Abstract
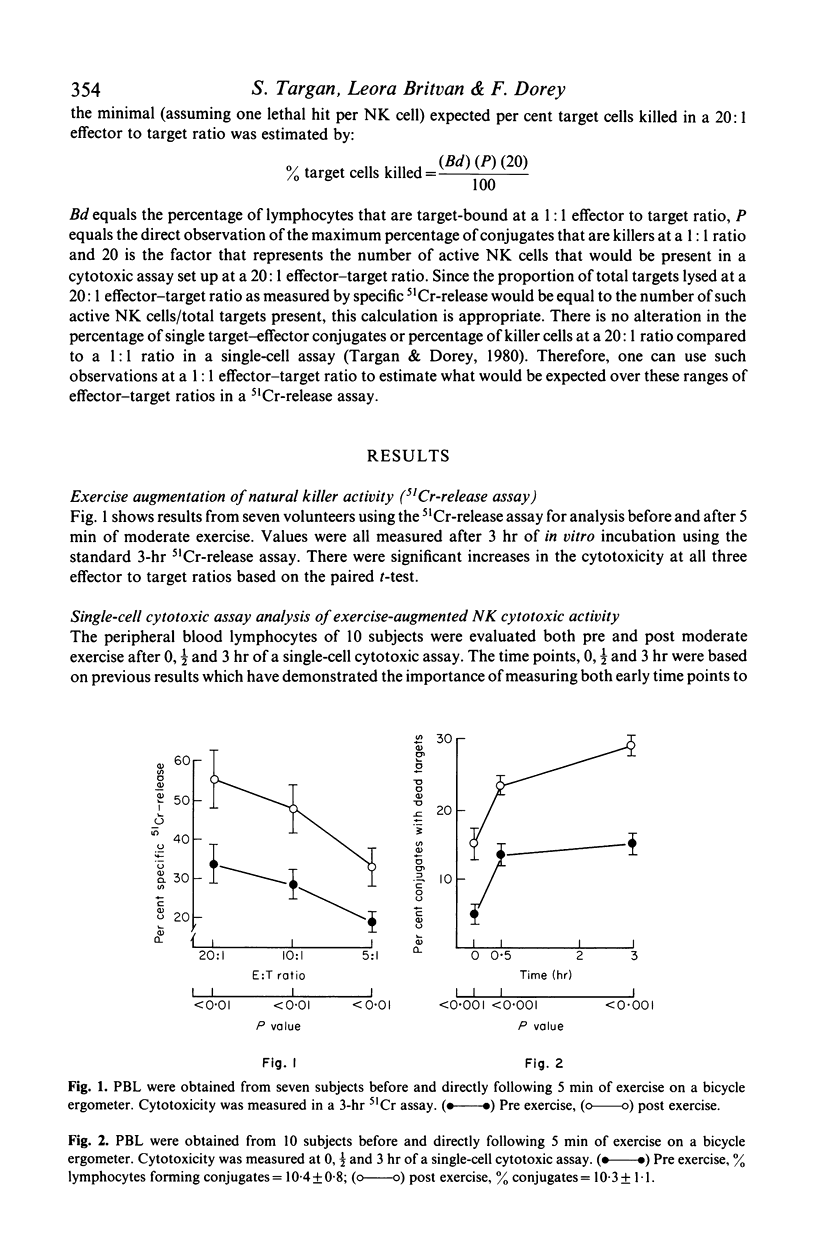
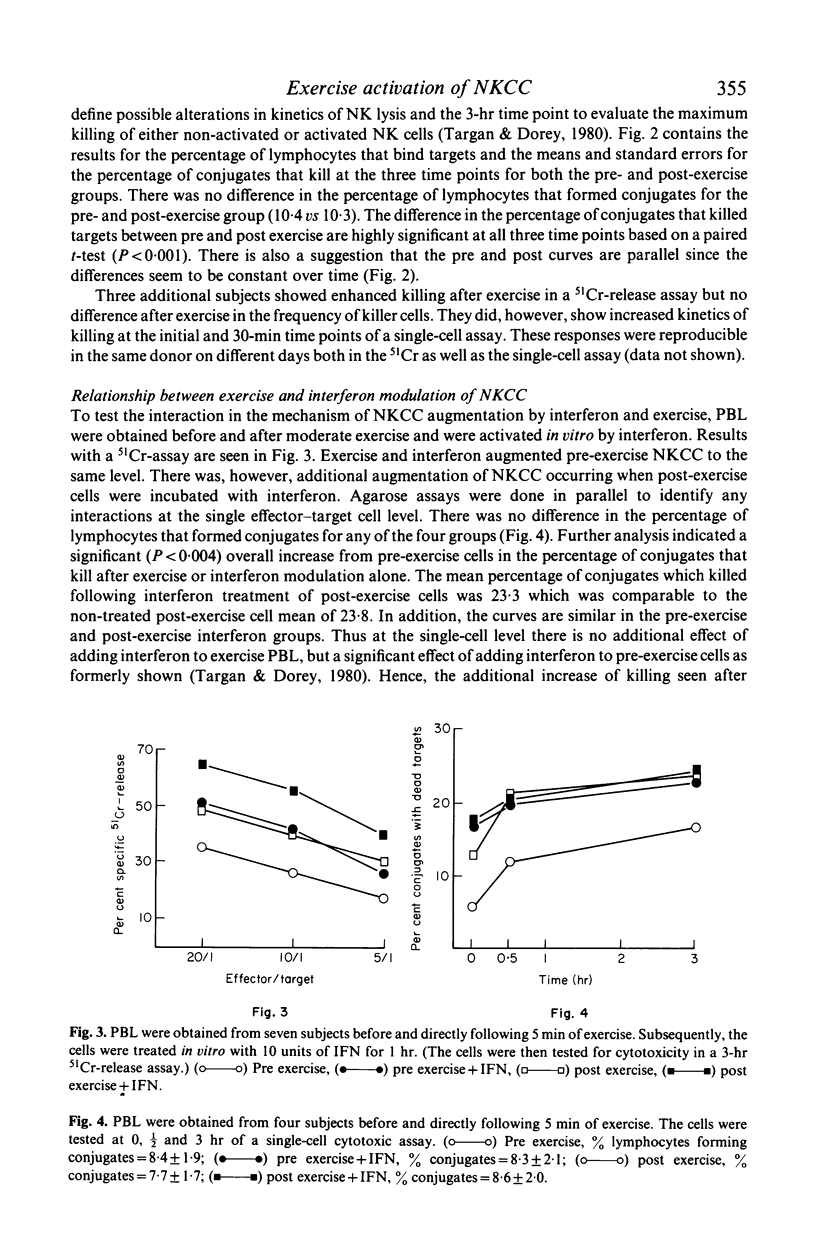
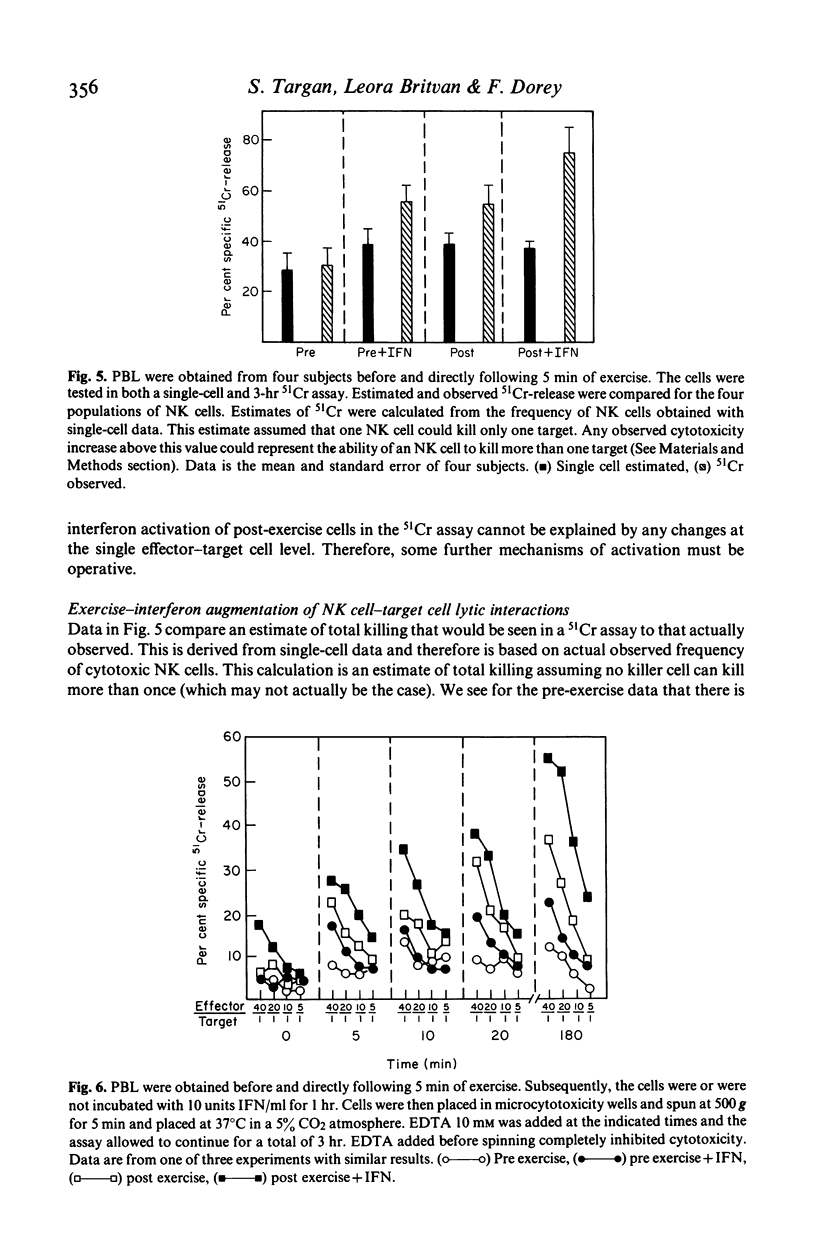
In the present study we examined the mechanism of human natural killer cellular cytotoxicity (NKCC) augmentation by 5 min of moderate exercise and its interrelationship to in vitro interferon (IFN) activation. Cytotoxicity was measured by employing both a single-cell cytotoxic assay and a standard 3-hr chromium-51 (51Cr) release assay. The former was used to assess changes at the single NK cell--target cell level and the latter to assess changes in overall lytic capacity of a given population of NK cells. Several findings were obtained: (1) moderate exercise augmented NKCC in vivo by recruiting a 'new' population of active cytotoxic NK cells. (2) This 'new' population of active cells probably was derived from cells which can bind targets but are non-cytotoxic. (3) In a standard 51Cr-release assay, additional augmentation of these exercise-activated cells occurred in vitro following exposure to interferon. (4) This additional increase in cytotoxicity produced no alteration in the frequency of killer cells as viewed at the single cell level. (5) Thus interferon's capacity to increase further the overall lytic ability of exercise-activated NK cells was not due to its activation of an additional subset of pre-NK cells, but due to its increasing the capacity of effector--target lytic interactions (recycling) of the same set of NK and pre-NK cells.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berke G., Sullivan K. A., Amos D. B. Tumor immunity in vitro: destruction of a mouse ascites tumor through a cycling pathway. Science. 1972 Aug 4;177(4047):433–434. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4047.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djeu J. Y., Heinbaugh J. A., Holden H. T., Herberman R. B. Augmentation of mouse natural killer cell activity by interferon and interferon inducers. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):175–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridman W. H., Gresser I., Bandu M. T., Aguet M., Neauport-Sautes C. Interferon enhances the expression of Fc gamma receptors. J Immunol. 1980 May;124(5):2436–2441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm E., Bonavida B. Mechanism of cell-mediated cytotoxicity at the single cell level. I. Estimation of cytotoxic T lymphocyte frequency and relative lytic efficiency. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2861–2869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Djeu J., Kay H. D., Ortaldo J. R., Riccardi C., Bonnard G. D., Holden H. T., Fagnani R., Santoni A., Puccetti P. Natural killer cells: characteristics and regulation of activity. Immunol Rev. 1979;44:43–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00267.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Nunn M. E., Holden H. T., Staal S., Djeu J. Y. Augmentation of natural cytotoxic reactivity of mouse lymphoid cells against syngeneic and allogeneic target cells. Int J Cancer. 1977 Apr 15;19(4):555–564. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910190417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh K., Inoue M., Kataoka S., Kumagai K. Differential effect of interferon expression of IgG- and IgM-Fc receptors on human lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2589–2595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Targan S. In vitro induction of cytotoxic effector cells with spontaneous killer cell specificity. J Exp Med. 1978 Jun 1;147(6):1621–1636. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.6.1621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai M., Leclerc J. C., McVay-Boudreau L., Shen F. W., Cantor H. Direct evidence that natural killer cells in nonimmune spleen cell populations prevent tumor growth in vivo. J Exp Med. 1979 May 1;149(5):1260–1264. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.5.1260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koivisto V., Soman V., Nadel E., Tamborlane W. V., Felig P. Exercise and insulin: insulin binding, insulin mobilization, and counterregulatory hormone secretion. Fed Proc. 1980 Apr;39(5):1481–1486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauel J., Rudolf H., Chapuis B., Brunner K. T. Studies of allograft immunity in mice. II. Mechanism of target cell inactivation in vitro by sensitized lymphocytes. Immunology. 1970 Apr;18(4):517–535. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack S. B., Emmons S. L. Kinetic analysis of human spontaneous cell-mediated cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1979 Jul;123(1):160–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva A., Bonavida B., Targan S. Mode of action of interferon-mediated modulation of natural killer cytotoxic activity: recruitment of pre-NK cells and enhanced kinetics of lysis. J Immunol. 1980 Aug;125(2):479–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Targan S., Dorey F. Interferon activation of "pre-spontaneous killer" (pre-SK) cells and alteration in kinetics of lysis of both "pre-SK" and active SK cells. J Immunol. 1980 May;124(5):2157–2161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey D. E., Wolfe S. A., Durdik J. M., Henney C. S. BCG-induced murine effector cells. I. Cytolytic activity in peritoneal exudates: an early response to BCG. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):1145–1151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh R. M., Jr Mouse natural killer cells: induction specificity, and function. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):1631–1635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh R. M., Jr, Zinkernagel R. M. Heterospecific cytotoxic cell activity induced during the first three days of acute lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection in mice. Nature. 1977 Aug 18;268(5621):646–648. doi: 10.1038/268646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe S. A., Tracey D. E., Henney C. S. BCG-induced murine effector cells. II. Characterization of natural killer cells in peritoneal exudates. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):1152–1158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarling J. M., Eskra L., Borden E. C., Horoszewicz J., Carter W. A. Activation of human natural killer cells cytotoxic for human leukemia cells by purified interferon. J Immunol. 1979 Jul;123(1):63–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


