Abstract
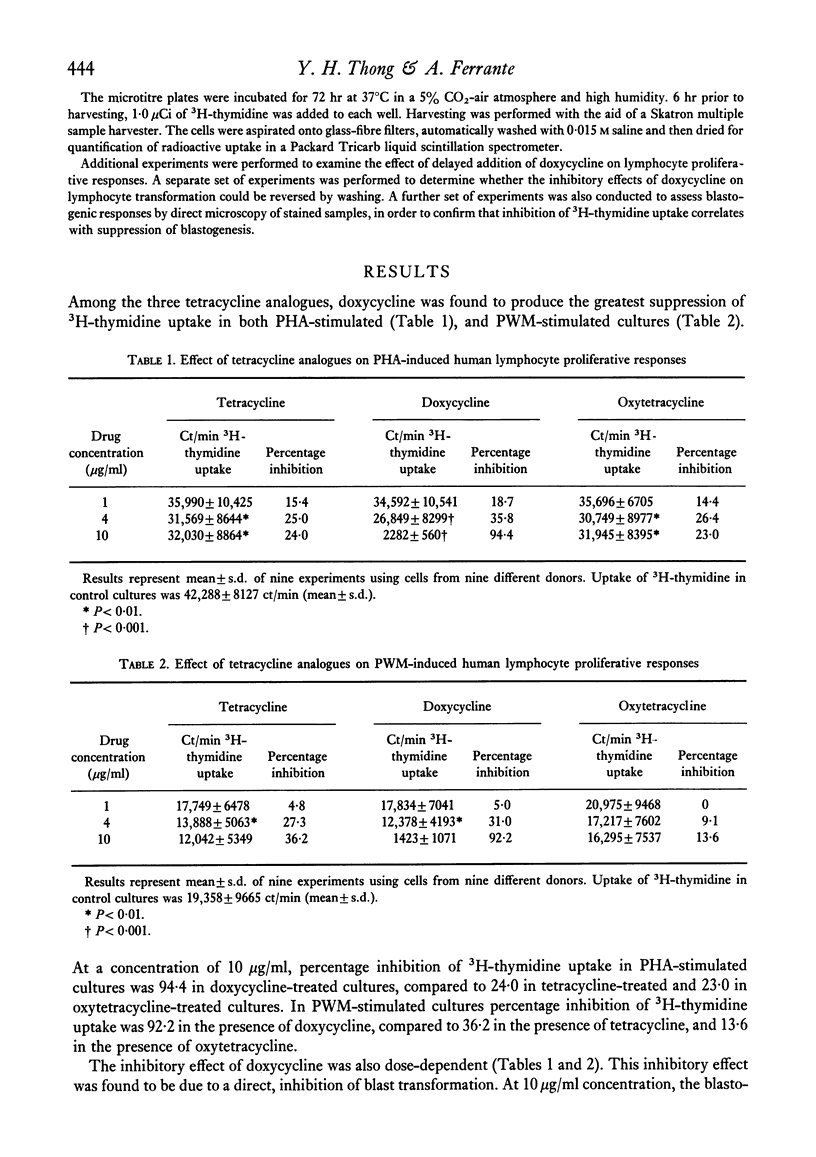
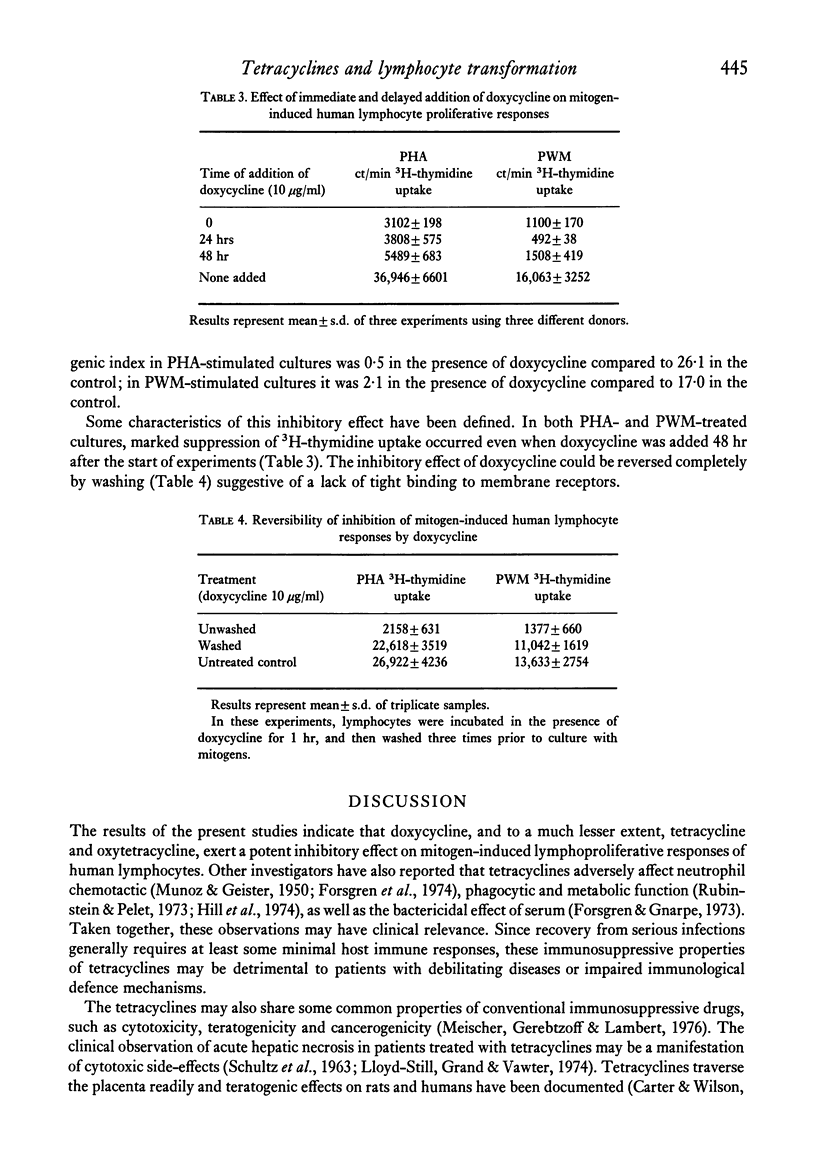
The effect of tetracyclines on mitogen-induced proliferative responses of human lymphocytes was examined. The results showed that of the three tetracycline analogues studied, doxycycline possessed the most potent inhibiting effects. This occurred at drug concentrations (1--10 micrograms/ml) easily attainable in serum during conventional dosage schedules. Other investigations have shown that tetracyclines also interfere with neutrophil function. Taken together, these findings may have clinical significance. Recovery from serious infections generally requires some minimal host immune responses, and the immunosuppressive side-effects of tetracyclines may have detrimental effects on patients with debilitating illnesses or impaired immunological defence mechanisms. Furthermore, tetracyclines may share some common properties of conventional immunosuppressive drugs, such as cytotoxicity, teratogenicity and cancerogenicity. The long-term use of tetracyclines for conditions such as chronic bronchitis, bronchiectasis and acne vulgaris needs to be re-examined.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Forsgren A., Schmeling D., Quie P. G. Effect of tetracycline on the phagocytic function of human leukocytes. J Infect Dis. 1974 Oct;130(4):412–415. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.4.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill H. R., Kaplan E. L., Dajani A. D., Wannamaker L. W., Quie P. G. Leukotactic activity and reduction of nitroblue tetrazolium by neutrophil granulocytes from patients with streptococcal skin infection. J Infect Dis. 1974 Mar;129(3):322–326. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.3.322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd-Still J. D., Grand R. J., Vawter G. F. Tetracycline hepatotoxicity in the differential diagnosis of postoperative jaundice. J Pediatr. 1974 Mar;84(3):366–370. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(74)80718-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUNOZ J., GEISTER R. Inhibition of phagocytosis by aureomycin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1950 Nov;75(2):367–370. doi: 10.3181/00379727-75-18201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. R., Warr G. A., Couch R. B., Yeager H., Knight V. Effects of tetracycline on leukotaxis. J Infect Dis. 1974 Feb;129(2):110–116. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.2.110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. R., Warr G., Couch R., Knight V. Chemotaxis of human leukocytes: responsiveness to Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 Apr;81(4):520–529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pato M. L. Tetracycline inhibits propagation of deoxyribonucleic acid replication and alters membrane properties. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Feb;11(2):318–323. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.2.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein A., Pelet B. False-negative N.B.T. tests due to transient malfunction of neutrophils. Lancet. 1973 Feb 17;1(7799):382–382. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90185-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHULTZ J. C., ADAMSON J. S., Jr, WORKMAN W. W., NORMAN T. D. FATAL LIVER DISEASE AFTER INTRAVENOUS ADMINISTRATION OF TETRACYCLINE IN HIGH DOSAGE. N Engl J Med. 1963 Nov 7;269:999–1004. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196311072691903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thong Y. H., Steele R. W., Vincent M. M., Hensen S. A., Bellanti J. A. Impaired in vitro cell-mediated immunity to rubella virus during pregnancy. N Engl J Med. 1973 Sep 20;289(12):604–606. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197309202891203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


