Abstract
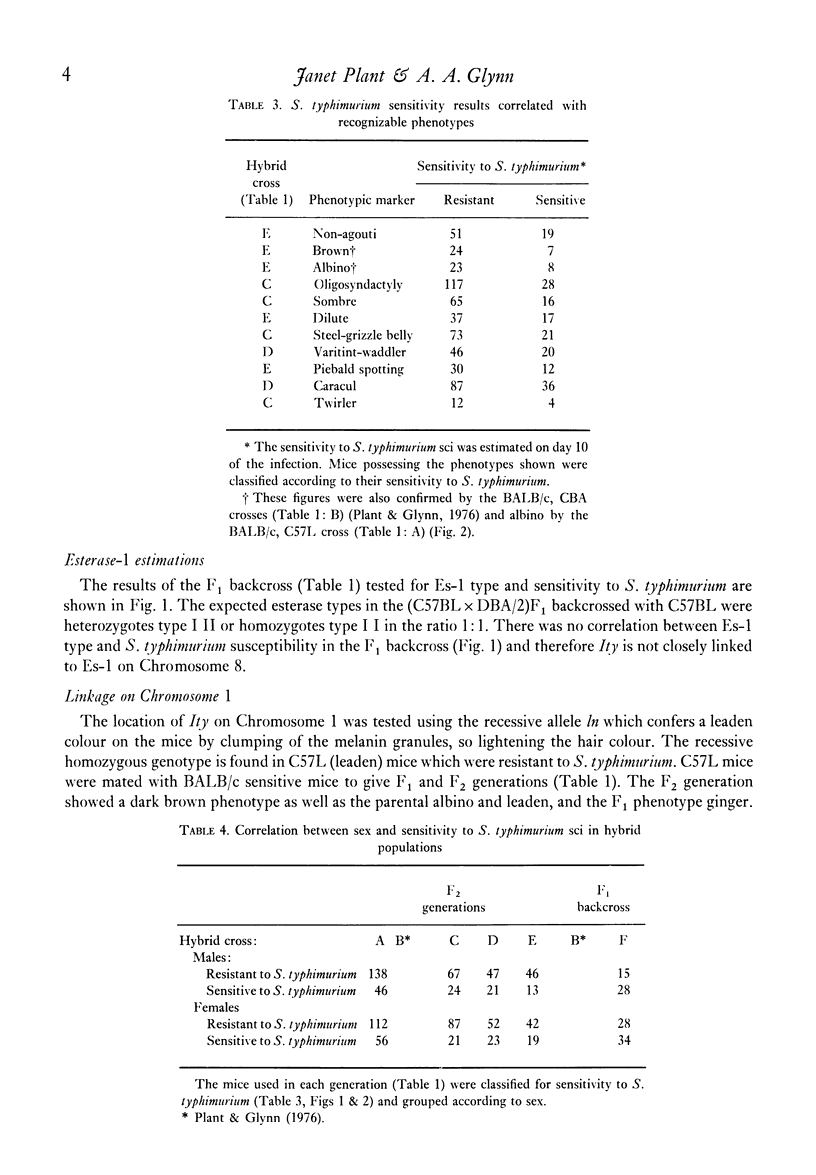
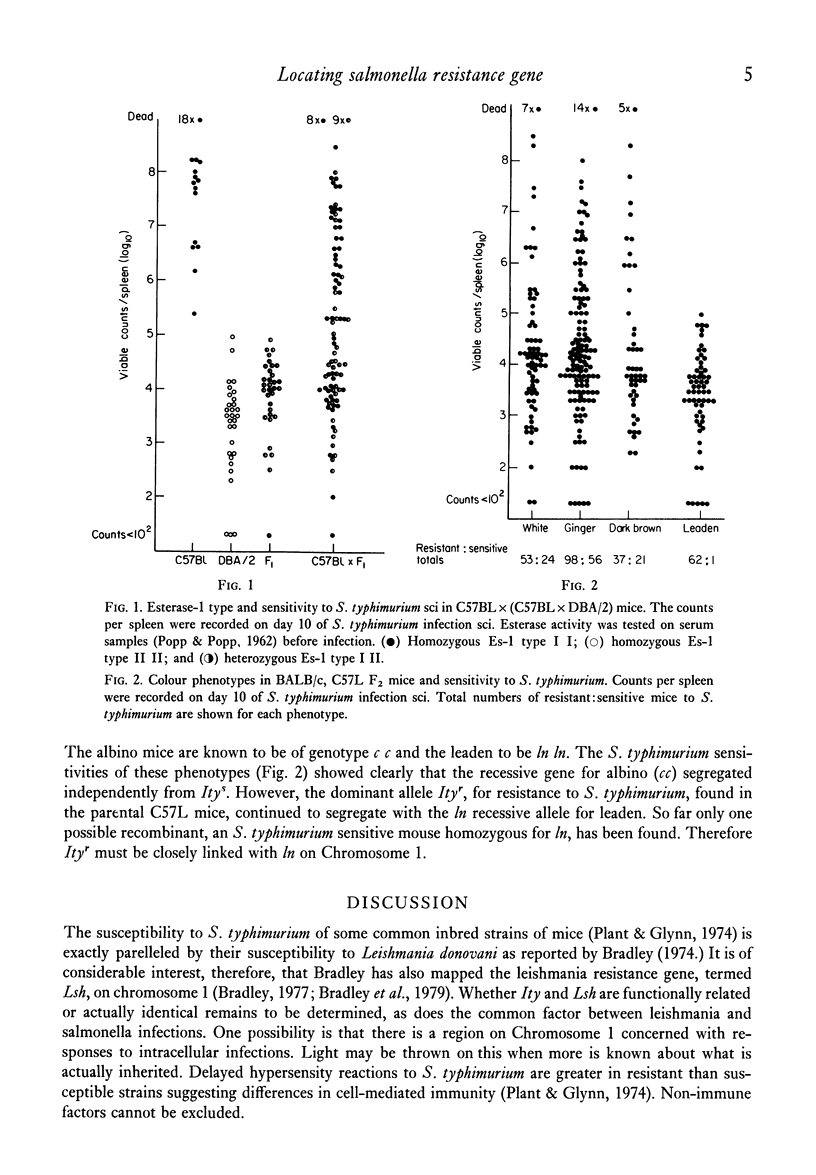
The inherited resistance of inbred mouse strains to Salmonella typhimurium injected subcutaneously has been reported to be controlled primarily by a single gene designated Ity. Resistant mice have the dominant allele Ityr and sensitive mice are homozygous for the recessive allele Itys. This paper describes studies undertaken to locate the gene using readily distinguishable phenotypes as chromosome markers. Appropriate F1 backcross and F2 generations of hybrids between resistant and susceptible inbred strains of mice, with or without the particular phenotypic markers, were tested both for susceptibility to salmonella sci and presence of the marker. Independent segregation of the characteristics eliminated all chromosomes except Chromosome 1. C57L mice resistant to S. typhimurium, Ityr Ityr and leaden, ln ln, located on Chromosome 1, were crossed with BALB/c mice sensitive to S. typhimurium and non-leaden. In the F2 generation mice, ln always segregated with Ityr. The presence of only one leaden mouse sensitive to S. typhimurium out of sixty leaden F2 mice tested linked Ityr closely with ln on Chromosome 1. This result will be of use in further experiments with hybrid populations by enabling us to predetermine resistance or sensitivity to S. typhimurium without infecting the mice, so permitting experiments on the nature of the inheritance in unsensitized mice.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blanden R. V., Mackaness G. B., Collins F. M. Mechanisms of acquired resistance in mouse typhoid. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):585–600. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. J. Letter: Genetic control of natural resistance to Leishmania donovani. Nature. 1974 Jul 26;250(464):353–354. doi: 10.1038/250353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. J. Regulation of Leishmania populations within the host. II. genetic control of acute susceptibility of mice to Leishmania donovani infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Oct;30(1):130–140. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. J., Taylor B. A., Blackwell J., Evans E. P., Freeman J. Regulation of Leishmania populations within the host. III. Mapping of the locus controlling susceptibility to visceral leishmaniasis in the mouse. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Jul;37(1):7–14. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOWEN J. W. Genetic effects in nonspecific resistance to infectious disease. Bacteriol Rev. 1960 Mar;24(1):192–200. doi: 10.1128/br.24.1.192-200.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LILLY F., BOYSE E. A., OLD L. J. GENETIC BASIS OF SUSCEPTIBILITY TO VIRAL LEUKAEMOGENESIS. Lancet. 1964 Dec 5;2(7371):1207–1209. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)91043-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Dixon F. J., Mitchell G. F., McDevitt H. O. Histocompatibility-linked genetic control of disease susceptibility. Murine lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection. J Exp Med. 1973 May 1;137(5):1201–1212. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.5.1201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POPP R. A., POPP D. M. Inheritance of serum esterases having different electrophoretic patterns. J Hered. 1962 May-Jun;53:111–114. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a107140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant J., Glynn A. A. Genetics of resistance to infection with Salmonella typhimurium in mice. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jan;133(1):72–78. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.1.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant J., Glynn A. A. Natural resistance to Salmonella infection, delayed hypersensitivity and Ir genes in different strains of mice. Nature. 1974 Mar 22;248(446):345–347. doi: 10.1038/248345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



