Abstract
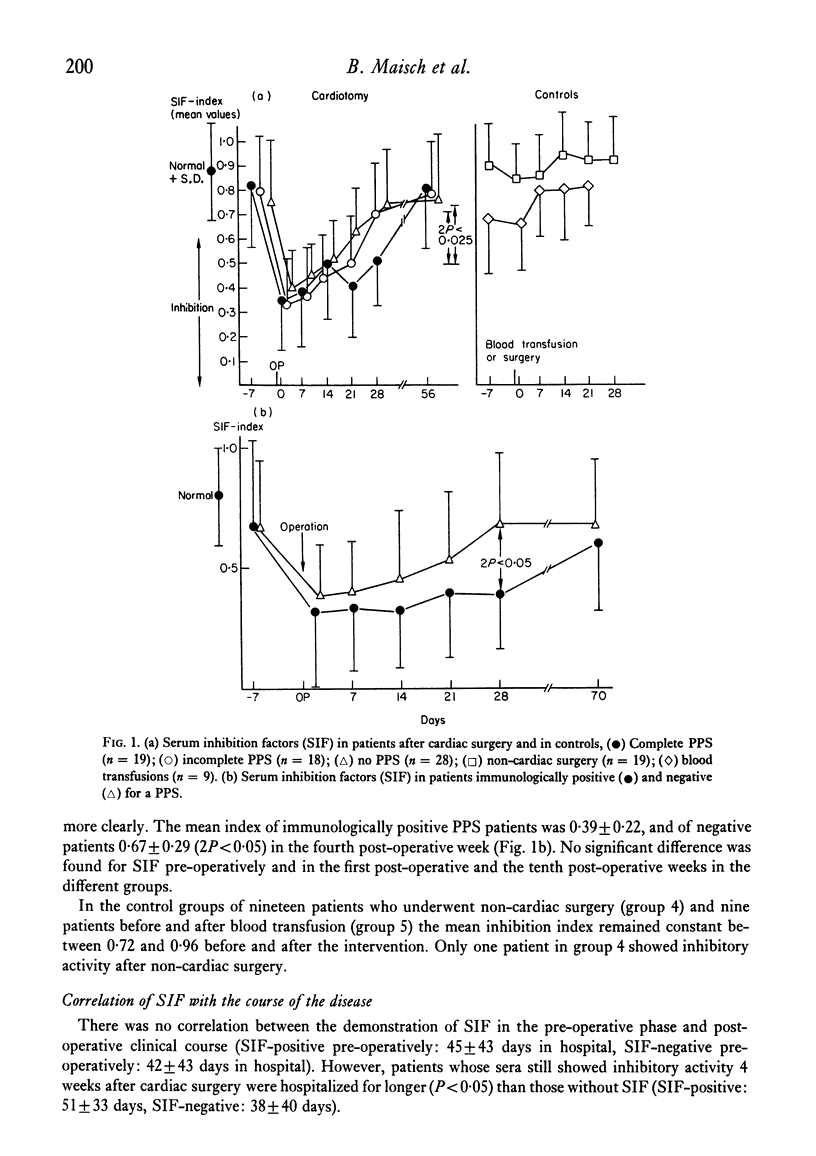
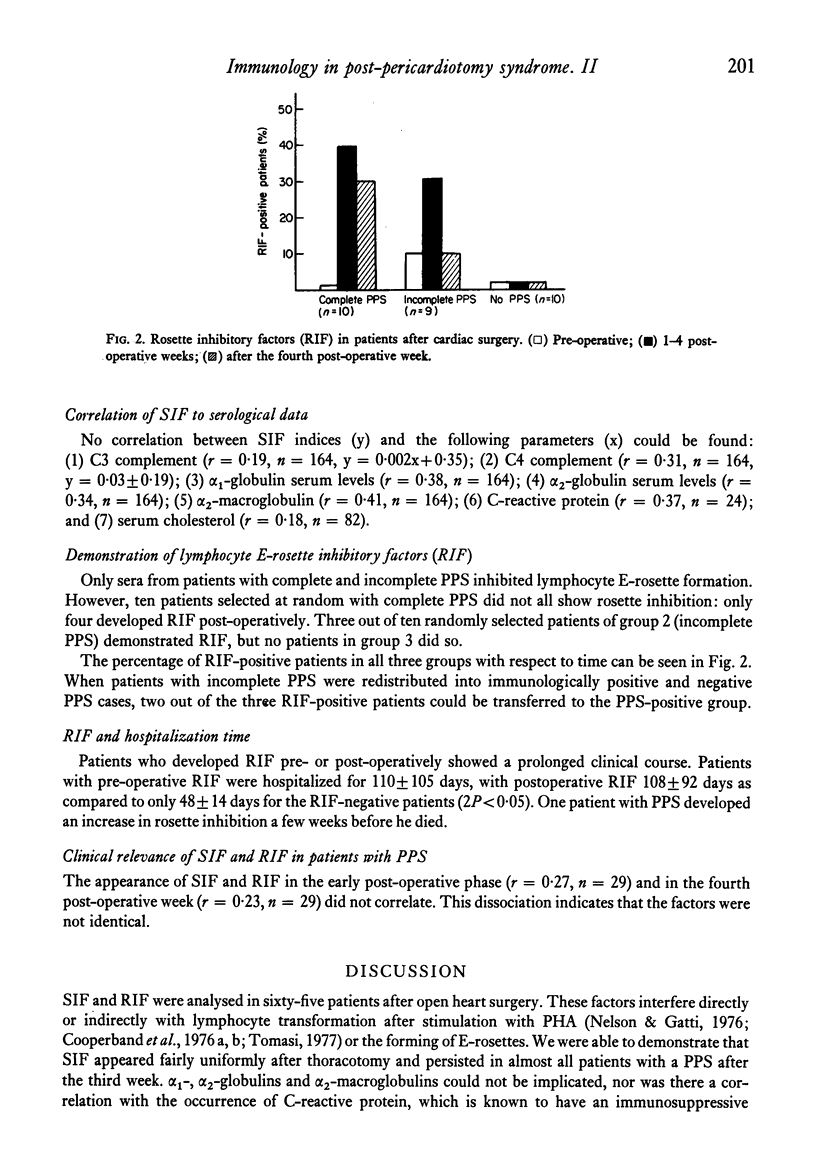
Serum inhibition factors (SIF) that suppress phytohaemagglutinin-induced blast transformation of normal lymphocytes, and lymphocyte E-rosette inhibitory factors (RIF) that inhibit the T cell-specific property of E-rosette formation were determined in sixty-five patients before and after cardiac surgery. SIF was found in the first post-operative week in almost all patients; patients with complete post-pericardiotomy syndrome (PPS) still had these factors in the fourth postoperative week. The appearance of SIF correlated well with the intensity of the PPS. Persistence of SIF in eleven out of eighteen patients with clinically incomplete PPS reaffirms the probability that they had an 'immunologically' positive PPS. RIF was to be found in one third of the patients with complete or incomplete PPS and may be of prognostic value. The two factors were not identical.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brattig N., Berg P. A. Serum inhibitory factors (SIF) in patients with acute and chronic hepatitis and their clinical significance. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Jul;25(1):40–49. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V., Edgington T. S. Human T lymphocyte "E" rosette function. I. A process modulated by intracellular cyclic AMP. J Exp Med. 1974 Oct 1;140(4):1122–1126. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.4.1122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V., Edgington T. S. Lymphocyte E rosette inhibitory factor: a regulatory serum lipoprotein. J Exp Med. 1975 Nov 1;142(5):1092–1107. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.5.1092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V., Routenberg J. A., Edgington T. S. Mechanisms responsible for defective human T-lymphocyte sheep erythrocyte rosette function associated with hepatitis B virus infections. J Clin Invest. 1976 May;57(5):1227–1238. doi: 10.1172/JCI108391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V., Routenberg J. A., Fiala M., Edgington T. S. Extrinsic modulation of human T-lymphocyte E rosette function associated with prolonged hepatocellular injury after viral hepatitis. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jan;59(1):134–142. doi: 10.1172/JCI108610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooperband S. R., Nimberg R., Schmid K., Mannick J. A. Humoral immunosuppressive factors. Transplant Proc. 1976 Jun;8(2):225–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELSTER S. K., WOOD H. F., SEELY R. D. Clinical and laboratory manifestations of the postcommissurotomy syndrome. Am J Med. 1954 Dec;17(6):826–838. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(54)90227-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espanol T., Todd G. B., Soothill J. F. The effect of anaesthesia on the lymphocyte response to phytohaemagglutinin. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Sep;18(1):73–79. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald M. G., Hosking C. S. Plasma inhibitors of lymphocyte response to phytohaemagglutinin in children with recurrent infections. Immunology. 1976 Jan;30(1):33–42. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluckman J. C., Beaufils H., Sanchez F. Inhibition of complement-dependent lymphocyte rosette formation by sera of patients with chronic glomerulonephritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Nov;26(2):247–252. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hainaut J., Kermarec J., Haguenauer G., Pernod J. Diagnostic des syndromes d'auto-immunisation en cardiologie par la réaction d'inhibition de migration des leucocytes. Ann Med Interne (Paris) 1974 Oct;125(10):711–718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantor F. S. Infection, anergy and cell-mediated immunity. N Engl J Med. 1975 Mar 20;292(12):629–634. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197503202921210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laufer A., Davies A. M. Experimental granulomatous myocarditis: genesis and immunological aspects. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1969 Jan 31;156(1):91–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1969.tb16720.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacSween R. N., Thomas M. A. Lymphocyte transformation by phytohaemagglutinin (PHA) and purified protein derivative (PPD) in primary biliary cirrhosis. Evidence of serum inhibitory factors. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Dec;15(4):523–533. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisch B., Berg P. A., Kochsiek K. Clinical significance of immunopathological findings in patients with post-pericardiotomy syndrome. I. Relevance of antibody pattern. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Nov;38(2):189–197. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortensen R. F., Osmand A. P., Gewurz H. Effects on C-reactive protein on the lymphoid system. I. Binding to thymus-dependent lymphocytes and alteration of their functions. J Exp Med. 1975 Apr 1;141(4):821–839. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. S., Gatti R. A. Humoral factors influencing lymphocyte transformation. Prog Allergy. 1976;21:261–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newberry W. M., Shorey J. W., Sanford J. P., Combes B. Depression of lymphocyte reactivity to phytohemagglutinin by serum from patients with liver disease. Cell Immunol. 1973 Jan;6(1):87–97. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newble D. I., Holmes K. T., Wangel A. G., Forbes I. J. Immune reactions in acute viral hepatitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Apr;20(1):17–28. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paronetto F., Popper H. Lymphocyte stimulation induced by halothane in patients with hepatitis following exposure to halothane. N Engl J Med. 1970 Aug 6;283(6):277–280. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197008062830602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penhale W. J., Farmer A., Maccuish A. C., Irvine W. J. A rapid micro-method for the phytohaemagglutinin-induced human lymphocyte transformation test. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Sep;18(1):155–167. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddle P. R., Berenbaum M. C. Postoperative depression of the lymphocyte response to phytohaemagglutinin. Lancet. 1967 Apr 8;1(7493):746–748. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91364-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


