Abstract
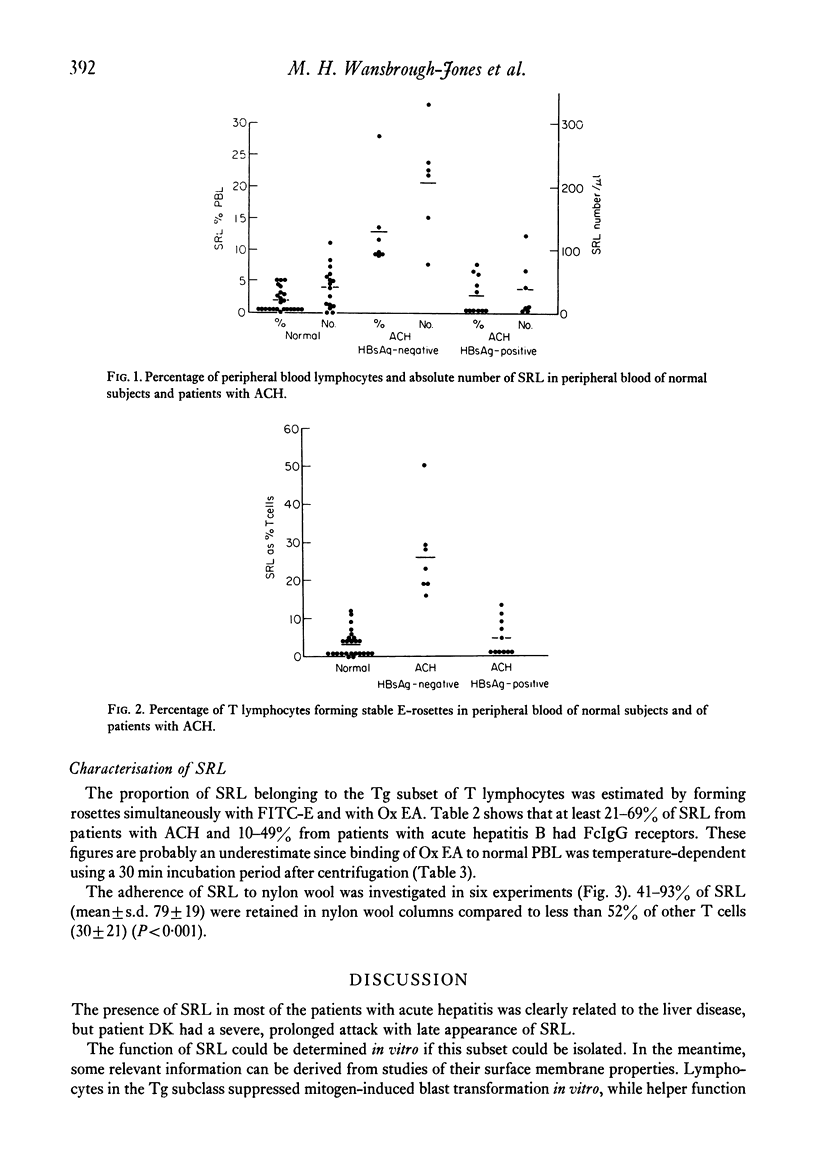
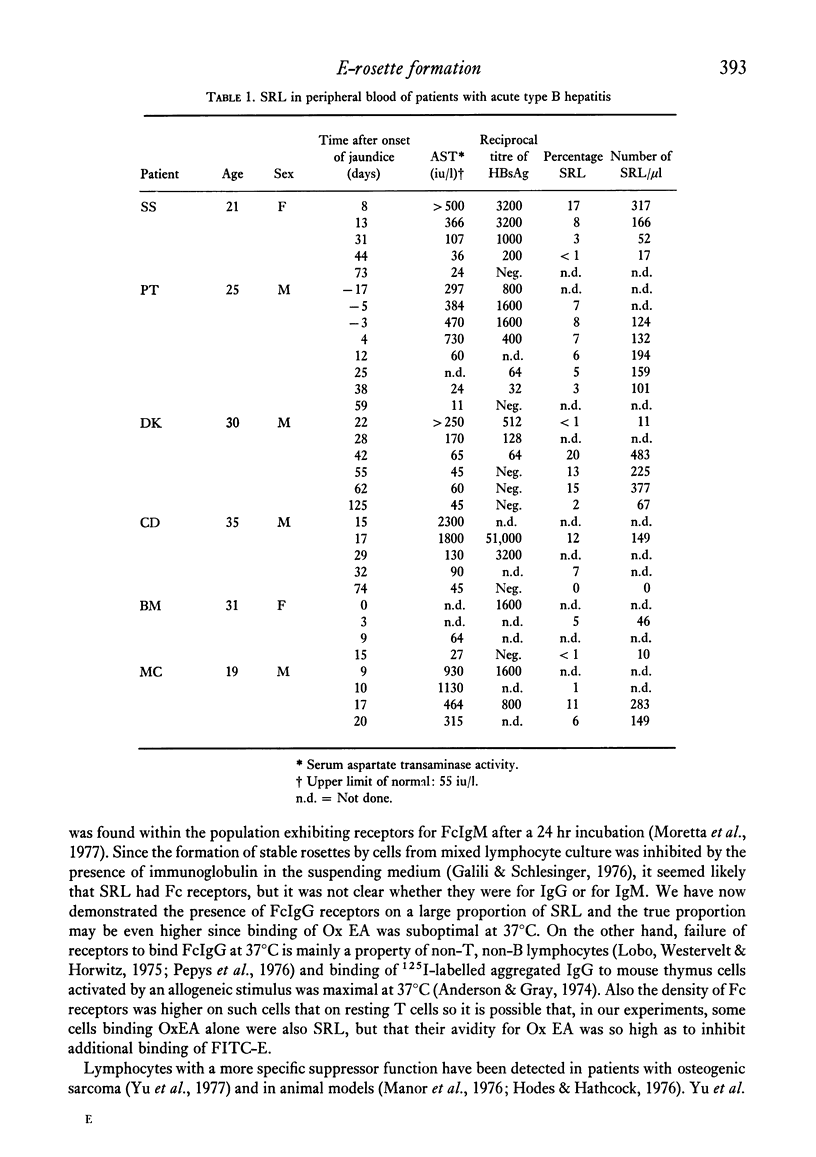
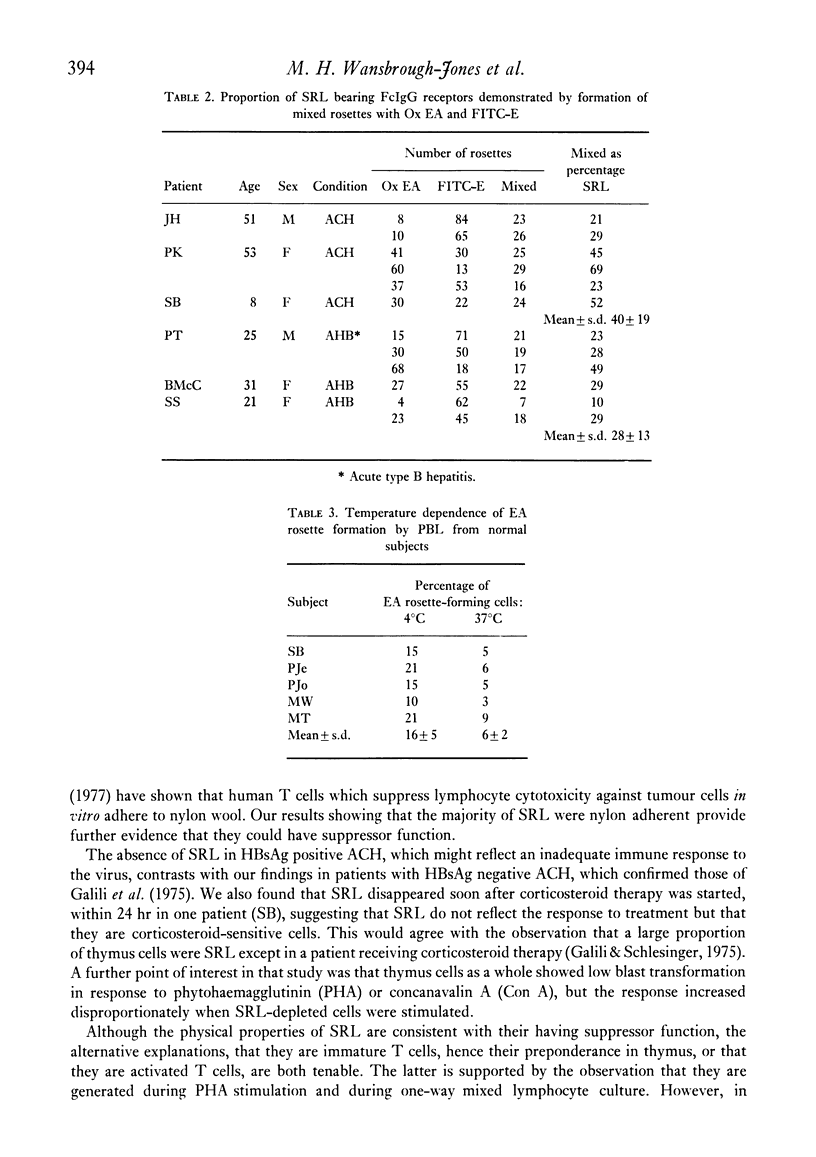
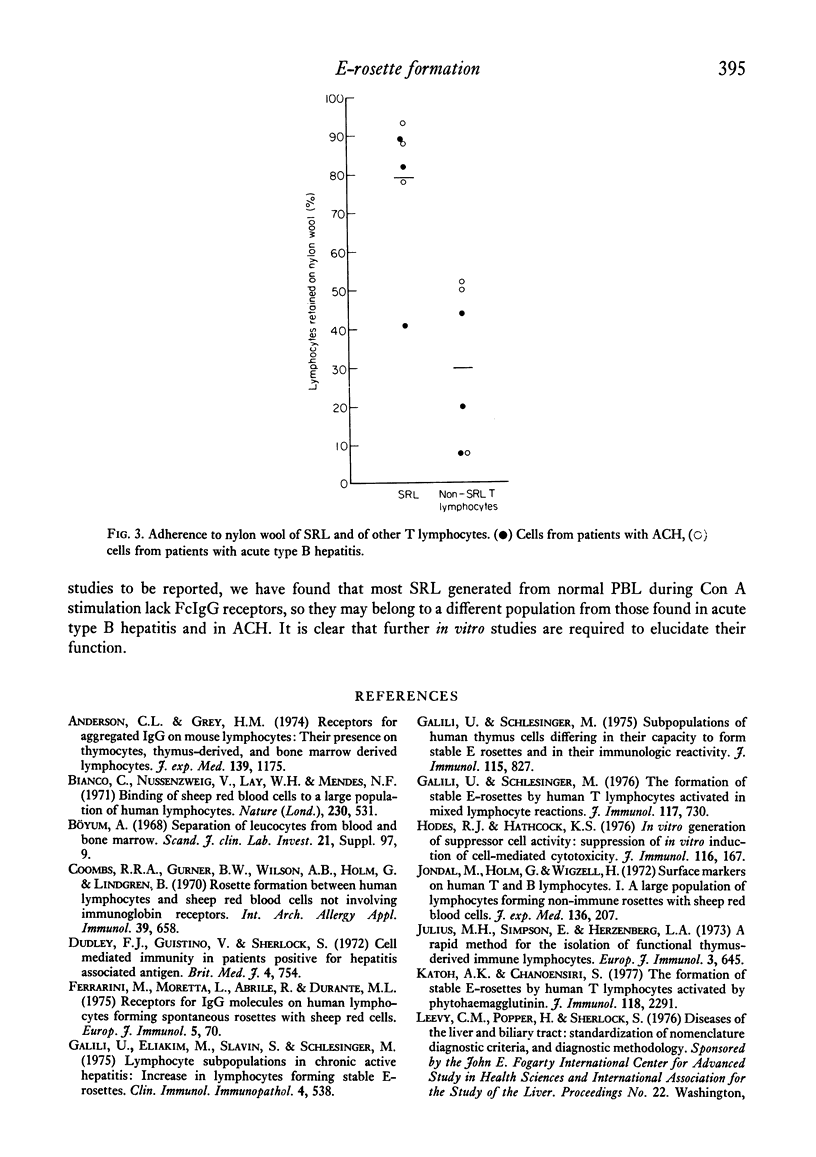
Lymphocytes forming E-rosettes with sheep erythrocytes which do not disintegrate at 37 degrees C have been demonstrated in increased numbers in peripheral blood of patients with acute type B hepatitis (6--20% of lymphocytes) and with HBsAg negative active chronic hepatitis (9--28% of lymphocytes). They were not increased in patients with HBsAg positive active chronic hepatitis. Such lymphocytes were adherent to nylon wool and a large proportion of them had FcIgG receptors (21--69%). These are properties of a subpopulation of T lymphocytes having suppressor function.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. L., Grey H. M. Receptors for aggregated IgG on mouse lymphocytes: their presence on thymocytes, thymus-derived, and bone marrow-derived lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1974 May 1;139(5):1175–1188. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coombs R. R., Gurner B. W., Wilson A. B., Holm G., Lindgren B. Rosette-formation between human lymphocytes and sheep red cells not involving immunoglobulin receptors. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1970;39(5-6):658–663. doi: 10.1159/000230390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley F. J., Giustino V., Sherlock S. Cell-mediated immunity in patients positive for hepatitis-associated antigen. Br Med J. 1972 Dec 30;4(5843):754–756. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5843.754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrarini M., Moretta L., Abrile R., Durante M. L. Receptors for IgG molecules on human lymphocytes forming spontaneous rosettes with sheep red cells. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Jan;5(1):70–72. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galili U., Eliakim M., Slavin S., Schlesinger M. Lymphocyte subpopulations in chronic active hepatitis: increase in lymphocytes forming stable E-rosettes. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1975 Nov;4(4):538–544. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(75)90095-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galili U., Schlesinger M. Subpopulations of human thymus cells differing in their capacity to form stable E-rosettes and in their immunologic reactivity. J Immunol. 1975 Sep;115(3):827–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galili U., Schlesinger M. The formation of stable E-rosettes by human T lymphocytes activated in mixed lymphocyte reactions. J Immunol. 1976 Sep;117(3):730–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodes R. J., Hathcock K. S. In vitro generation of suppressor cell activity: suppression of in vitro induction if cell-mediated cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):167–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Holm G., Wigzell H. Surface markers on human T and B lymphocytes. I. A large population of lymphocytes forming nonimmune rosettes with sheep red blood cells. J Exp Med. 1972 Aug 1;136(2):207–215. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh A. K., Charoensiri S. The formation of stable E-rosettes by human T lymphocytes activated by phytohemagglutinin. J Immunol. 1977 Jun;118(6):2291–2292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lay W. H., Mendes N. F., Bianco C., Nussenzweig V. Binding of sheep red blood cells to a large population of human lymphocytes. Nature. 1971 Apr 23;230(5295):531–532. doi: 10.1038/230531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobo P. I., Westervelt F. B., Horwitz D. A. Identification of two populations of immunoglobulin-bearing lymphocytes in man. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 1):116–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manor Y., Treves A. J., Cohen I. R., Feldman M. Transition from T cell protection to T cell enhancement during tumor growth in an allogeneic host. Transplantation. 1976 Oct;22(4):360–366. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197610000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta L., Webb S. R., Grossi C. E., Lydyard P. M., Cooper M. D. Functional analysis of two human T-cell subpopulations: help and suppression of B-cell responses by T cells bearing receptors for IgM or IgG. J Exp Med. 1977 Jul 1;146(1):184–200. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.1.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wansbrough-Jones M., Mirjah D., Druguet M., Pepys M. B. Temperature dependence of antigen-specific rosette formation by lymphocytes from immunised mice. J Immunol Methods. 1977;15(3):291–297. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West W. H., Payne S. M., Weese J. L., Herberman R. B. Human T lymphocyte subpopulations: correlation between E-rosette-forming affinity and expression of the Fc receptor. J Immunol. 1977 Aug;119(2):548–554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf B., Janeway C. A., Jr, Coombs R. R., Catty D., Gell P. G., Kelus A. S. Immunoglobulin determinants on the lymphocytes of normal rabbits. 3. As4 and As6 determinants on individual lymphocytes and the concept of allelic exclusion. Immunology. 1971 Jun;20(6):931–944. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wybran J., Fudenberg H. H. Thymus-derived rosette-forming cells in various human disease states: cancer, lymphoma, bacterial and viral infections, and other diseases. J Clin Invest. 1973 May;52(5):1026–1032. doi: 10.1172/JCI107267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu A., Watts H., Jaffe N., Parkman R. Concomitant presence of tumor-specific cytotoxic and inhibitor lymphocytes in patients with osteogenic sarcoma. N Engl J Med. 1977 Jul 21;297(3):121–127. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197707212970301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


