Abstract
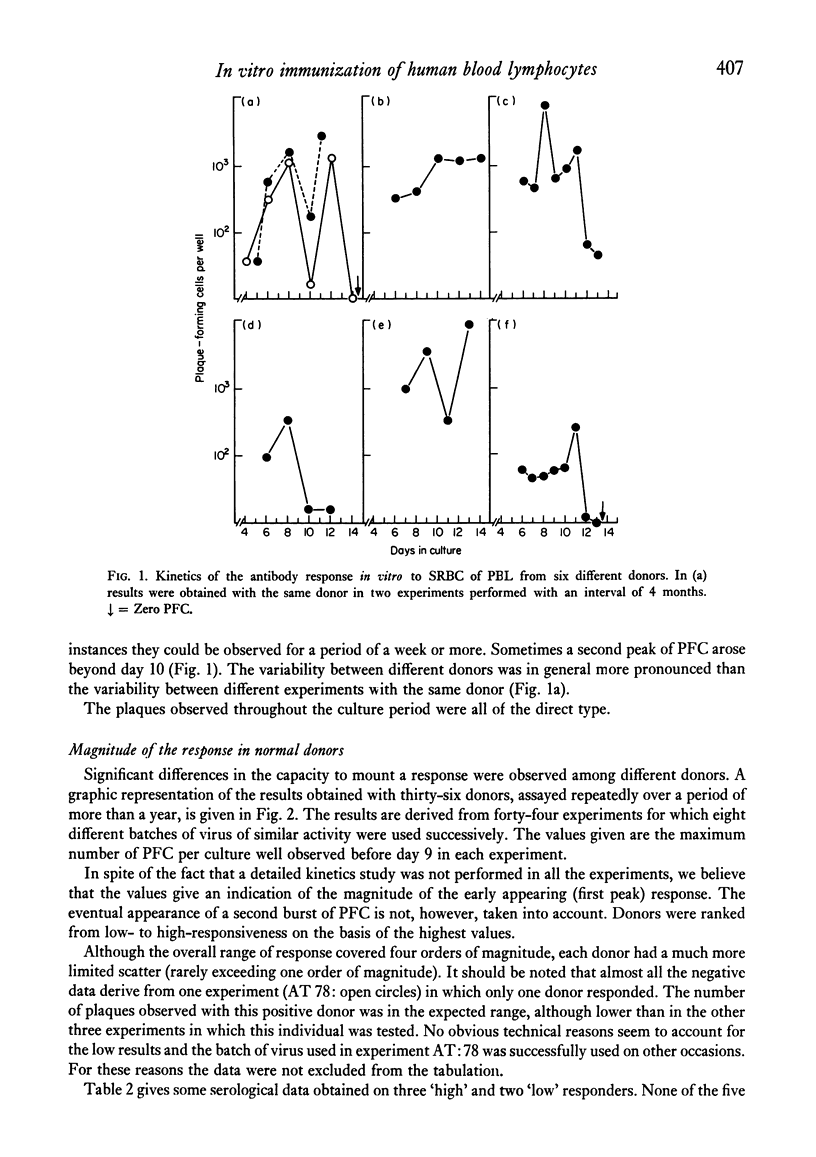
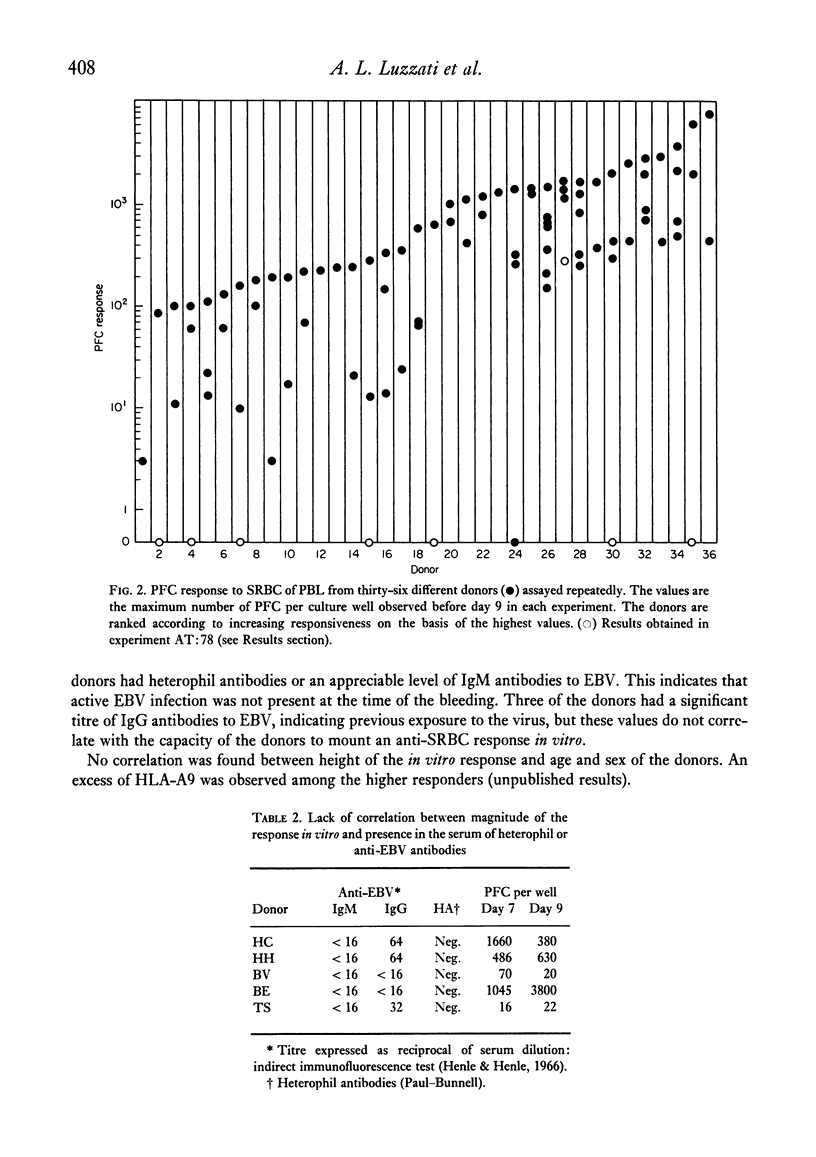
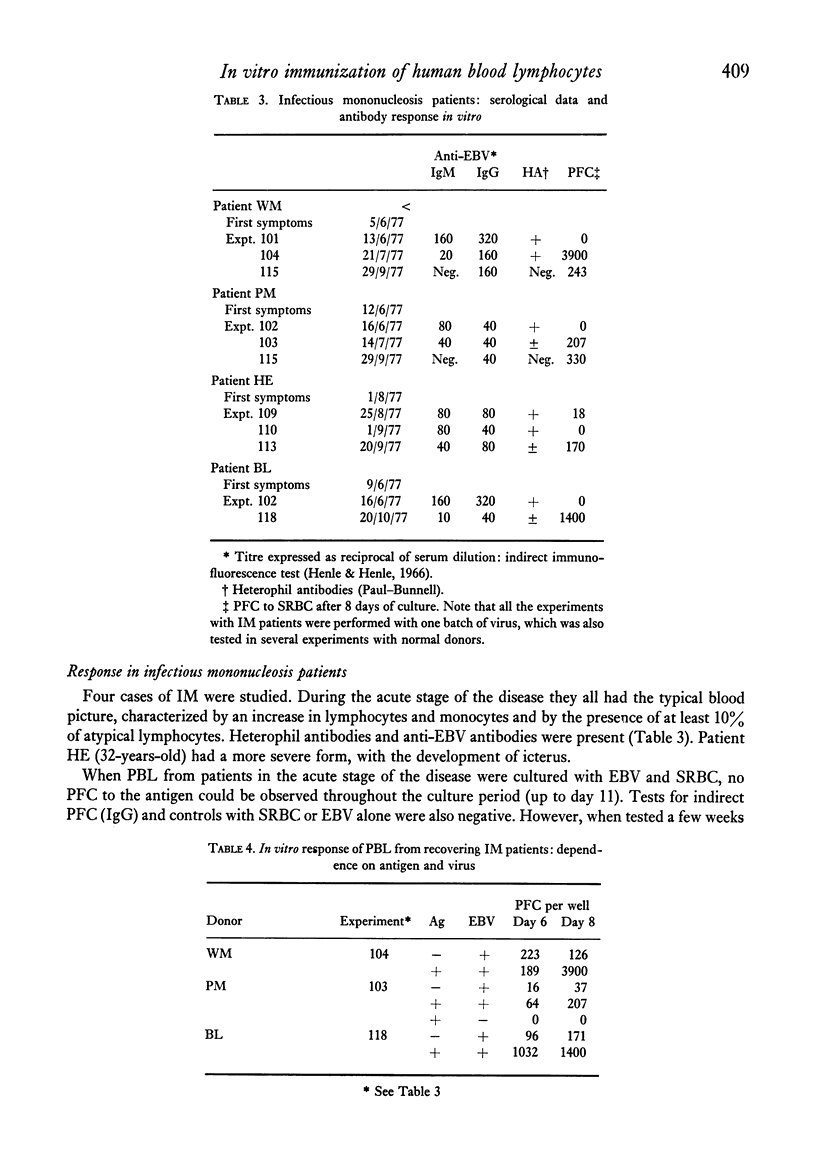
Normal human peripheral blood lymphocytes, stimulated in vitro with SRBC in the presence of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), gave rise to plaque-forming cells (PFC) specific for the antigen. PFC levels were very low before day 4 and increased thereafter, reaching a maximum around day 8. However, the kinetics of the response varied considerably from donor to donor and from experiment to experiment. In some instances a second peak of PFC was obtained beyond day 10. Large differences in the magnitude of the response were observed among different normal donors, the overall responsiveness range covering four orders of magnitude. Peripheral blood lymphocytes from infectious mononucleosis patients in the acute stage of the disease, when a high titre of heterophil and anti-EBV antibodies were present, did not give rise to PFC. A return to normal responses was observed during recovery from the disease.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ando I., Fachet J. Genetic control of primary and secondary IgG responses to sheep erythrocytes in mice. Scand J Immunol. 1977;6(6-7):601–606. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1977.tb02139.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter R. L. Infectious mononucleosis: model for self-limiting lymphoproliferation. Lancet. 1975 Apr 12;1(7911):846–849. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)93014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichmann K., Braun D. G., Krause R. M. Influence of genetic factors on the magnitude and the heterogeneity of the immune response in the rabbit. J Exp Med. 1971 Jul 1;134(1):48–65. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.1.48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein M. A., Achong B. G. Pathogenesis of infectious mononucleosis. Lancet. 1977 Dec 17;2(8051):1270–1273. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92673-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein M. A., Achong B. G. Recent progress in Epstein-Barr virus research. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:421–445. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.002225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber P., Hoyer B. H. Induction of cellular DNA synthesis in human leukocytes by Epstein-Barr virus. Nature. 1971 May 7;231(5297):46–47. doi: 10.1038/231046a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerper P., Whang-Peng J., Monroe J. H. Transformation and chromosome changes induced by Epstein-Barr virus in normal human leukocyte cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jul;63(3):740–747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.3.740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M. F., Brown G. Epstein-Barr virus binding sites on lymphocyte subpopulations and the origin of lymphoblasts in cultured lymphoic cell lines and in the blood of patients with infectious mononucleosis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1975 Mar;3(4):514–524. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(75)90076-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haider S., Coutinho M. de L., Emond R. T., Sutton R. N. Tuberculin anergy and infectious mononucleosis. Lancet. 1973 Jul 14;2(7820):74–74. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)93265-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W. Immunofluorescence in cells derived from Burkitt's lymphoma. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1248–1256. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1248-1256.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Diehl V., Kohn G., Zur Hausen H., Henle G. Herpes-type virus and chromosome marker in normal leukocytes after growth with irradiated Burkitt cells. Science. 1967 Sep 1;157(3792):1064–1065. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3792.1064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Klein G. Surface markers on human B and T lymphocytes. II. Presence of Epstein-Barr virus receptors on B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1973 Dec 1;138(6):1365–1378. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.6.1365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luzzati A. L., Hengartner H., Schreier M. H. Induction of plaque-forming cells in cultured human lymphocytes by combined action of antigen and EB virus. Nature. 1977 Sep 29;269(5627):419–420. doi: 10.1038/269419a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luzzati A. L., Lafleur L. Suppressor cells in rabbit peripheral blood. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Feb;6(2):125–129. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luzzati A. L., Taussig M. J., Meo T., Pernis B. Induction of an antibody response in cultures of human peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1976 Sep 1;144(3):573–585. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.3.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangi R. J., Niederman J. C., Kelleher J. E., Jr, Dwyer J. M., Evans A. S., Kantor F. S. Depression of cell-mediated immunity during acute infectious mononucleosis. N Engl J Med. 1974 Nov 28;291(22):1149–1153. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197411282912202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Lipman M. Release of infectious Epstein-Barr virus by transformed marmoset leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):190–194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Lisco H., Kohn H. I., Stitt D., Enders J. F. Establishment of cell lines from normal adult human blood leukocytes by exposure to Epstein-Barr virus and neutralization by human sera with Epstein-Barr virus antibody. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Sep;137(4):1459–1465. doi: 10.3181/00379727-137-35810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope J. H., Horne M. K., Scott W. Identification of the filtrable leukocyte-transforming factor of QIMR-WIL cells as herpes-like virus. Int J Cancer. 1969 May 15;4(3):255–260. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910040302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosén A., Gergely P., Jondal M., Klein G., Britton S. Polyclonal Ig production after Epstein-Barr virus infection of human lymphocytes in vitro. Nature. 1977 May 5;267(5606):52–54. doi: 10.1038/267052a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svedmyr E., Jondal M. Cytotoxic effector cells specific for B Cell lines transformed by Epstein-Barr virus are present in patients with infectious mononucleosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1622–1626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorley-Lawson D. A., Chess L., Strominger J. L. Suppression of in vitro Epstein-Barr virus infection. A new role for adult human T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1977 Aug 1;146(2):495–508. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.2.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


