Abstract
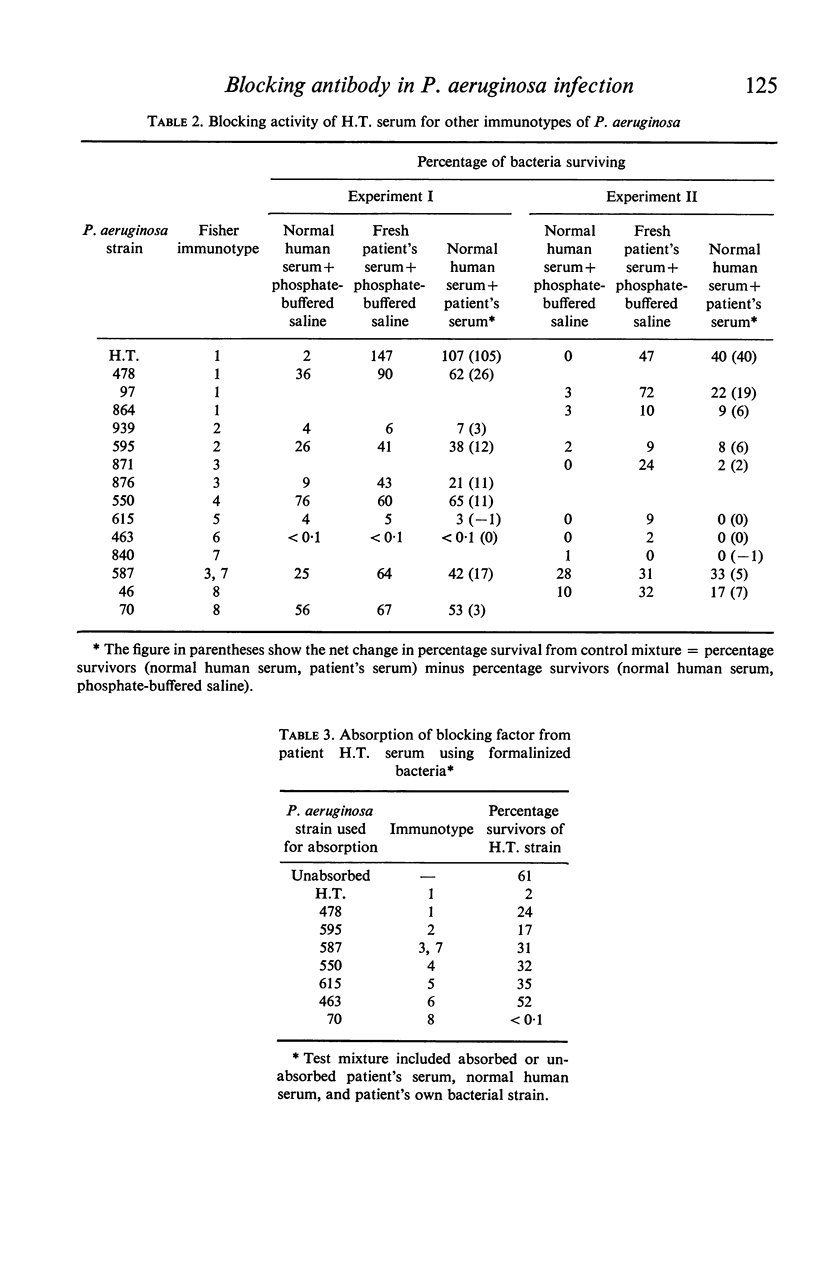
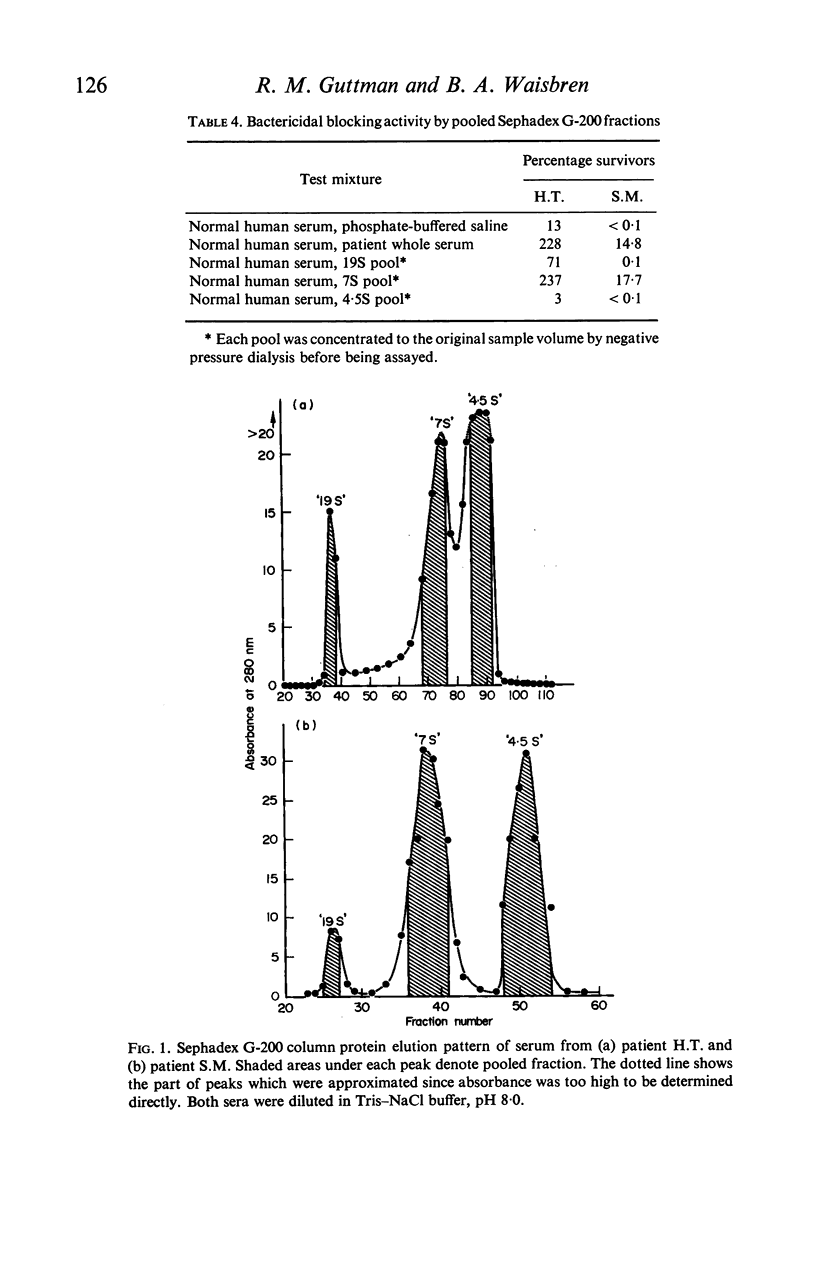
A factor has been demonstrated in the serum of some patients with chronic Gram-negative infections which specifically blocks bactericidal activity against the infecting organism. Sera with this factor, that had been obtained from patients suffering from chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections, were fractionated by Sephadex G-200 and DEAE-Sephadex column chromatography. Blocking activity was detected in the Sephadex G-200 '7S' peak and eluted from the DEAE column along with the serum IgG. Immunoelectrophoresis studies of this material along with pure IgG showed that the bactericidal blocking factor in these patients was IgG. The blocking factor was specific in its ability to protect bacteria, and could be absorbed from the serum by the particular bacterial strain isolated from the patient. Possible clinical importance of blocking activity by IgG is suggested by the persistent nature of the Ps. aeruginosa infections in these patients.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borsos T., Rapp H. J. Complement fixation on cell surfaces by 19S and 7S antibodies. Science. 1965 Oct 22;150(3695):505–506. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3695.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Becker E. L. The effect of carbamylation and amidination of rabbit gamma-G-antibody on its ability to fix complement. J Immunol. 1968 Feb;100(2):395–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher M. W., Devlin H. B., Gnabasik F. J. New immunotype schema for Pseudomonas aeruginosa based on protective antigens. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):835–836. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.835-836.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAINES S., LANDY M. Prevalence of antibody to Pseudomonas in normal human sera. J Bacteriol. 1955 Jun;69(6):628–633. doi: 10.1128/jb.69.6.628-633.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GELOTTE B., FLODIN P., KILLANDER J. Fractionation of human plasma proteins by gel filtration and zone electrophoresis or ion-exchange chromatography. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1962 Sep;Suppl 1:319–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gower P. E., Taylor P. W., Koutsaimanis K. G., Roberts A. P. Serum bactericidal activity in patients with upper and lower urinary tract infections. Clin Sci. 1972 Jul;43(1):13–22. doi: 10.1042/cs0430013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KILLANDER J., HOGMAN C. F. Fractionation of human blood group antibodies by gel filtration. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1963;15 (Suppl 69):130–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louria D. B., Smith J. K., Brayton R. G., Buse M. Anti-Candida factors in serum and their inhibitors. I. Clinical and laboratory observations. J Infect Dis. 1972 Feb;125(2):102–114. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.2.102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MICHAEL J. G., ROSEN F. S. ASSOCIATION OF "NATURAL" ANTIBODIES TO GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA WITH THE GAMMA-1-MACROGLOBULINS. J Exp Med. 1963 Oct 1;118:619–626. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.4.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. W. An antibactericidal factor in the serum of two patients with infections of the upper urinary tract. Clin Sci. 1972 Jul;43(1):23–30. doi: 10.1042/cs0430023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waisbren B. A., Brown I. A factor in the serum of patients with persisting infection that inhibits the bactericidal activity of normal serum against the organism that is causing the infection. J Immunol. 1966 Sep;97(3):431–437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedermann D., Wiedermannová D., Vaerman J. P., Heremans J. F. A longitudinal study of serum alpha-1-antitrypsin, alpha-2-macroglobulin, transferrin, immunoglobulins IgG, IgA and IgM, and H- and O-agglutinin titers in children following infection with Salmonella enteritidis. J Infect Dis. 1970 Jan;121(1):74–77. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.1.74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]