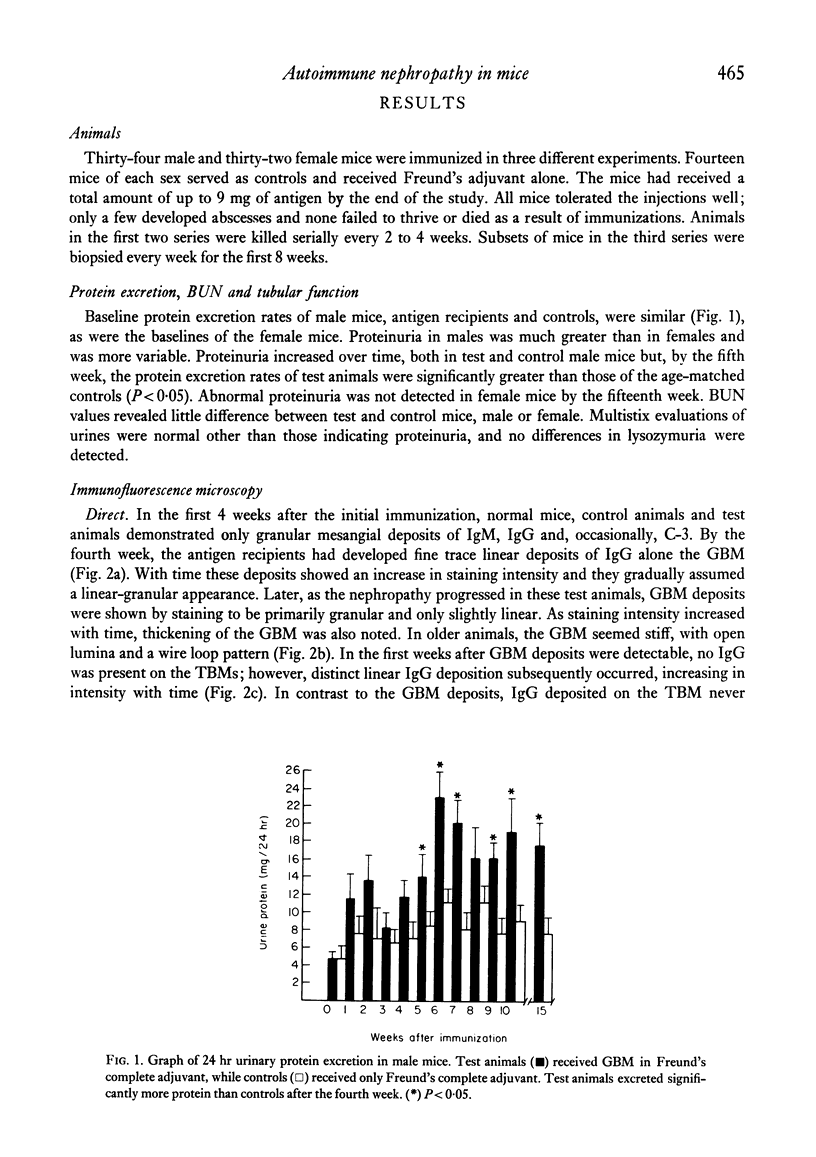
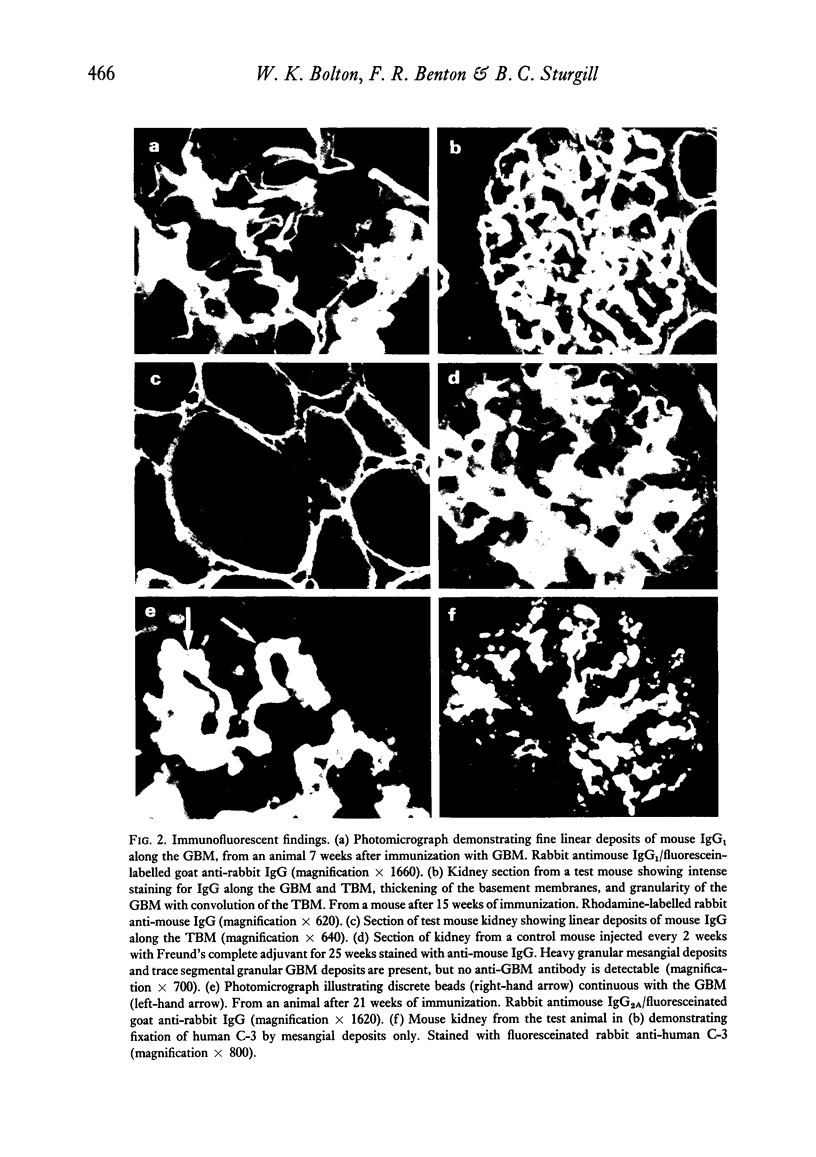
Abstract
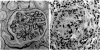
We produced an autoimmune glomerulotubular nephropathy in Swiss-Webster mice using human glomerular antigen in Freund's complete adjuvant. The disease is associated with circulating antibody to both mouse and human glomerular basement membranes (GBM) and tubular basement membranes (TBM). All mouse IgG subgroups are deposited initially in a linear pattern along the GBM and TBM. IgG deposition remains linear, while that of the other subgroups assumes a granular GBM pattern with continued linear TBM deposits. Despite tissue deposition of antibody capable of C-3 fixation, no C-3 is found in vivo along the GMB or TBM, nor is there C-3 fixation in vitro. This appears to be related to spatial limitations of IgG molecule attachment to basement membranes. A unique ultrastructural lesion of the GMB developed, characterized by periodic expansions of the lamina rara externa to form a beaded pattern. Eluate of nephritic kidneys contained all subgroups of IgG, but mainly IgG1 fixed in vitro to mouse kidney and in vivo when injected intravenously into normal mice. Fixation of other IgG subgroups in vivo may have resulted from antibody formation to abnormally formed GBM, thereby accounting for the peculiar ultrastructural findings and tissue fixation characteristics of the eluted immunoglobulin. Abnormal proteinuria without glycosuria or lysozymuria developed in test animals as compared to controls. Our model is similar in certain aspects to previously described models of Stebley nephritis, but differs because of the total involvement of TBMs, unique ultrastructural lesions, and dissimilarity to other reports of this model in mice.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agodoa L. C., Striker G. E., George C. R., Glassock R., Quadracci L. J. The appearance of nonlinear deposits of immunoglobulins in Goodpasture's syndrome. Am J Med. 1976 Sep;61(3):407–413. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90379-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avasthi P. S., Avasthi P., Tokuda S., Anderson R. E., Williams R. C., Jr Experimental glomerulonephritis in the mouse. I. The model. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Nov;9(5):667–676. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton W. K., Benton F. R., Maclay J. G., Sturgill B. C. Spontaneous glomerular sclerosis in aging Sprague-Dawley rats. I. Lesions associated with mesangial IgM deposits. Am J Pathol. 1976 Nov;85(2):277–302. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couser W. G., Spargo B. H., Stilmant M. M., Lewis E. J. Experimental glomerulonephritis in the guinea pig. II. Ultrastructural lesions of the basement membrane associated with proteinuria. Lab Invest. 1975 Jan;32(1):46–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couser W. G., Stilmant M., Lewis E. J. Experimental glomerulonephritis in the guinea pig. I. Glomerular lesions associated with antiglomerular basement membrane antibody deposits. Lab Invest. 1973 Aug;29(2):236–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffsten P. E., Hill C. L., Klahr S. Studies of abluminuria and proteinuria in normal mice and mice with immune complex glomerulonephritis. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Dec;86(6):920–930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer J. R., Elema J. D., Vernier R. L. Unilateral renal disease in the rat. II. Glomerular mesangial uptake of colloidal carbon in unilateral aminonucleoside nephrosis and nephrotoxic serum nephritis. Lab Invest. 1976 Mar;34(3):250–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAKOWER C. A., GREENSPON S. A. Localization of the nephrotoxic antigen within the isolated renal glomerulus. AMA Arch Pathol. 1951 Jun;51(6):629–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagrue G., Xheneumont S., Branellec A., Weil B. Letter: Lymphokines and nephrotic syndrome. Lancet. 1975 Feb 1;1(7901):271–272. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91164-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis E. J., Busch G. J., Schur P. H. Gamma G globulin subgroup composition of the glomerular deposits in human renal diseases. J Clin Invest. 1970 Jun;49(6):1103–1113. doi: 10.1172/JCI106326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhaul J. J., Jr, Dixon F. J. Characterization of human anti-glomerular basement membrane antibodies eluted from glomerulonephritic kidneys. J Clin Invest. 1970 Feb;49(2):308–317. doi: 10.1172/JCI106240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhaul J. J., Jr, Dixon F. J. Characterization of immunoglobulin G anti-glomerular basement membrane antibodies eluted from kidneys of patients with glomerulonephritis. II. IgG subtypes and in vitro complement fixation. J Immunol. 1971 Sep;107(3):678–684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEBLAY R. W. Glomerulonephritis induced in monkeys by injections of heterologous glomerular basement membrane and Freund's adjuvant. Nature. 1963 Mar 23;197:1173–1176. doi: 10.1038/1971173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEBLAY R. W. Glomerulonephritis induced in sheep by injections of heterologous glomerular basement membrane and Freund's complete adjuvant. J Exp Med. 1962 Aug 1;116:253–272. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.2.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler M. W., Venkatachalam M. A., Cotran R. S. Glomerular epithelium: structural alterations induced by polycations. Science. 1975 Aug 1;189(4200):390–393. doi: 10.1126/science.1145209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalhoub R. J. Pathogenesis of lipoid nephrosis: a disorder of T-cell function. Lancet. 1974 Sep 7;2(7880):556–560. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91880-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UNANUE E., DIXON F. J. EXPERIMENTAL GLOMERULONEPHRITIS. IV. PARTICIPATION OF COMPLEMENT IN NEPHROTOXIC NEPHRITIS. J Exp Med. 1964 Jan 1;119:965–982. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.6.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Dixon F. J. Experimental allergic glomerulonephritis induced in the rabbit with heterologous renal antigens. J Exp Med. 1967 Jan 1;125(1):149–162. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.1.149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]