Abstract
Serial serum samples from 113 patients with different forms of HBV-related liver disease and HBsAg carriership were tested for the presence of HBsAg, anti-HBc, anti-HBs, and HBsAg-anti-HBs immune complexes (IC). Eight patients with acute type B hepatitis had the irmultiple serum samples tested in an average period of time from 68 days before the appearance of clinical symptoms up to 277 days after the onset of clinical symptoms. In the remaining cases serum samples were obtained during the period after the appearance of clinical symptoms.
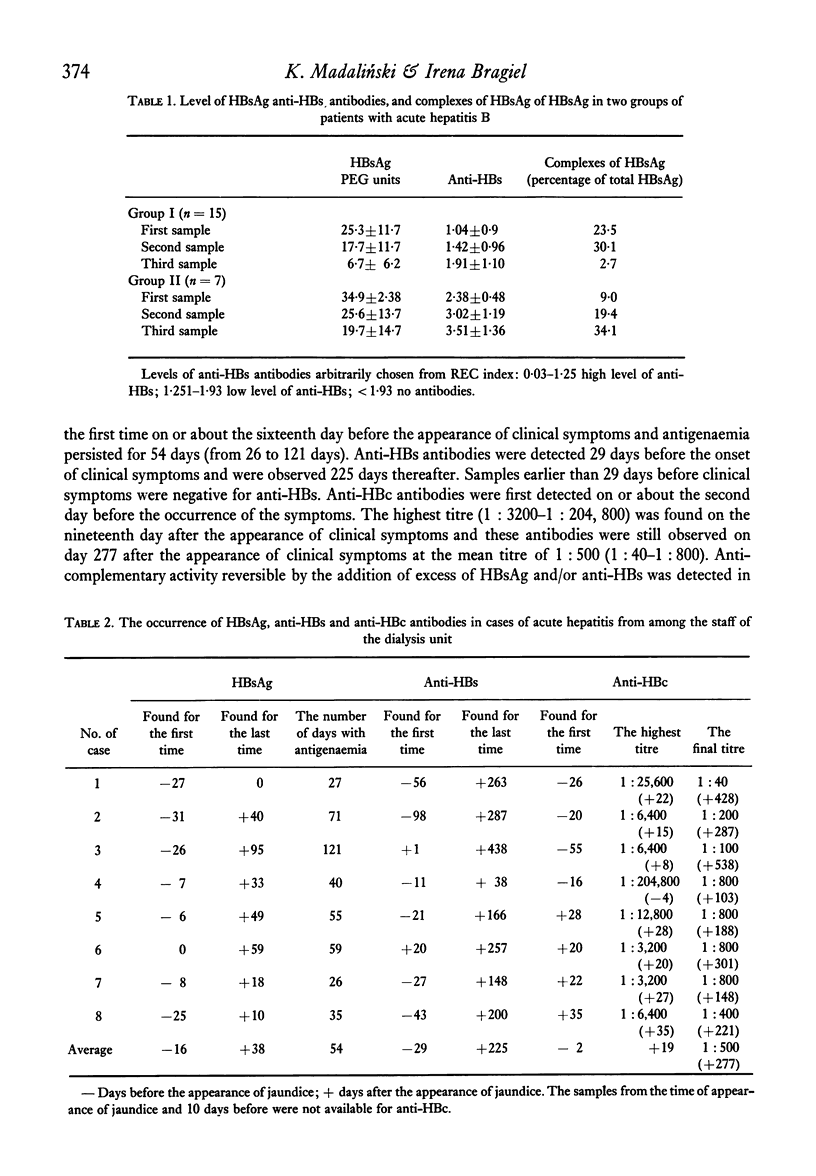
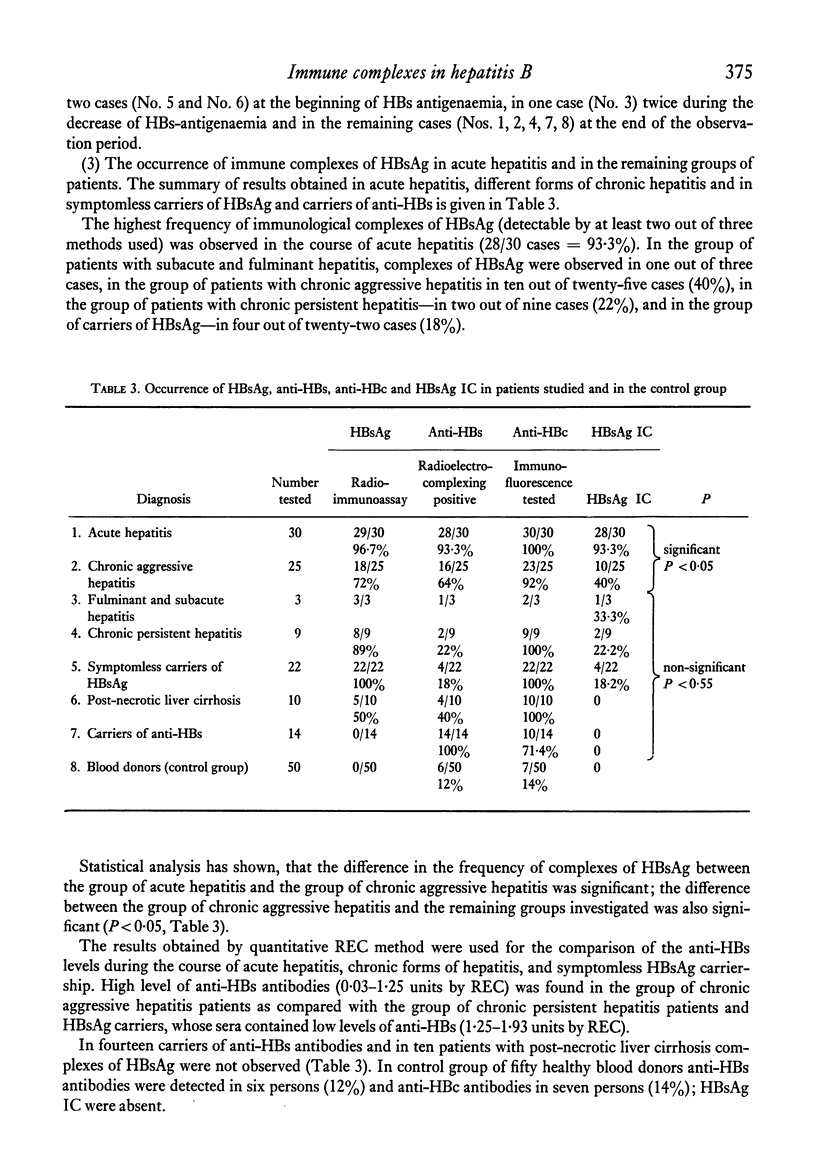
The highest frequency of immune complexes of HBsAg was observed in acute hepatitis (twenty-eight out of thirty examined cases—93·3%). The patients showing high level of anti-HBs response eliminated HBsAg from the circulation earlier than the patients showing low level of anti-HBs response. In chronic aggressive hepatitis the frequency of HBsAg complexes was higher (ten out of twenty-five cases—40%) than in chronic persistent hepatitis (two out of nine cases—22%); HBsAg complexes were found in four out of twenty-two symptomless carriers of HBsAg (18%).
The obtained results are in agreement with the hypothesis that an optimal humoral immune response at the acute stage of hepatitis type B results in rapid elimination of HBV antigens. Conversely, an inadequate response at this stage favours replication of the virus in hepatocytes, prolongation of HBs antigenaemia, and the appearance of chronic forms of hepatitis.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almeida J. D., Waterson A. P. Immune complexes in hepatitis. Lancet. 1969 Nov 8;2(7628):983–986. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90540-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker L. F., Peterson M. R., Shulman N. R., Murray R. Antibody responses in viral hepatitis, type B. JAMA. 1973 Feb 26;223(9):1005–1008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brzosko W. J., Madaliński K., Krawczyński K., Nowoslawski A. Duality of hepatitis B antigen and its antibody. I. Immunofluorescence studies. J Infect Dis. 1973 Apr;127(4):424–428. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.4.424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P., Wilchek M., Anfinsen C. B. Selective enzyme purification by affinity chromatography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):636–643. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daugharty H., Gogel R. Platelet aggregation by hepatitis B surface antigen-antibody complexes. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):752–758. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.752-758.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Inadequate antibody response to hBAg or suppressor T-cell defect in development of active chronic hepatitis. Lancet. 1974 Dec 28;2(7896):1543–1545. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90287-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerin J. L., Holland P. V., Purcell R. H. Australia antigen: large-scale purification from human serum and biochemical studies of its proteins. J Virol. 1971 May;7(5):569–576. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.5.569-576.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoofnagle J. H., Gerety R. J., Barker L. F. Antibody to hepatitis-B-virus core in man. Lancet. 1973 Oct 20;2(7834):869–873. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler P. F. Clinical immune complex disease. Manifestations in systemic lupus erythematosus and hepatitis B virus infection. Medicine (Baltimore) 1973 Sep;52(5):419–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosmidis J. C., Leader-Williams L. K. Complement levels in acute infectious hepatitis and serum hepatitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 May;11(1):31–35. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. H., Tribollet E., Knoepfel M., Madalinski K., Miescher P. A. PEG test: a new radioimmunoassay for the detection of hepatitis B antigen. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1974 Jan 26;104(4):128–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander J. J., Alter H. J., Purcell R. H. Frequency of antibody to hepatitis-associated antigen as measured by a new radioimmunoassay technique. J Immunol. 1971 May;106(5):1166–1171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinsky R. J., Cameron J. S., Soothill J. F. Serum immune complexes and disease activity in lupus nephritis. Lancet. 1977 Mar 12;1(8011):564–567. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91998-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lurhuma A. Z., Cambiaso C. L., Masson P. L., Heremans J. F. Detection of circulating antigen-antibody complexes by their inhibitory effect on the agglutination of IgG-coated particles by rheumatioid factor of Clq. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Aug;25(2):212–226. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mcintosh R. M., Koss M. N., Gocke K. J. The nature and incidence of cryoproteins in hepatitis B antigen (HbsAg) positive patients. Q J Med. 1976 Jan;45(177):23–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mims C. A. Factors in the mechanism of persistence of viral infections. Prog Med Virol. 1974;18(0):1–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J. O., Dietrichson O., Juhl E. Incidence and meaning of the "e" determinant among hepatitis-B-antigen positive patients with acute and chronic liver diseases. Report from the Copenhagen Hepatitis Acuta Programme. Lancet. 1974 Oct 19;2(7886):913–915. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91127-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notkins A. L., Mage M., Ashe W. K., Mahar S. Neutralization of sensitized lactic dehydrogenase virus by anti-gammglobulin. J Immunol. 1968 Feb;100(2):314–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowoslawski A., Krawczynski K., Nazarewicz T., Slusarczyk J. Immunopathological aspects of hepatitis type B. Am J Med Sci. 1975 Sep-Oct;270(2):229–239. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197509000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nydegger U. E., Lambert P. H., Gerber H., Miescher P. A. Circulating immune complexes in the serum in systemic lupus erythematosus and in carriers of hepatitis B antigen. Quantitation by binding to radiolabeled C1q. J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;54(2):297–309. doi: 10.1172/JCI107765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Dixon F. J. Immune complex disease in chronic viral infections. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 2):32s–40s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B. Virus neutralization and virus-induced immune complex disease. Virus-antibody union resulting in immunoprotection or immunologic injury--two sides of the same coin. Prog Med Virol. 1975;19:84–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince A. M., Burke K. Serum hepatitis antigen (SH): rapid detection by high voltage immunoelectroosmophoresis. Science. 1970 Aug 7;169(3945):593–595. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3945.593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell R. H., Holland P. V., Walsh J. H., Wong D. C., Morrow A. G., Chanock R. M. A complement-fixation test for measuring Australia antigen and antibody. J Infect Dis. 1969 Sep;120(3):383–386. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.3.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHULMAN N. R., MARDER V. J., HILLER M. C., COLLIER E. M. PLATELET AND LEUKOCYTE ISOANTIGENS AND THEIR ANTIBODIES: SEROLOGIC PHYSIOLOGIC AND CLINICAL STUDIES. Prog Hematol. 1964;4:222–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt N. J., Lennette E. H. Complement fixation and immunodiffusion tests for assay of hepatitis-associated "Australia" antigen and antibodies. J Immunol. 1970 Sep;105(3):604–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherlock S. Predicting progression of acute type-B hepatitis to chronicity. Lancet. 1976 Aug 14;2(7981):354–356. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92607-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman N. R., Barker L. F. Virus-like antigen, antibody, and antigen-antibody complexes in hepatitis measured by complement fixation. Science. 1969 Jul 18;165(3890):304–306. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3890.304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons M. J. Detection of hepatitis B antibody by radioelectrocomplexing. Bull World Health Organ. 1973;48(4):499–501. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stannard L. M., Moodie J., Keen G. A., Kipps A. Electron microscopic study of the distribution of the Australia antigen in individual sera of 50 serologically positive blood donors and two patients with serum hepatitis. J Clin Pathol. 1973 Mar;26(3):209–216. doi: 10.1136/jcp.26.3.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trepo C. G., Robert D., Motin J., Trepo D., Sepetjian M., Prince A. M. Hepatitis B antigen (HBSAg) and/or antibodies (anti-HBS and anti-HBC) in fulminant hepatitis: pathogenic and prognostic significance. Gut. 1976 Jan;17(1):10–13. doi: 10.1136/gut.17.1.10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wands J. R., Mann E., Alpert E., Isselbacher K. J. The pathogenesis of arthritis associated with acute hepatitis-B surface antigen-positive hepatitis. Complement activation and characterization of circulating immune complexes. J Clin Invest. 1975 May;55(5):930–936. doi: 10.1172/JCI108022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


