Abstract
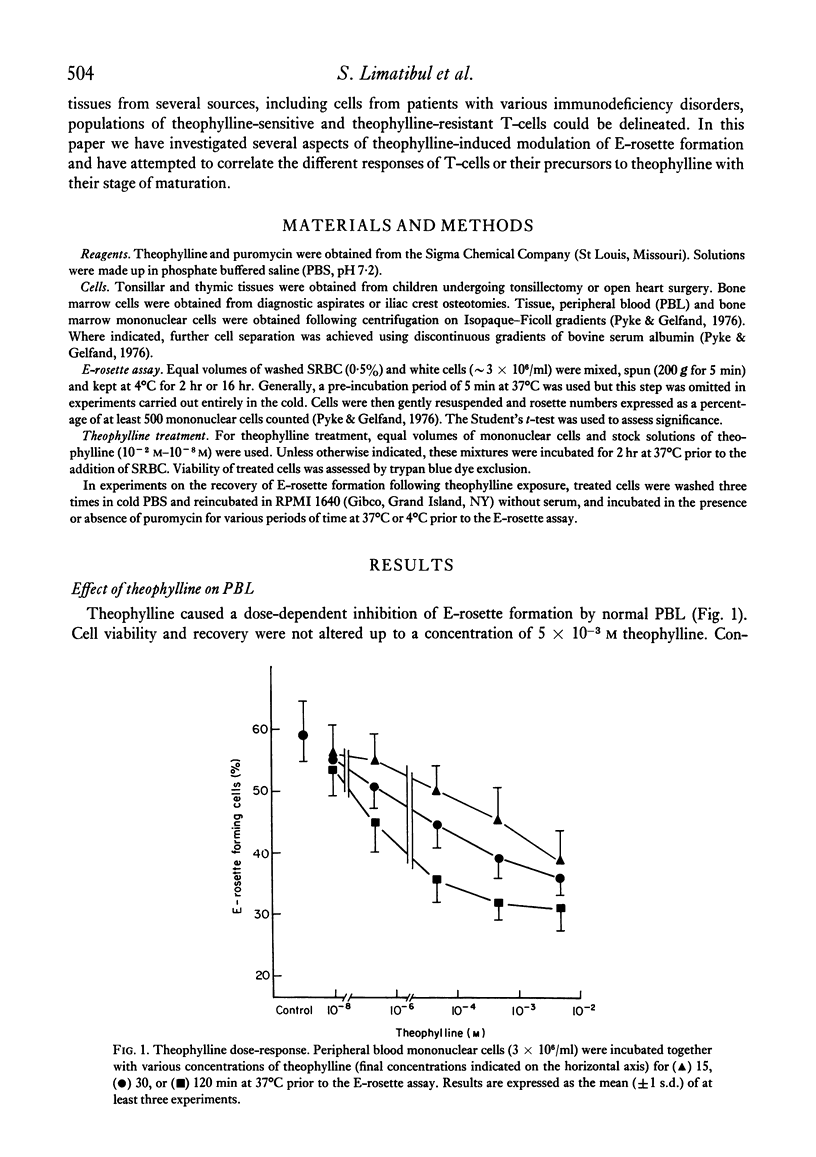
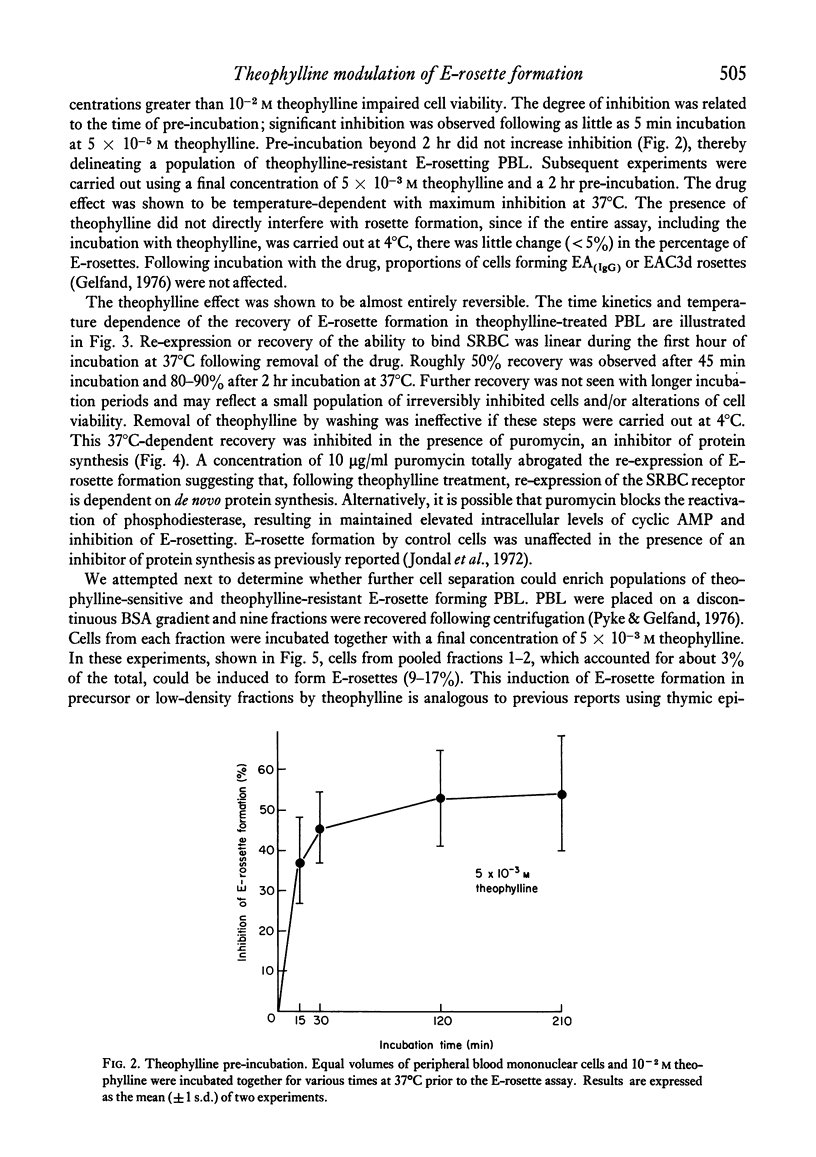
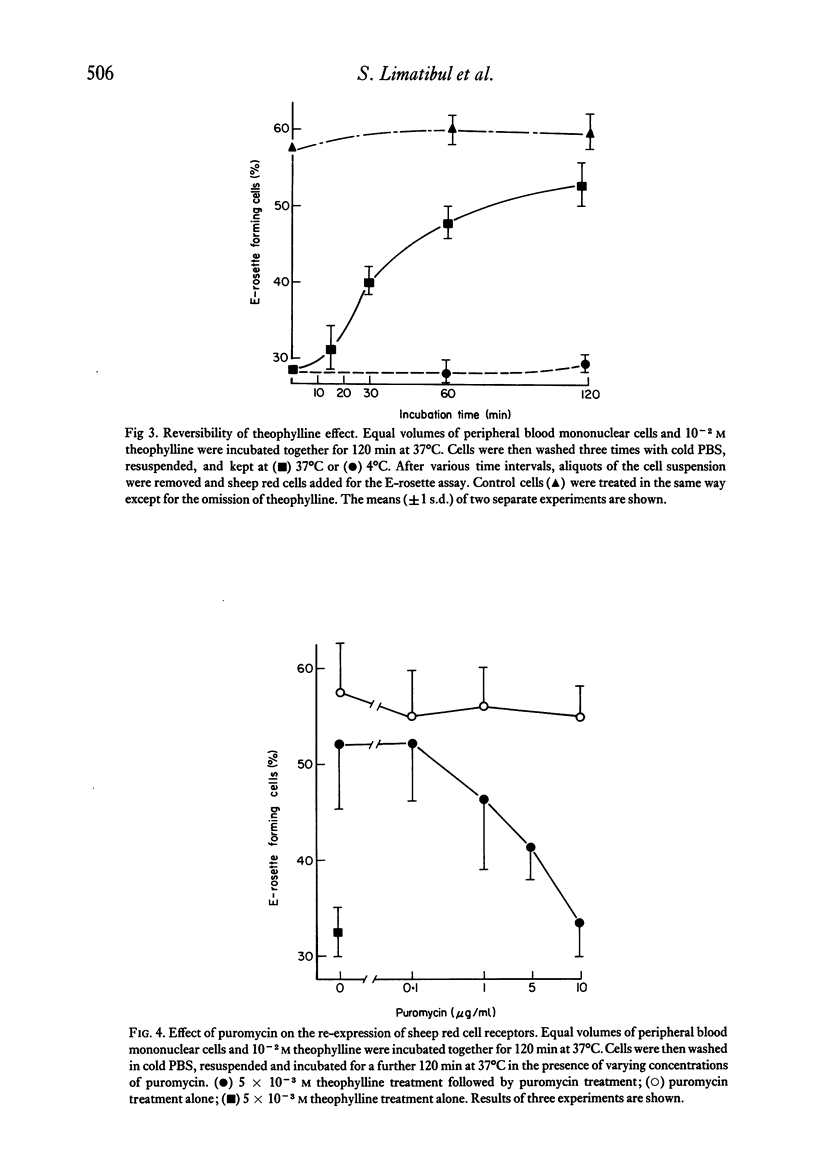
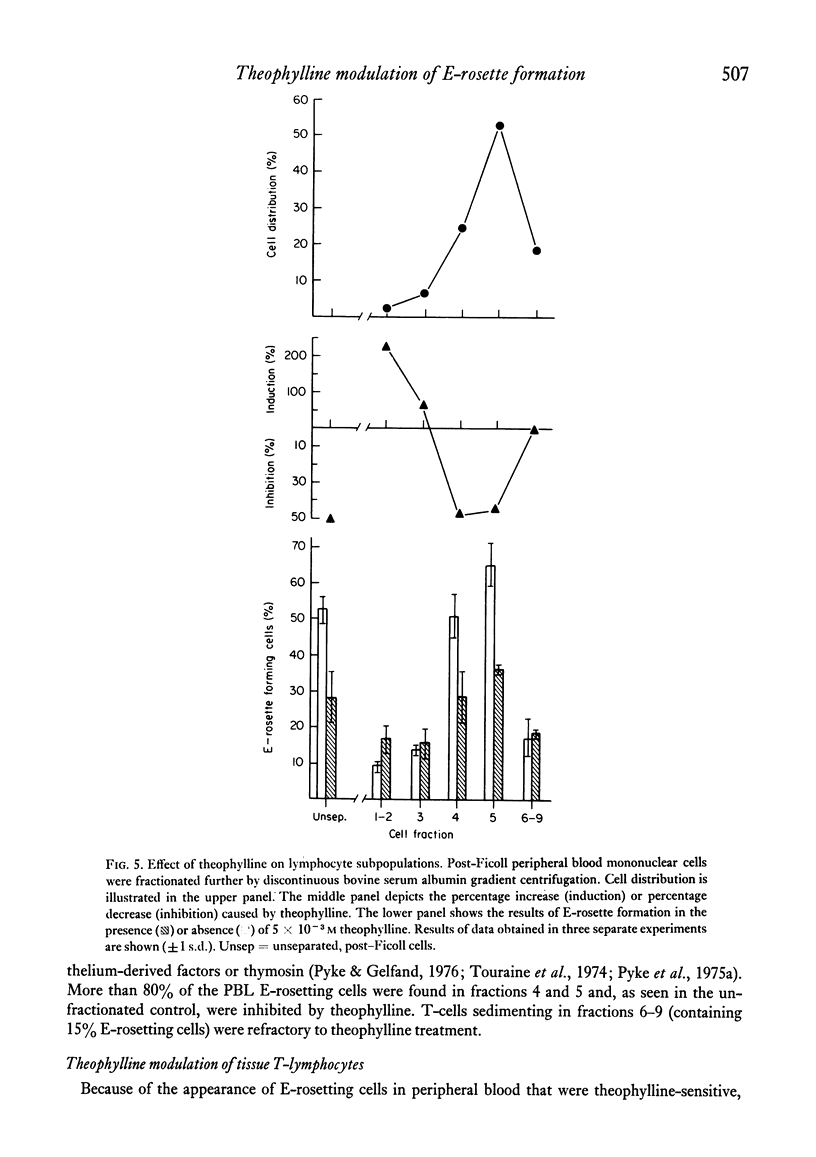
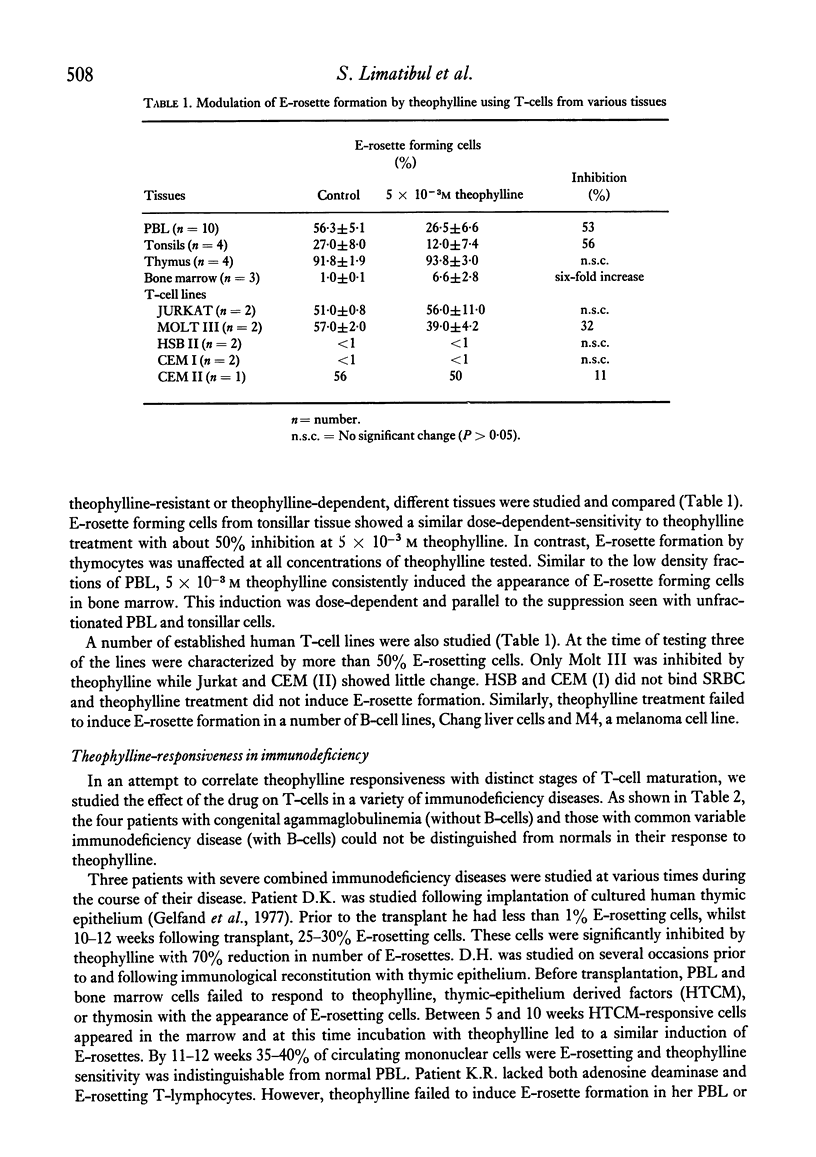
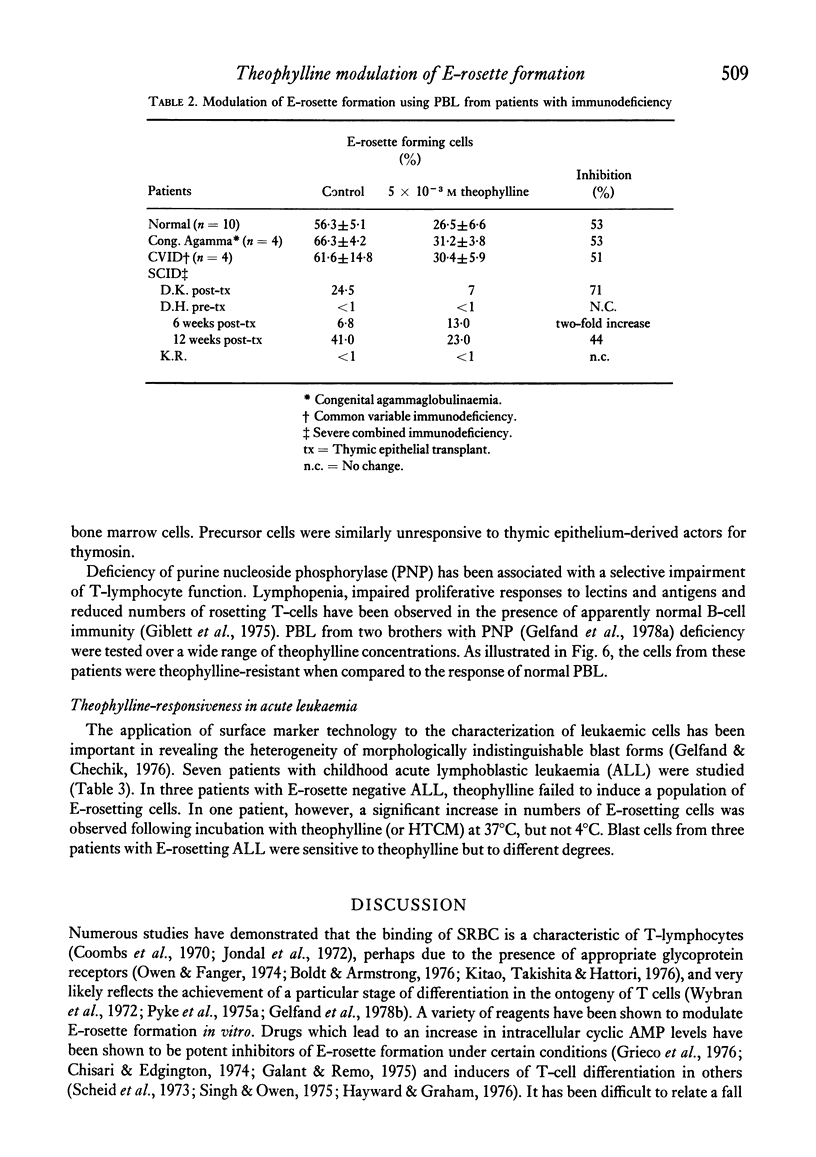
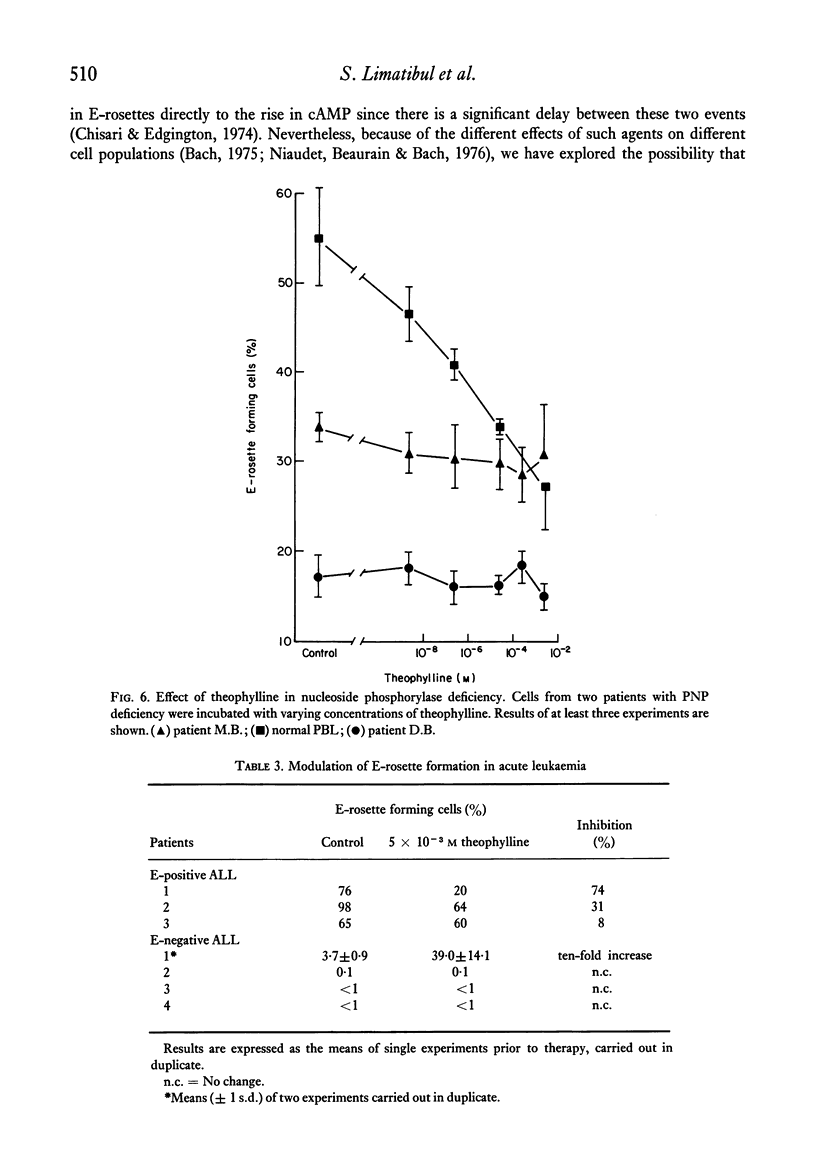
The binding of unsensitized sheep erythrocytes is a characteristic of human thymus dependent T-lymphocytes. We have investigated the effect of theophylline on E-rosette formation using cells from normal individuals, and patients with immunodeficiency or acute lymphoblastic leukaemia, and have attempted to correlate the influence of the drug on distinct T-lymphocyte subpopulations. Three subpopulations of E-rosetting T-lymphocytes can be delineated: theophylline-sensitive T-cells which lose the capacity to form E-rosettes following treatment; theophylline-resistant T-cells which are unaffected by the drug; and theophylline-dependent cells which acquire the ability to form E-rosettes following incubation with theophylline. The action of theophylline was shown to be dose-dependent, temperature-dependent and reversible. Reversibility or re-expression of the receptor for sheep red cells could be blocked by the addition of puromycin. In peripheral blood, E-rosetting T-lymphocytes were roughly divided into two equal populations, one sensitive, the other resistant. Thymocytes were shown to be entirely theophylline-resistant, whereas a small population of cells in peripheral blood and bone marrow were induced to become E-rosetting in the presence of theophylline. Induction by theophylline may be effective at a distinct stage of precursor T-cell differentiation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bach J. F., Carnaud C. Thymic factors. Prog Allergy. 1976;21:342–408. doi: 10.1159/000399402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach M. A. Differences in Cyclic AMP Changes after Stimulation by Prostaglandins and Isoproterenol in Lymphocyte Subpopulations. J Clin Invest. 1975 May;55(5):1074–1081. doi: 10.1172/JCI108008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boldt D. H., Armstrong J. P. Rosette formation between human lymphocytes and sheep erythrocytes. Inhibition of rosette formation by specific glycopeptides. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):1068–1078. doi: 10.1172/JCI108349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borella L., Sen L. E receptors on blasts from untreated acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL): comparison of temperature dependence of E rosettes formed by normal and leukemic lymphoid cells. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 1):187–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chechik B. E., Pyke K. W., Gelfand E. W. Human thymus/leukemia-associated antigen in normal and leukemic cells. Int J Cancer. 1976 Nov 15;18(5):551–556. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910180502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V., Edgington T. S. Human T lymphocyte "E" rosette function. I. A process modulated by intracellular cyclic AMP. J Exp Med. 1974 Oct 1;140(4):1122–1126. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.4.1122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coombs R. R., Gurner B. W., Wilson A. B., Holm G., Lindgren B. Rosette-formation between human lymphocytes and sheep red cells not involving immunoglobulin receptors. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1970;39(5-6):658–663. doi: 10.1159/000230390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dosch H-M, Gelfand E. W. Generation of human plaque-forming cells in culture: tissue distribution, antigenic and cellular requirements. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):302–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galant S. P., Remo R. A. Beta-adrenergic inhibition of human T lymphocyte rosettes. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 2):512–513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand E. W., Chechik B. E. Editorial: Unmasking the heterogeneity of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 1976 Jan 29;294(5):275–276. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197601292940511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand E. W., Dosch H. M., Biggar W. D., Fox I. H. Partial purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency. Studies of lymphocyte function. J Clin Invest. 1978 Apr;61(4):1071–1080. doi: 10.1172/JCI109006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand E. W. Role of the C3 receptor in antibody-dependent cytotoxicity. Transplantation. 1976 Jan;21(1):73–75. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197601000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giblett E. R., Ammann A. J., Wara D. W., Sandman R., Diamond L. K. Nucleoside-phosphorylase deficiency in a child with severely defective T-cell immunity and normal B-cell immunity. Lancet. 1975 May 3;1(7914):1010–1013. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91950-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grieco M. H., Siegel I., Goel Z. Modulation of human T lymphocyte rosette formation by autonomic agonists and cyclic nucleotides. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1976 Jul;58(1 Pt 2):149–159. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(76)90150-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Holm G., Wigzell H. Surface markers on human T and B lymphocytes. I. A large population of lymphocytes forming nonimmune rosettes with sheep red blood cells. J Exp Med. 1972 Aug 1;136(2):207–215. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp R. G., Duquesnoy R. J. Lymphoid cell adenylate cyclase activity after x-irradiation and cortisone treatment. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 1):660–664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitao T., Takeshita M., Hattori K. Studies on glycopeptide released by trypsin from sheep erythrocytes. J Immunol. 1976 Jul;117(1):310–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niaudet P., Beaurain G., Bach M. A. Differences in effect of isoproterenol stimulation on levels of cyclic AMP in human B and T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Nov;6(11):834–836. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830061117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen F. L., Fanger M. W. Studies on the human T-lymphocyte population. II. The use of a T-cell specific antibody in the partial isolation and characterization of the human lymphocyte receptor for sheep red blood cells. J Immunol. 1974 Oct;113(4):1138–1144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyke K. W., Dosch H., Ipp M. M., Gelfand E. W. Demonstration of an intrathymic defect in a case of severe combined immunodeficiency disease. N Engl J Med. 1975 Aug 28;293(9):424–428. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197508282930904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyke K. W., Gelfand E. W. Detection of T-precursor cells in human bone marrow and foetal liver. Differentiation. 1976 Jun 4;5(2-3):189–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1976.tb00914.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyke K. W., Rawlings G. A., Gelfand E. W. Isolation and characterization of the sheep erythrocyte receptor in man. J Immunol. 1975 Jul;115(1):211–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid M. P., Hoffmann M. K., Komuro K., Hämmerling U., Abbott J., Boyse E. A., Cohen G. H., Hooper J. A., Schulof R. S., Goldstein A. L. Differentiation of T cells induced by preparations from thymus and by nonthymic agents. J Exp Med. 1973 Oct 1;138(4):1027–1032. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.4.1027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore A., Dosch H., Gelfand E. W. Induction and separation of antigen-dependent T helper and T suppressor cells in man. Nature. 1978 Aug 10;274(5671):586–587. doi: 10.1038/274586a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh U., Owen J. J. Studies on the effect of various agents on the maturation of thymus stem cells. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Apr;5(4):286–288. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukimoto I., Wong K. Y., Lampkin B. C. Surface markers and prognostic factors in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 1976 Jan 29;294(5):245–248. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197601292940503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wybran J., Carr M. C., Fudenberg H. H. The human rosette-forming cell as a marker of a population of thymus-derived cells. J Clin Invest. 1972 Oct;51(10):2537–2543. doi: 10.1172/JCI107069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dicke KA Hooft J. I., van Bekkum D. W. The selective elimination of immunologically competent cells from bone marrow and lymphatic cell mixtures. II. Mouse spleen cell fractionation on a discontinuous albumin gradient. Transplantation. 1968 Jul;6(4):562–570. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196807000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


