Abstract
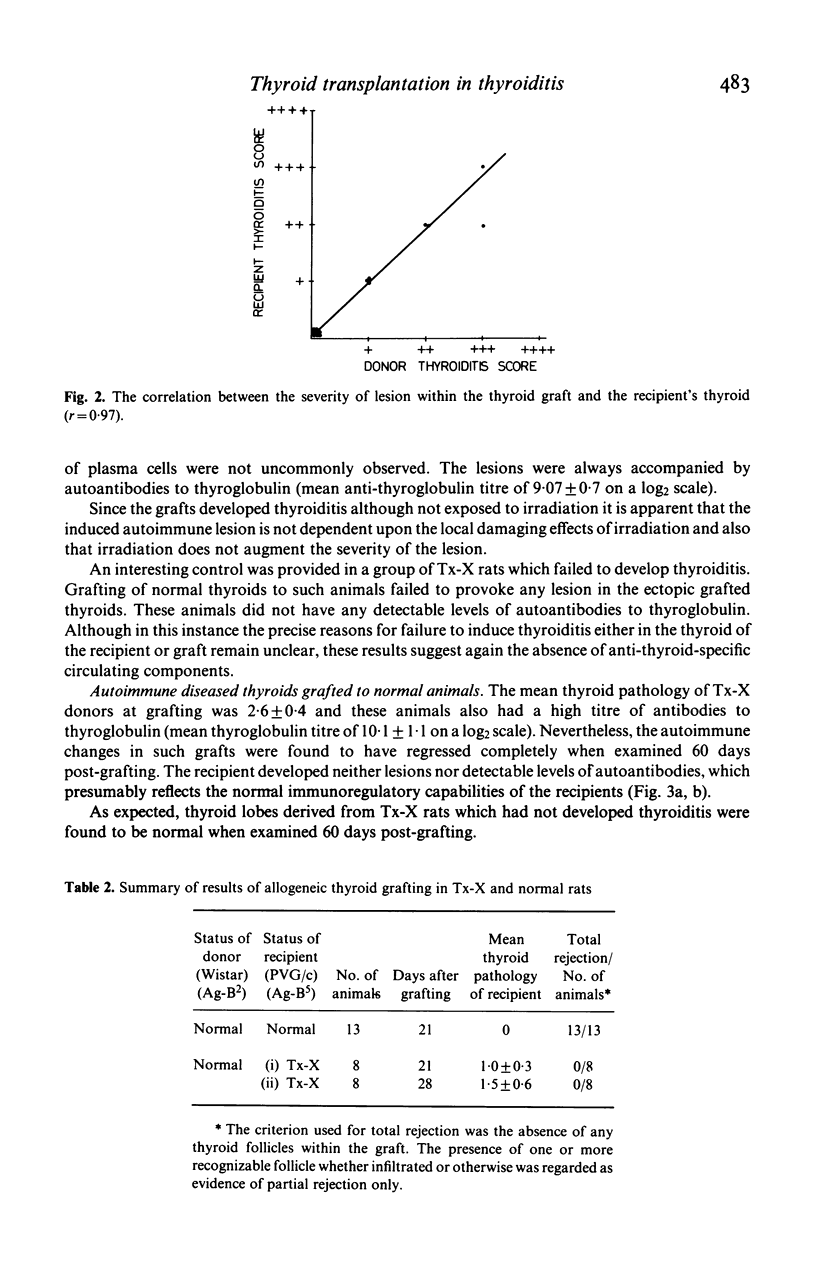
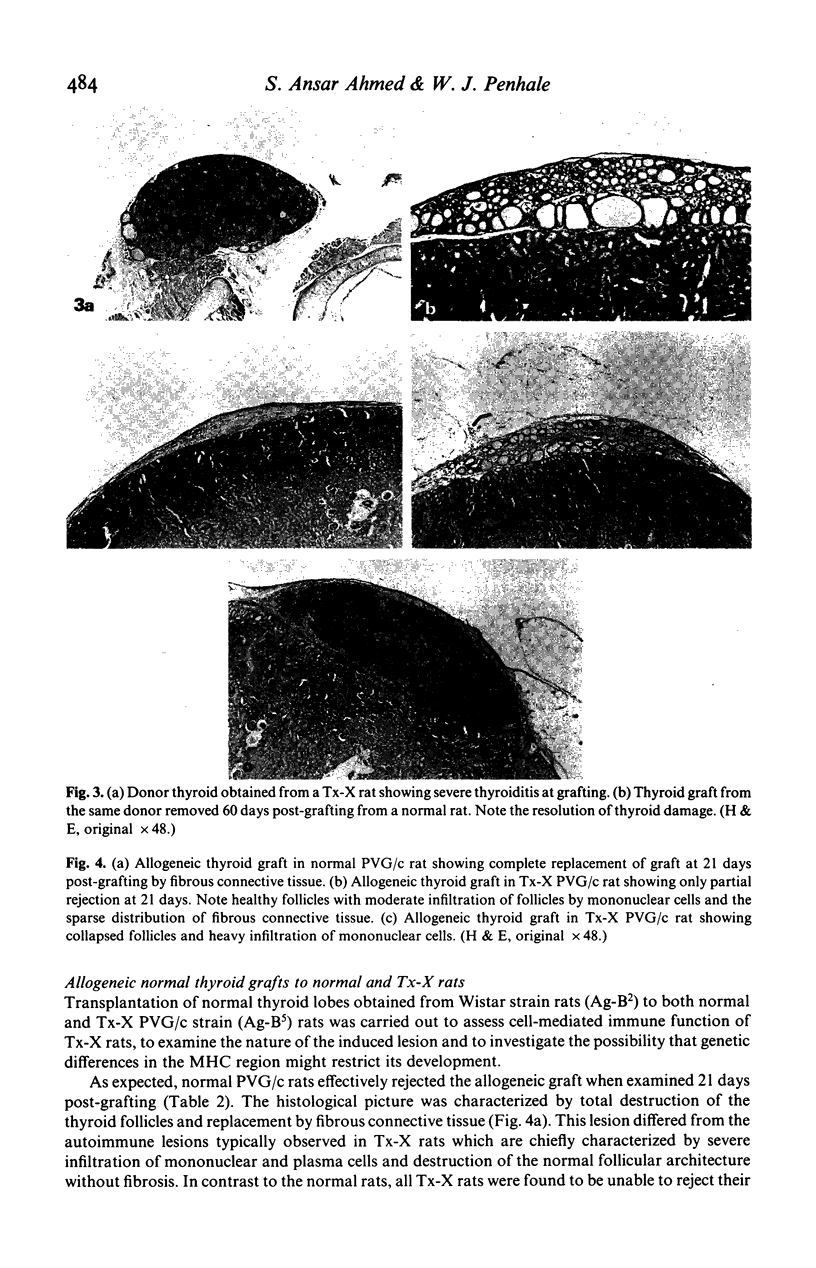
Post-irradiation transplantation of normal thyroids under the renal capsule of syngenetic thymectomized and irradiated (Tx-X) rats leads to the development of thyroiditis in the ectopic grafted thyroids. A close correlation was observed between the extent of the lesions in the grafted and recipient's own thyroid. The histopathology of both grafted and recipient thyroid was similar and was characterized by infiltration with mononuclear cells together with some plasma cells. Conversely, grafting of affected thyroids from Tx-X rats to normal animals resulted in the regression of the lesion in the graft and no evidence thyroiditis was observed in either the graft or the recipient's thyroid when these were examined 60 days post-grafting. Thyroids derived from normal animals grafted to syngenetic normal rats were found to remain healthy and intact over a 60-day period. In contrast to normal animals, Tx-X rats were unable to reject totally in transplanted allogeneic thyroids by 28 days post-grafting, suggesting that some impairment of cell-mediated immunity follows this treatment. These findings indicate that the pathological change occurring in the thyroid gland of Tx-X rats is not attributable to the local effect of irradiation of the thyroids and adds further support to the concept that the process is immunologically mediated by thyroid-specific circulating components in the absence of normal immune regulatory function.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Nun A., Maron R., Ron Y., Cohen I. R. H-2 gene products influence susceptibility of target thyroid gland to damage in experimental autoimmune thyroiditis. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Feb;10(2):156–159. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostoff J. Migration inhibition studies in human disease. Proc R Soc Med. 1970 Sep;63(9):905–906. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calder E. A., McLeman D., Barnes E. W., Irvine W. J. The effect of thyroid antigens on the in vitro migration of leucocytes from patients with Hashimoto thyroiditis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Dec;12(4):429–438. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper M. D., Raymond D. A., Peterson R. D., South M. A., Good R. A. The functions of the thymus system and the bursa system in the chicken. J Exp Med. 1966 Jan 1;123(1):75–102. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLAX M. H., JANKOVIC B. D., SELL S. Experimental allergic thyroiditis in the guinea pig. I. Relationship of delayed hypersensitivity and circulating antibody to the development of thyroiditis. Lab Invest. 1963 Jan;12:119–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajdu A., Rona G. Spontaneous thyroiditis in laboratory rats. Experientia. 1969 Dec 15;25(12):1325–1327. doi: 10.1007/BF01897529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANKOVIC B. D., ISVANESKI M., KILOSEVIC D., POPESKOVIC L. Delayed hypersensitive reactions in bursectomized chickens. Nature. 1963 Apr 20;198:298–299. doi: 10.1038/198298a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANKOVIC B. D., WAKSMAN B. H., ARNASON B. G. Role of the thymus in immune ractions in rats. I. The immunologic response to bovine serum albumin (antibody formation, Arthus reactivity, and delayed hypersensitivity) in rats thymectomized or splenectomized at various times after birth. J Exp Med. 1962 Aug 1;116:159–176. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.2.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kite J. H., Jr, Wick G., Twarog B., Witebsky E. Spontaneous thyroiditis in an obese strain of chickens. II. Investigations on the development of the disease. J Immunol. 1969 Dec;103(6):1331–1341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin M. S., Salvin S. B. Further studies on the mechanism of experimental autoimmune thyroiditis in guinea pigs. Properties of thyroid cytotoxic factor (TCF) and its relationship to pathogenesis of the disease. Cell Immunol. 1976 Dec;27(2):188–199. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90228-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCMASTER P. R., LERNER E. M., 2nd, EXUM E. D. The relationship of delayed hypersensitivity and circulating antibody to experimental allergic thyroditis in inbred guinea pigs. J Exp Med. 1961 Apr 1;113:611–624. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.4.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER J. F. Immunological function of the thymus. Lancet. 1961 Sep 30;2(7205):748–749. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(61)90693-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penhale W. J., Farmer A., Irvine W. J. Thyroiditis in T cell-depleted rats. Influence of strain, radiation dose, adjuvants and antilymphocyte serum. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Sep;21(3):362–375. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penhale W. J., Farmer A., McKenna R. P., Irvine W. J. Spontaneous thyroiditis in thymectomized and irradiated Wistar rats. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Oct;15(2):225–236. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penhale W. J., Irvine W. J., Inglis J. R., Farmer A. Thyroiditis in T cell-depleted rats: suppression of the autoallergic response by reconstitution with normal lymphoid cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Jul;25(1):6–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman D. A., Rose N. R. Autoimmunity in methylcholanthrene-induced and spontaneous thyroiditis in Buffalo strain rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Nov;138(2):579–584. doi: 10.3181/00379727-138-35945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]