Abstract
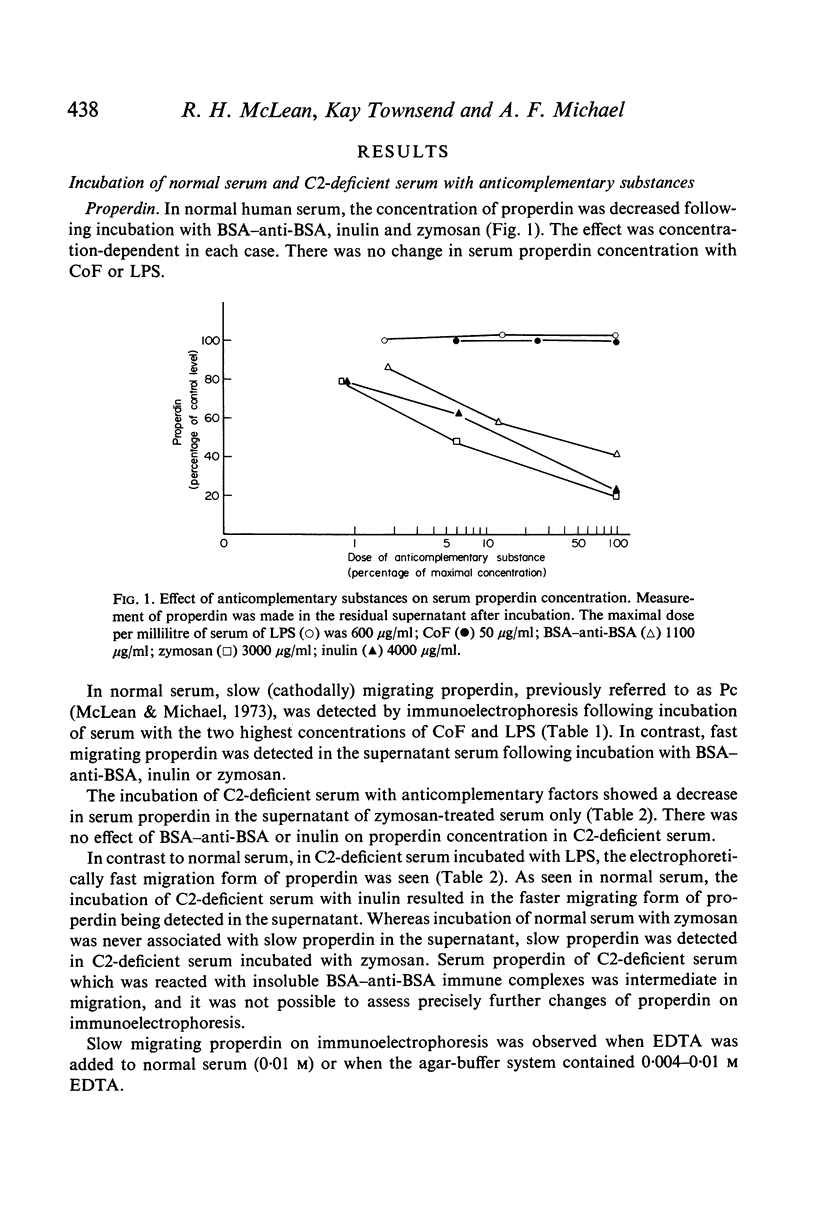
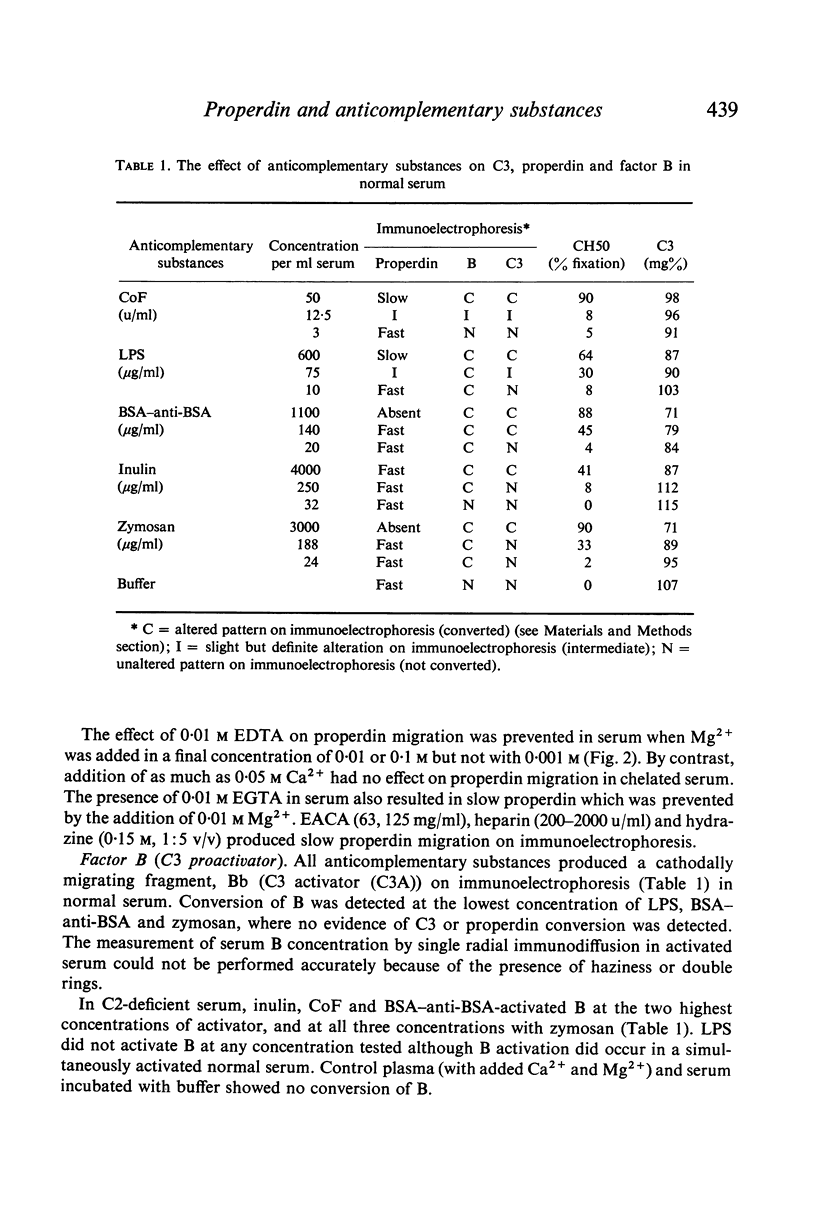
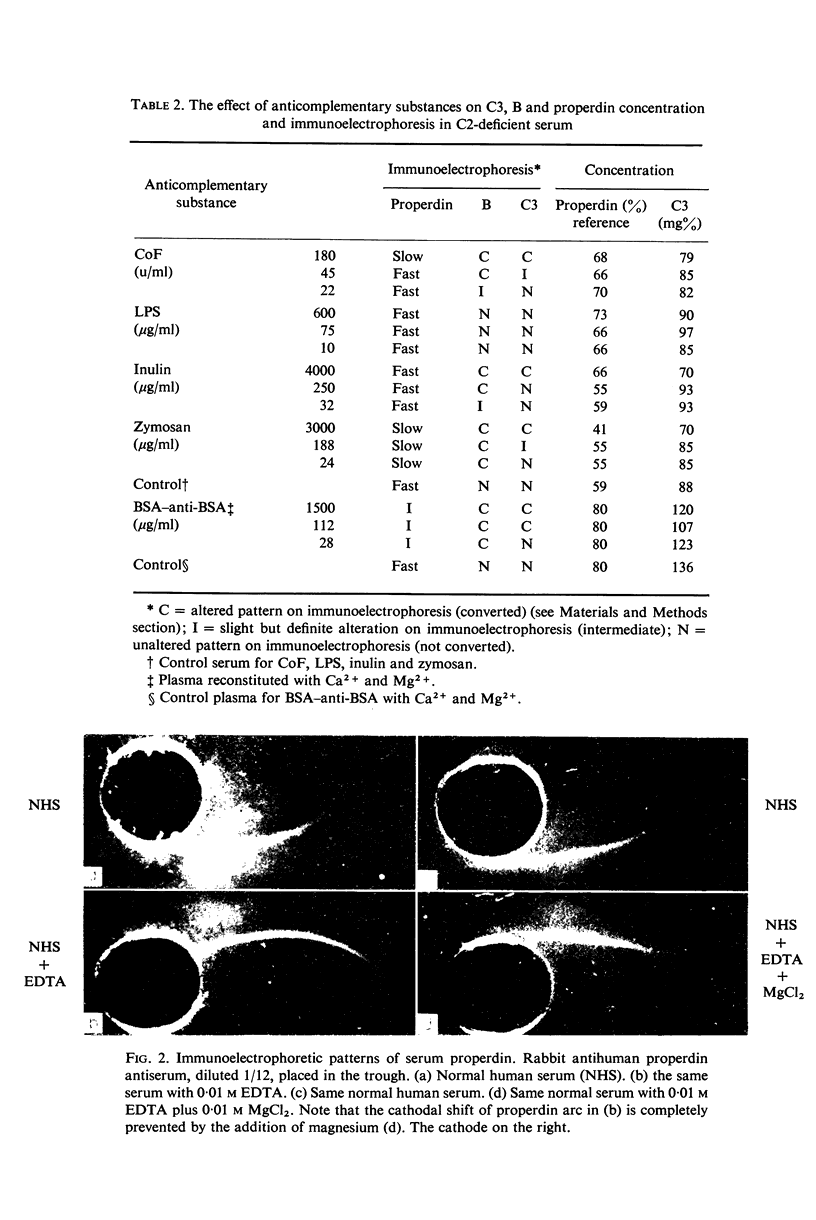
The effect of anticomplementary substances, including zymosan, cobra venom, endotoxin, inulin and immune complexes, on serum properdin concentration and immunoelectrophoretic mobility was studied. In normal serum, zymosan, inulin and immune complexes 'fixed' properdin, while in C2-deficient serum, only zymyosan 'fixed' properdin. Slowly migrating properdin (P) was detected in normal serum following activation by endotoxin and cobra venom but in C2-deficient serum only with cobra venom. Endotoxin did not activate the alternative pathway proteins studied in C2-deficient serum. Fast migrating properdin (P) represented activated properdin and occured as a result of activation of properdin in the Noble agar medium used for electrophoresis provided sufficient cofactors, including Mg2+, were present.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brade V., Lee G. D., Nicholson A., Shin H. S., Mayer M. M. The reaction of zymosan with the properdin system in normal and C4-deficienct guinea pig serum. Demonstration of C3- and C5-cleaving multi-unit enzymes, both containing factor B, and acceleration of their formation by the classical complement pathway. J Immunol. 1973 Nov;111(5):1389–1400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day N. K., Geiger H., McLean R., Michael A., Good R. A. C2 deficiency. Development of lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jul;52(7):1601–1607. doi: 10.1172/JCI107337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensky J., Hinz C. F., Jr, Todd E. W., Wedgwood R. J., Boyer J. T., Lepow I. H. Properties of highly purified human properdin. J Immunol. 1968 Jan;100(1):142–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gewurz H., Shin H. S., Mergenhagen S. E. Interactions of the complement system with endotoxic lipopolysaccharide: consumption of each of the six terminal complement components. J Exp Med. 1968 Nov 1;128(5):1049–1057. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.5.1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Götze O., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The role of properdin in the alternate pathway of complement activation. J Exp Med. 1974 Jan 1;139(1):44–57. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.1.44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson F. R., Agnello V., Williams R. C., Jr Opsonic activity in human serum deficient in C2. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):141–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane M. A., May J. E., Frank M. M. Interactions of the classical and alternate complement pathway with endotoxin lipopolysaccharide. Effect on platelets and blood coagulation. J Clin Invest. 1973 Feb;52(2):370–376. doi: 10.1172/JCI107193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus R. L., Shin H. S., Mayer M. M. An alternate complement pathway: C-3 cleaving activity, not due to C4,2a, on endotoxic lipopolysaccharide after treatment with guinea pig serum; relation to properdin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1351–1354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean R. H., Michael A. F. Properdin anc C3 proactivator: alternate pathway components in human glomerulonephritis. J Clin Invest. 1973 Mar;52(3):634–644. doi: 10.1172/JCI107225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean R. H., Michael A. F. The immunoelectrophoretic pattern of properdin in fresh and aged human serum. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Nov;141(2):403–407. doi: 10.3181/00379727-141-36786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J., Fjellström K. E. Isolation of the anticomplementary protein from cobra venom and its mode of action on C3. J Immunol. 1971 Dec;107(6):1666–1672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J., Götze O. C3 proactivator convertase and its mode of action. J Exp Med. 1972 Apr 1;135(4):1003–1008. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.4.1003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PILLEMER L., BLUM L., LEPOW I. H., ROSS O. A., TODD E. W., WARDLAW A. C. The properdin system and immunity. I. Demonstration and isolation of a new serum protein, properdin, and its role in immune phenomena. Science. 1954 Aug 20;120(3112):279–285. doi: 10.1126/science.120.3112.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PILLEMER L., BLUM L., LEPOW I. H., WURZ L., TODD E. W. The properdin system and immunity. III. The zymosan assay of properdin. J Exp Med. 1956 Jan 1;103(1):1–13. doi: 10.1084/jem.103.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J. K., Snyderman R., Mergenhagen S. E. Activation of complement by endotoxin: a role for 2 globulin, C1, C4 and C2 in the consumption of terminal complement components by endotoxin-coated erythrocytes. J Immunol. 1972 Aug;109(2):334–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickering R. J., Michael A. F., Jr, Herdman R. C., Good R. A., Gewurz H. The complement system in chronic glomerulonephritis: three newly associated aberrations. J Pediatr. 1971 Jan;78(1):30–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(71)80261-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyderman R., Gewurz H., Mergenhagen S. E., Jensen J. Effect of C4 depletion on the utilization of the terminal components of guinea-pig complement by endotoxin. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 2;231(22):152–154. doi: 10.1038/newbio231152a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitzel A. E., Spitzer R. E. The utilization of properdin in the alternate pathway of complement activation: isolation of properdin convertase. J Immunol. 1974 Jan;112(1):56–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westberg N. G., McLean R. H., Michael A. F. Determination of serum properdin levels by immunodiffusion. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1973;44(1):155–160. doi: 10.1159/000230924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


