Abstract
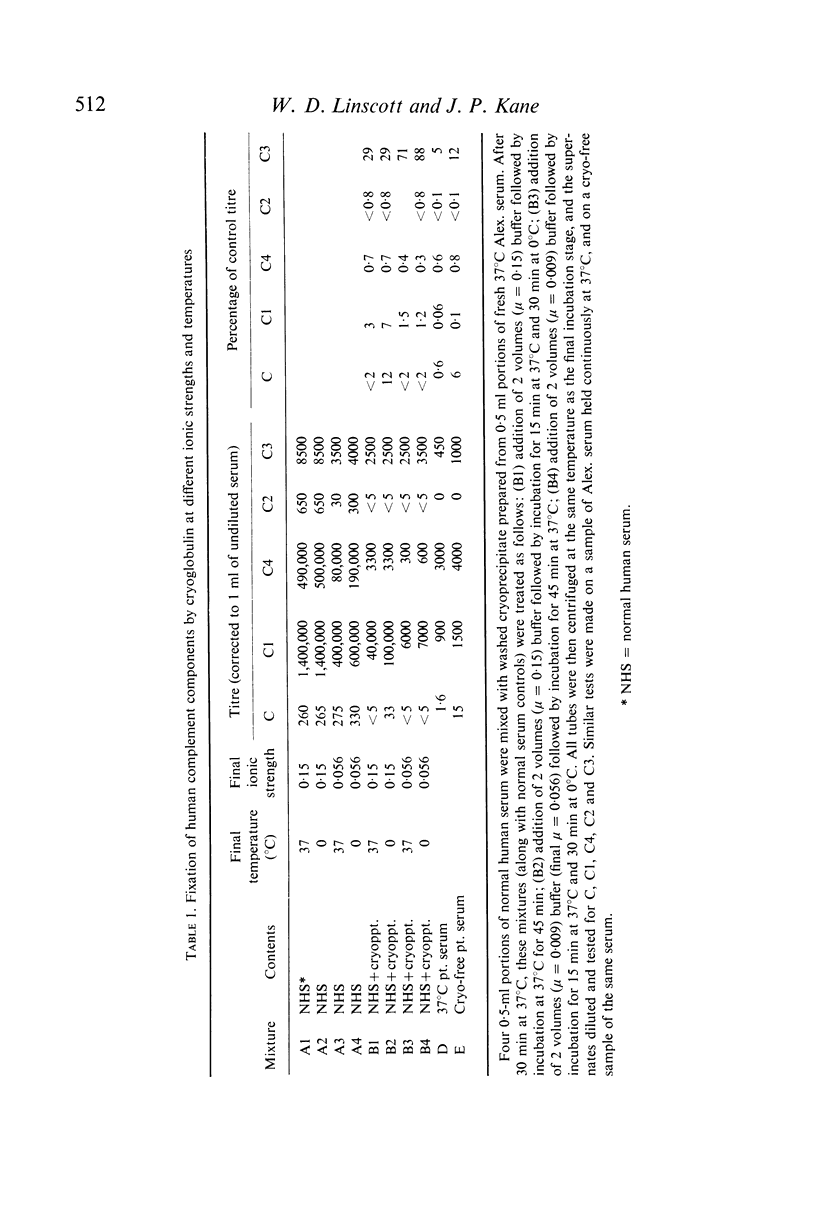
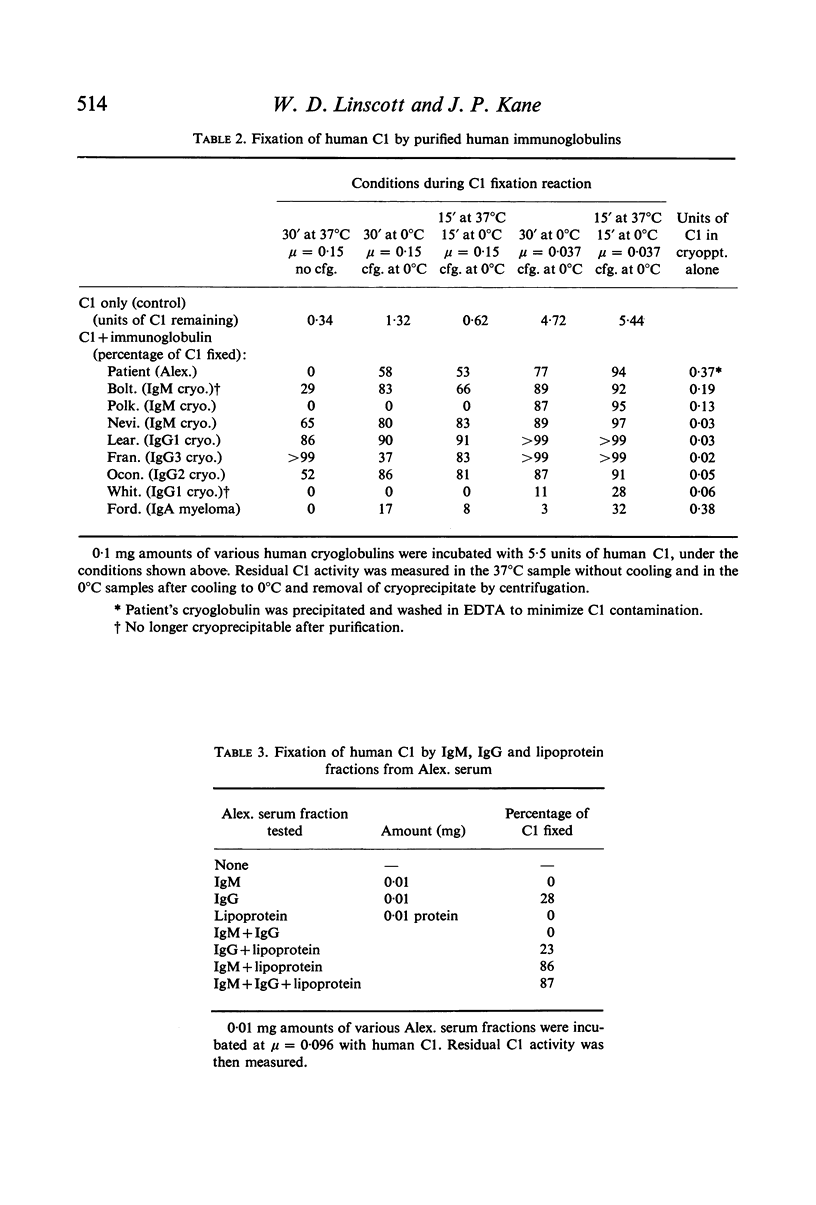
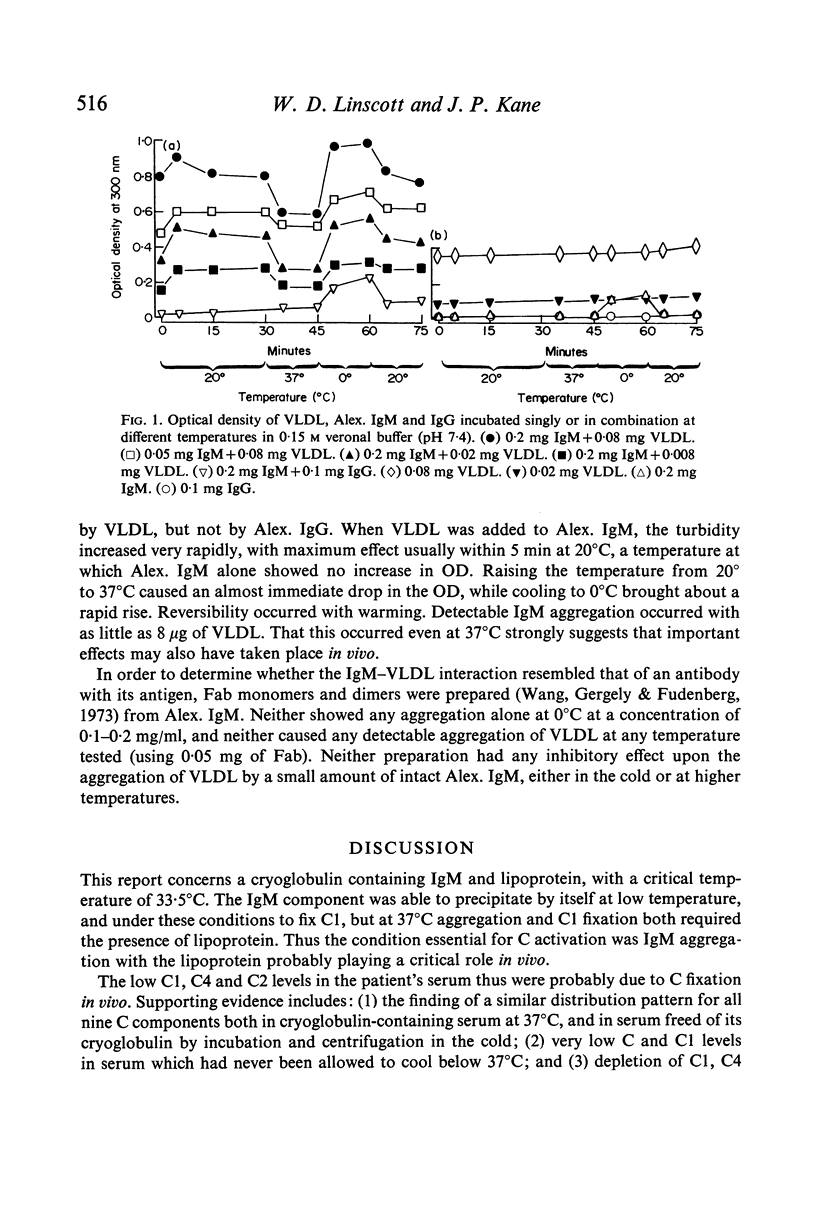
Serum from a patient with an IgM-lipoprotein cryoglobulin, both before and after removal of the cryoprecipitate at 0 degrees C, had extremely low levels of whole complement (C), C1, C4 and C2, while amounts of the remaining components were normal or only slightly reduced. The cryopredipitate, when added to fresh normal human serum, reproduced this pattern of C fixation. Separation of the patients's serum at 37 degrees C into its lipoprotein, IgG and IgM fractions revealed that the IgM alone would precipitate at 0 degrees C. This precipitation was unaffected by the patients's IgG, but was markedly enhanced by extremely small amounts of the patient's d less than 1-075 lipoprotein fraction or of homologous very low density lipoprotein (VLDL). Aggregation occurred even at 37 degrees C in the presence of VLDL. Fixation of semi-purified human C1 paralleled these results closely: it occurred with the patient's IgM alone at 0 degrees but not at 37 degrees C, while IgM in the presence of the patient's lipoprotein, or of VLDL from normal serum, fixed C1 strongly at 37 degrees as well as at 0 degrees C. Fab dimers and monomers prepared from the patient's IgM did not aggregate in the cold, even in the presence of lipoprotein, and did not inhibit the aggregation of intact IgM in the presence of VLDL, at any temperature. All three highly purified IgM cryoglobulins, and three of four IgG cryoglobulins, fixed C1 strongly. The IgG preparation which failed to fix C1 was the only one which had lost its cryoprecipitability during purification. Measurement of C3 or whole C levels may be an insensitive method for detecting C fixation in cryoglobulinaemia. It is suggested that analysis for C1, C4 or C2 should be employed instead.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Augener W., Grey H. M., Cooper N. R., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The reaction of monomeric and aggregated immunoglobulins with C1. Immunochemistry. 1971 Nov;8(11):1011–1020. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90489-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsos T., Rapp H. J. Immune hemolysis: a simplified method for the preparation of EAC'4 with guinea pig or with human complement. J Immunol. 1967 Aug;99(2):263–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costanzi J. J., Coltman C. A., Jr, Donaldson V. H. Activation of complement by a monoclonal cryoglobulin associated with cold urticaria. J Lab Clin Med. 1969 Dec;74(6):902–910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grey H. M., Kohler P. F. Cryoimmunoglobulins. Semin Hematol. 1973 Apr;10(2):87–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linscott W. D. Complement fixation: the effects of IgG and IgM antibody concentration on C1-binding affinity. J Immunol. 1970 Oct;105(4):1013–1023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linscott W. D. Immune hemolysis: serial studies of the dissociability of IgG and IgM anti-Forssman antibodies using the C'la fixation and transfer technique. J Immunol. 1969 Apr;102(4):986–992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linscott W. D. The effects of ionic strength, temperature, and antibody class and avidity on fixation and transfer of the first component of complement. J Immunol. 1969 Apr;102(4):993–1001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez J. S., Kohler P. F. Variant "Goodpasture's syndrome"? The need for immunologic criteria in rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis and hemorrhagic pneumonitis. Ann Intern Med. 1971 Jul;75(1):67–76. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-75-1-67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer M., Franklin E. C., Elias K., McCluskey R. T., Cooper N. Cryoglobulinemia--a clinical and laboratory study. II. Cryoglobulins with rheumatoid factor activity. Am J Med. 1966 Jun;40(6):837–856. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(66)90200-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPP H. J., BORSOS T. EFFECTS OF LOW IONIC STRENGTH ON IMMUNE HEMOLYSIS. J Immunol. 1963 Dec;91:826–832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riethmüller G., Meltzer M., Franklin E., Miescher P. A. Serum complement levels in patients with mixed (IgM-IgG) cryoglobulinaemia. Clin Exp Immunol. 1966 Jul;1(3):337–339. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore B., Shore V. Isolation and characterization of polypeptides of human serum lipoproteins. Biochemistry. 1969 Nov;8(11):4510–4516. doi: 10.1021/bi00839a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. C., Gergely J., Fudenberg H. H. Amino acid sequences at constant and variable regions of heavy chains of monotypic immunoglubulins G and M of a single patient. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 30;12(3):528–534. doi: 10.1021/bi00727a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. C., Wells J. V., Fudenberg H. H. Chemical analyses of cryoglobulins. Immunochemistry. 1974 Jul;11(7):341–345. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(74)90186-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


