Abstract
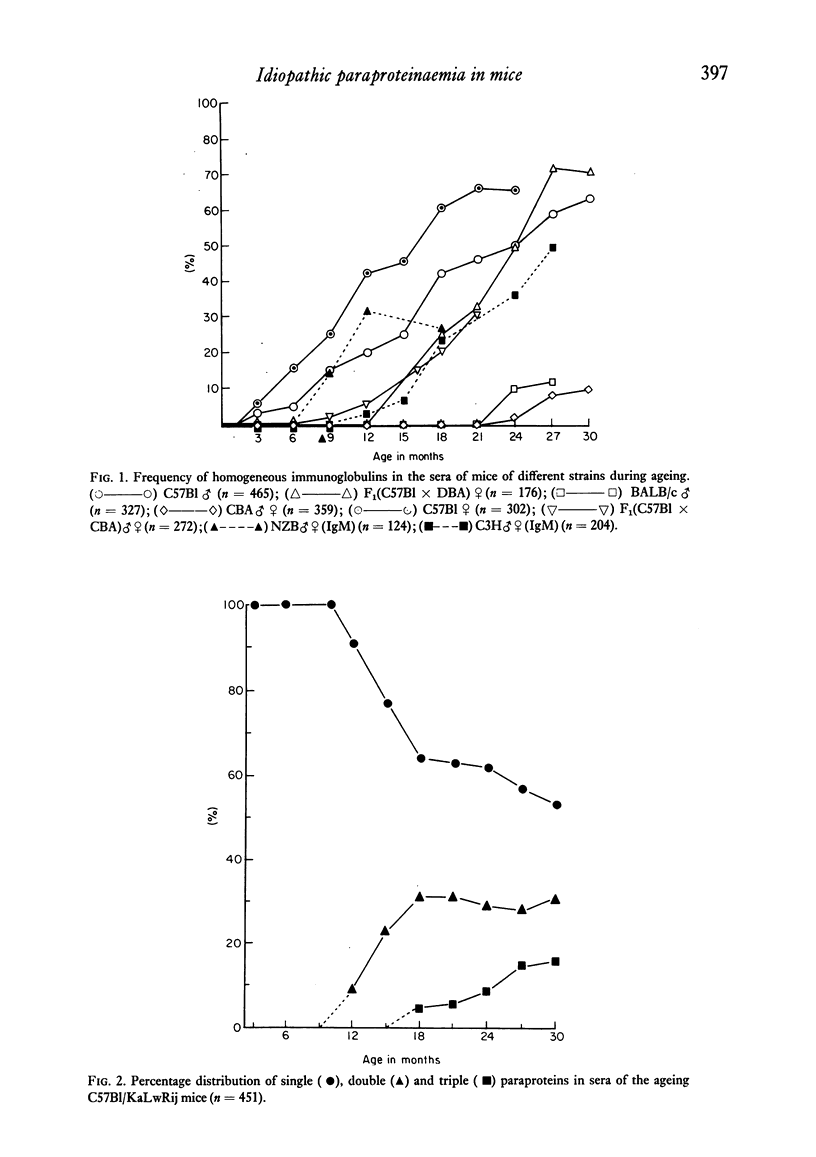
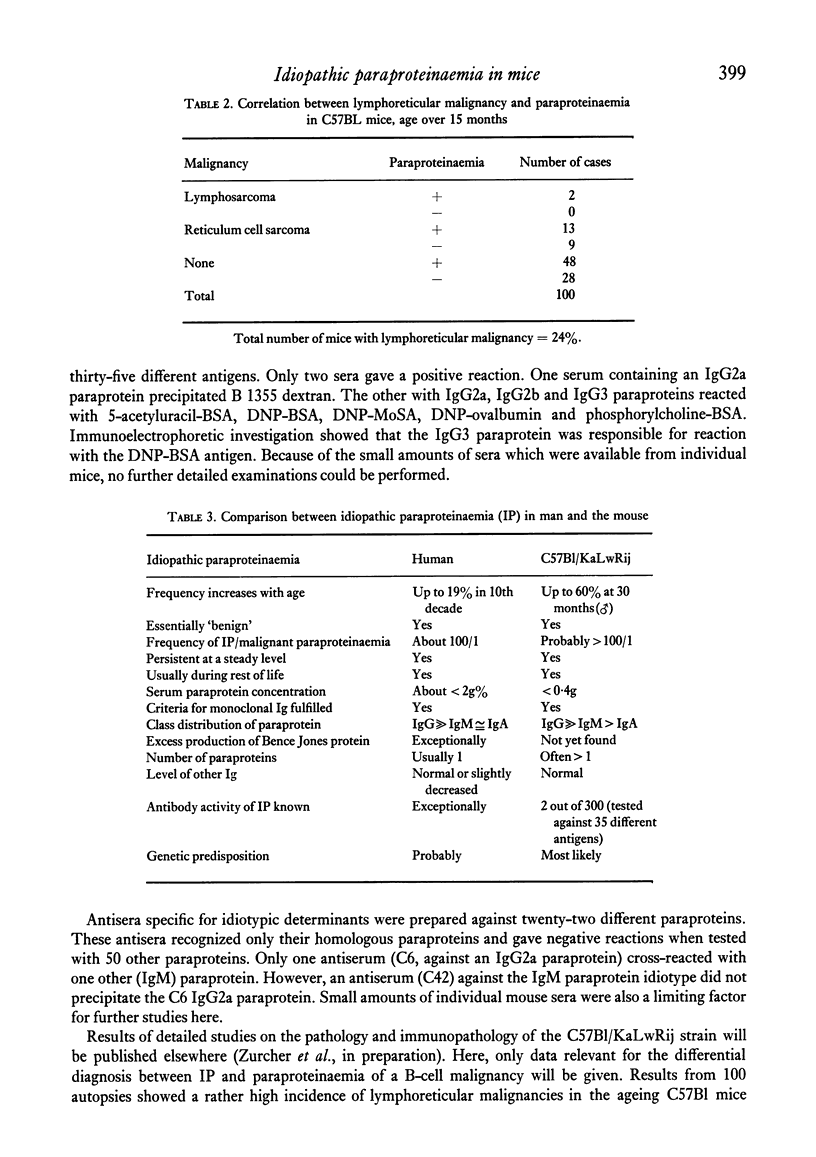
A search for a suitable animal model for studies on idiopathic paraproteinaemia showed that an age-dependent increase in the appearance of homogeneous immunoglobulins in serum was common to all of the seven mouse strains investigated to date. The highest frequency was found in C57Bl/KaLwRij mice. Further investigations in this strain demonstrated that, except for some quantitative differences, most of the features of human and C57BL Mouse idiopathic paraproteinaemia were essentially the same. No clear-cut correlation was found between the idiopathic paraproteinaemia and, in the old C57B1 mice, a rather frequently occurring reticulum cell sarcoma B and amyloidosis. The mouse idiopathic paraproteinaemia can be regarded as an analogue of the human idiopathic paraproteinaemia and therefore as a suitable model for further experimental studies.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelsson U., Bachmann R., Hällén J. Frequency of pathological proteins (M-components) om 6,995 sera from an adult population. Acta Med Scand. 1966 Feb;179(2):235–247. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1966.tb05453.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloemmen F. J., Rádl J., Haaijman J. J., Van den Berg P., Schuit H. R., Hijmans W. Microfluorometric evaluation of the specificity of fluorescent antisera against mouse immunoglobulins with the defined antigen substrate spheres (DASS) system. J Immunol Methods. 1976;10(4):337–355. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cejka J., Kithier K. A simple method for the classification and typing of monoclonal immunoglobulins. Immunochemistry. 1976 Jul;13(7):629–631. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(76)90176-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUNN T. B. Normal and pathologic anatomy of the reticular tissue in laboratory mice, with a classification and discussion of neoplasms. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1954 Jun;14(6):1281–1433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englisová M., Englis M., Kyral V., Kourílek K., Dvorák K. Changes of immunoglobulin synthesis in old people. Exp Gerontol. 1968 Aug;3(2):125–127. doi: 10.1016/0531-5565(68)90019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hällén J. Discrete gammaglobulin (M-)components in serum. Clinical study of 150 subjects without myelomatosis. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1966;462:1–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kersey J. H., Spector B. D., Good R. A. Primary immunodeficiency and malignancy. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1975;11(1):289–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijers K. A., De Leeu M. B., Voormolen-Kălova M. The multiple occurrence of myeloma and asymptomatic paraproteinaemia within one family. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Oct;12(2):185–193. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter M. Immunoglobulin-producing tumors and myeloma proteins of mice. Physiol Rev. 1972 Jul;52(3):631–719. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1972.52.3.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radl J., Dooren L. H., Morell A., Skvaril F., Vossen J. M., Uittenbogaart C. H. Immunoglobulins and transient paraproteins in sera of patients with the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome: a follow-up study. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Aug;25(2):256–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radl J., Swart A. C., Mestecky J. The nature of the polymeric serum IgA in man. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Nov;150(2):482–484. doi: 10.3181/00379727-150-39061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radl J., de Glopper E., de Groot G. A rapid, simple, and reliable technique for preparation of antisera against idiotypes of homogeneous immunoglobulins. Vox Sang. 1978 Jul-Aug;35(1-2):10–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1978.tb02894.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rádl J., Hollander C. F. Homogeneous immunoglobulins in sera of mice during aging. J Immunol. 1974 Jun;112(6):2271–2273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligmann M., Brouet J. C. Antibody activity of human myeloma globulins. Semin Hematol. 1973 Apr;10(2):163–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelberg H. L. Biological activities of immunoglobulins of different classes and subclasses. Adv Immunol. 1974;19(0):259–294. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60254-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Camp B. G., Cole J., Peetermans M. E. HLA antigens and homogeneous immunoglobulins. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1977 May;7(3):315–318. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(77)90063-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voormolen-Kalova M., van den Berg P., Rádl J. Immunoglobulin levels as related to age in nonhuman primates in captivity. I. Chimpanzees. J Med Primatol. 1974;3(6):335–342. doi: 10.1159/000460104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawadzki Z. A., Edwards G. A. Nonmyelomatous monoclonal immunoglobulinemia. Prog Clin Immunol. 1972;1:105–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


