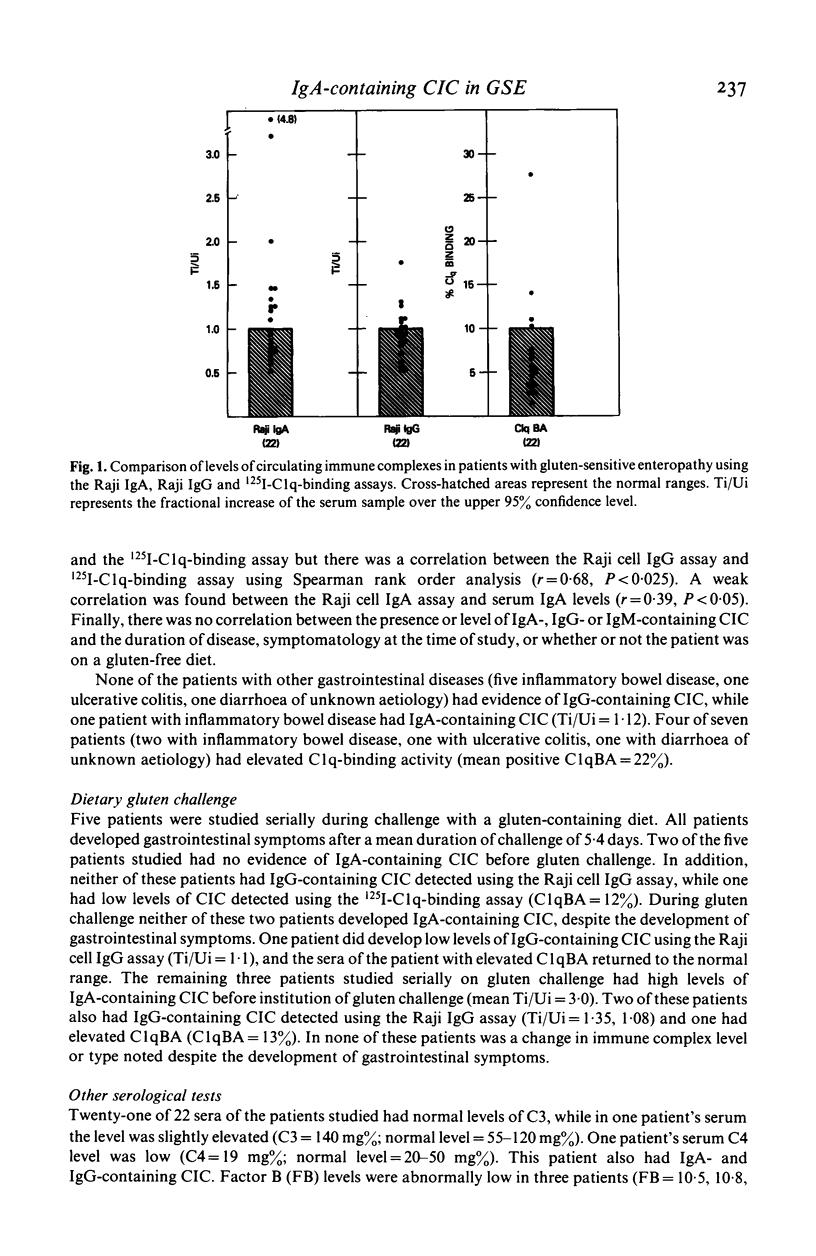
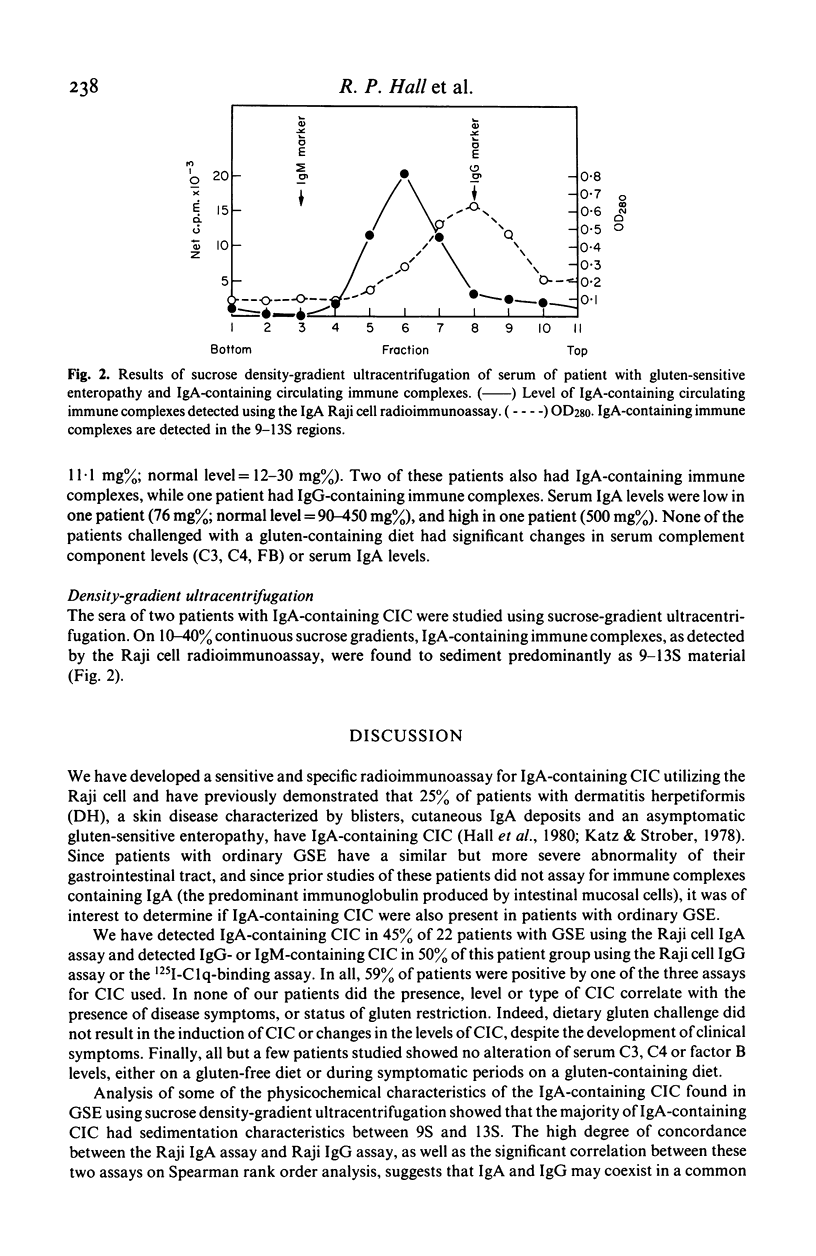
Since mucosal immune response involving IgA may be particularly important in the pathogenesis of gluten-sensitive enteropathy (GSE), we examined the sera of 22 patients with GSE for IgA-containing circulating immune complexes using a sensitive radioimmunoassay, the Raji cell assay for IgA-containing circulating immune complexes. The Raji cell assay for IgG-containing circulating immune complexes and the 125I-C1q-binding assay were also used to measure IgG- or IgM-containing circulating immune complexes in these patients. Ten of 22 (45%) patients had IgA-containing circulating immune complexes, while 11 of 22 (50%) had IgG- or IgM-containing circulating immune complexes. Thirteen of 22 (59%) patients had circulating immune complexes detected by at least one of the assays used. Neither the presence nor level of immune complexes correlated with disease activity in any of the patients studied. Five patients, whose disease was well controlled on a gluten-free diet, were studied serially during dietary challenge with gluten. It was found that IgA-containing circulating immune complexes did not develop or increase in amount in the serum of these patients despite the induction of gastrointestinal symptoms. In addition, no significant change in IgG- or IgM- containing circulating immune complexes occurred in any of the challenged patients. No significant abnormalities of serum complement levels (C3, C4, factor B) were detected in any of the patients including those challenged with gluten. Sucrose density-gradient ultracentrifugation studies revealed that the IgA-containing circulating immune complexes had sedimentation characteristics between 9S and 13S. The presence of circulating immune complexes in only 59% of patients with GSE, their lack of correlation with disease activity, and their failure to change during dietary gluten challenge suggests that circulating immune complexes do not play a primary role in the pathogenesis of GSE.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Doe W. F., Booth C. C., Brown D. L. Evidence for complement-binding immune complexes in adult coeliac disease, Crohn's disease, and ulcerative colitis. Lancet. 1973 Feb 24;1(7800):402–403. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90254-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falchuk Z. M., Strober W. Gluten-sensitive enteropathy: synthesis of antigliadin antibody in vitro. Gut. 1974 Dec;15(12):947–952. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.12.947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Götze O., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The C3-activator system: an alternate pathway of complement activation. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 2):90s–108s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R. P., Lawley T. J., Heck J. A., Katz S. I. IgA-containing circulating immune complexes in dermatitis herpetiformis, Henoch-Schönlein purpura, systemic lupus erythematosus and other diseases. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Jun;40(3):431–437. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz S. I., Strober W. The pathogenesis of dermatitis herpetiformis. J Invest Dermatol. 1978 Feb;70(2):63–75. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12541202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawley T. J., Moutsopoulos H. M., Katz S. I., Theofilopoulos A. N., Chused T. M., Frank M. M. Demonstration of circulating immune complexes in Sjögren's syndrome. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1382–1387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb P. M., Strober W., Falchuk Z. M., Laster L. Incorporation of L-leucine-14C into immunoglobulins by jejunal biopsies of patients with celiac sprue and other gastrointestinal diseases. J Clin Invest. 1971 Mar;50(3):559–569. doi: 10.1172/JCI106525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed I., Holborow E. J., Fry L., Thompson B. R., Hoffbrand A. V., Stewart J. S. Multiple immune complexes and hypocomplementaemia in dermatitis herpetiformis and coeliac disease. Lancet. 1976 Sep 4;1(7984):487–490. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90787-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Dixon F. J., Bokisch V. A. Binding of soluble immune complexes to human lymphoblastoid cells. I. Characterization of receptors for IgG Fc and complement and description of the binding mechanism. J Exp Med. 1974 Oct 1;140(4):877–894. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.4.877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Wilson C. B., Dixon F. J. The Raji cell radioimmune assay for detecting immune complexes in human sera. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jan;57(1):169–182. doi: 10.1172/JCI108257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodroffe A. J., Border W. A., Theofilopoulos A. N., Götze O., Glassock R. J., Dixon F. J., Wilson C. B. Detection of circulating immune complexes in patients with glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1977 Oct;12(4):268–278. doi: 10.1038/ki.1977.111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



