Abstract
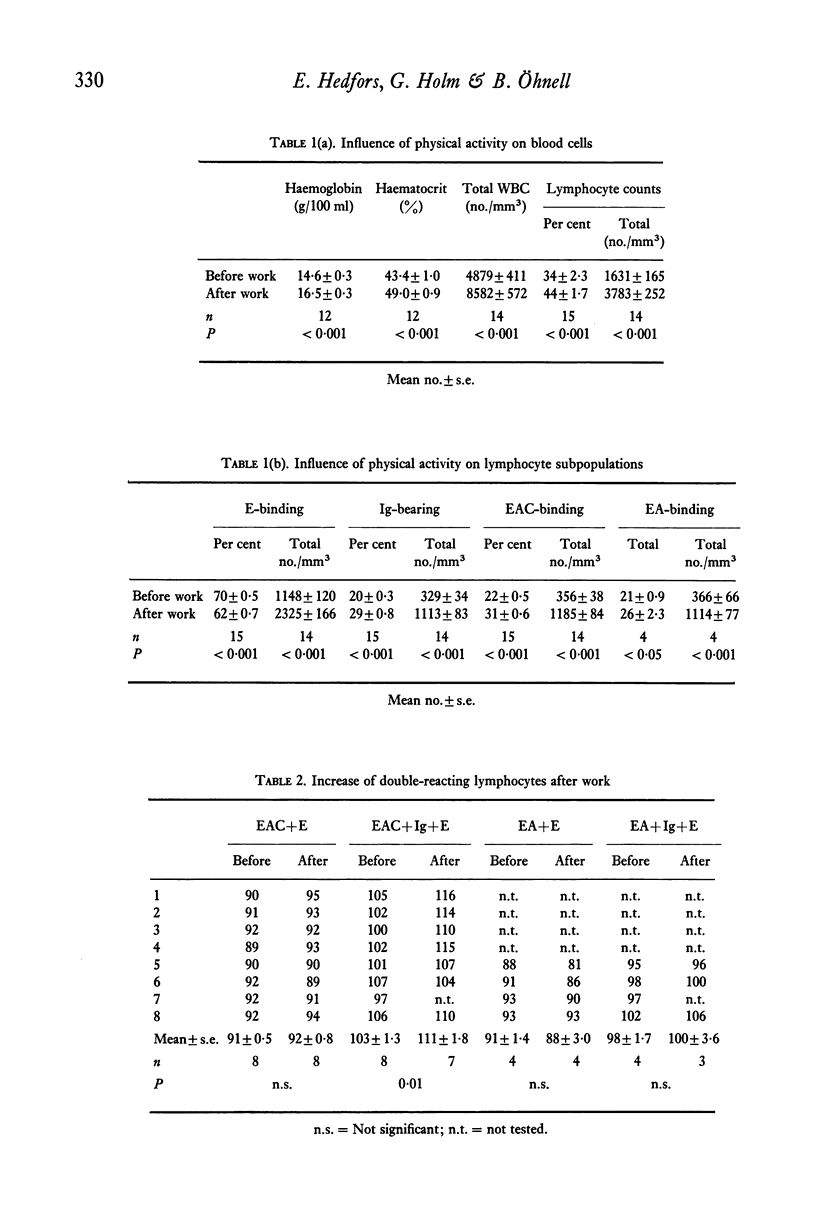
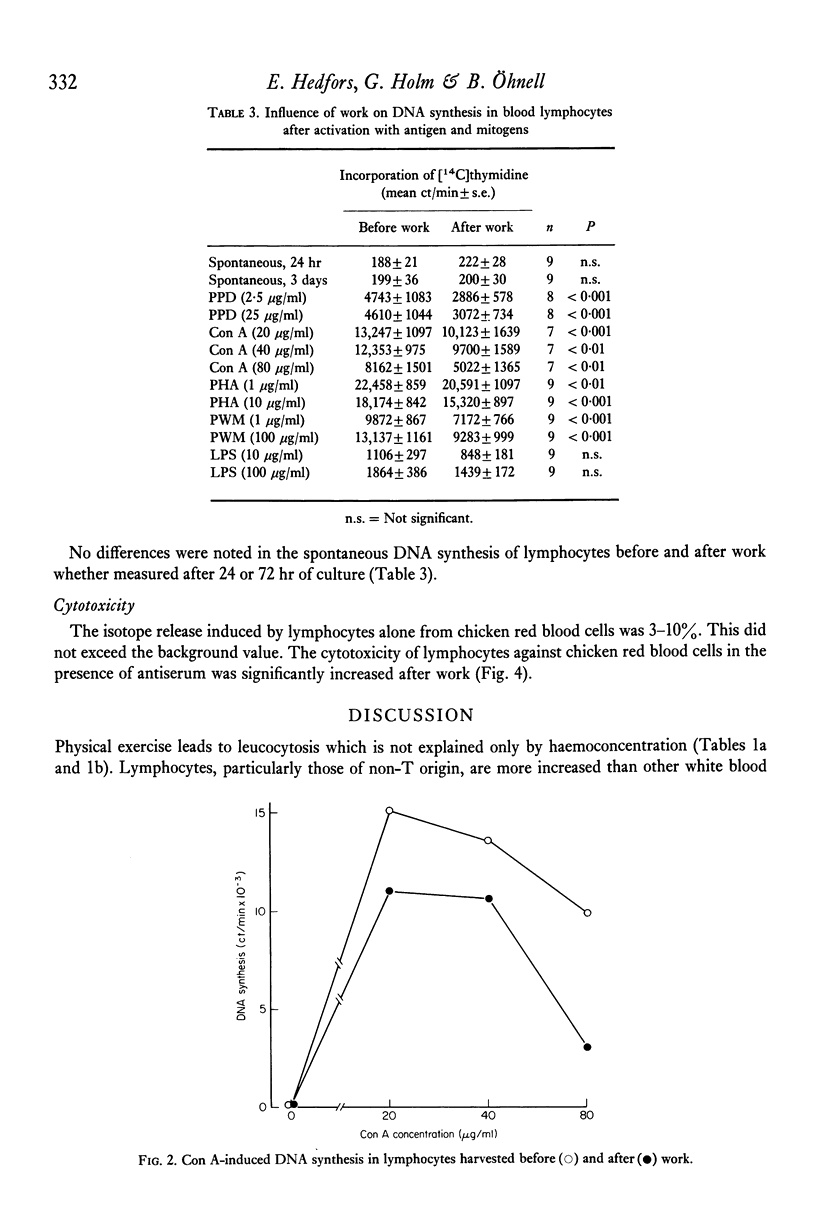
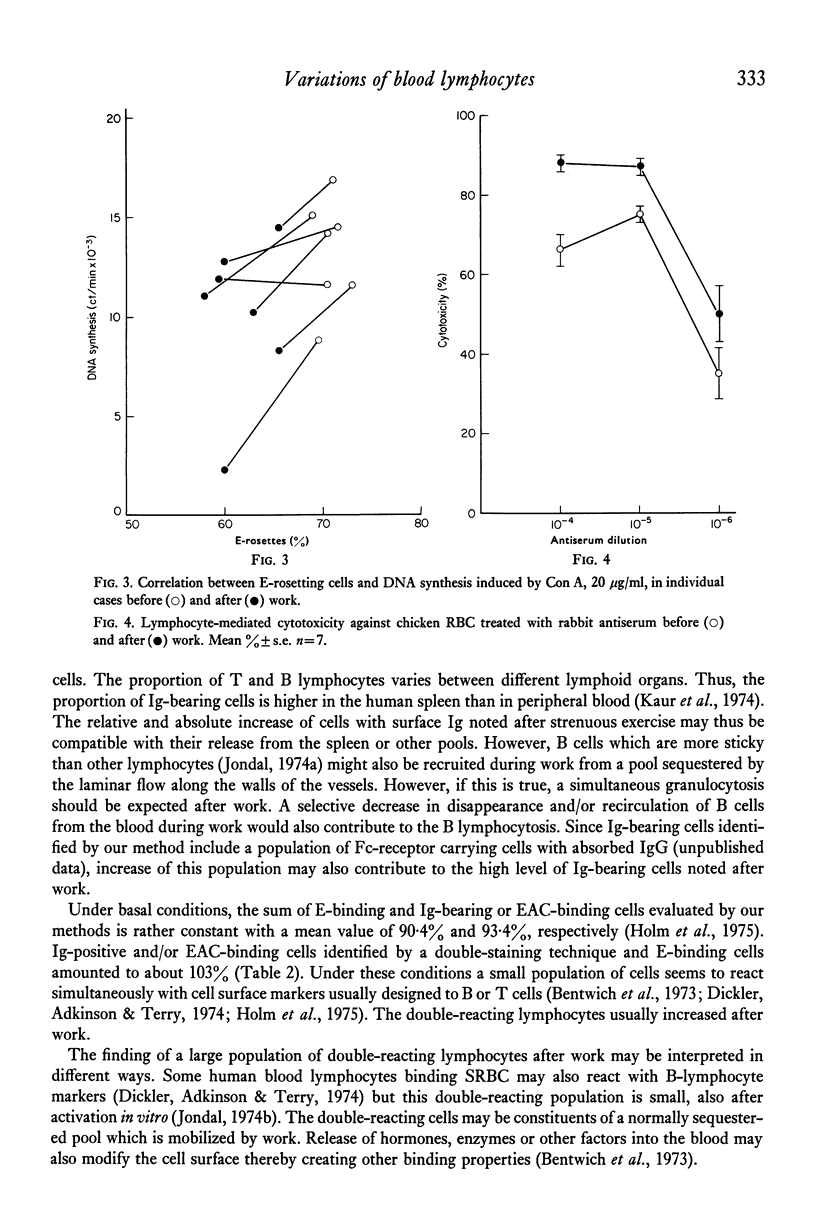
Highly purified peripheral blood lymphocytes from healthy individuals were obtained from samples collected before and after a standardized bicycle ergometer test. The physical activity resulted in a marked increase of circulating lymphocytes. The proportion of T lymphocytes estimated as cells forming rosettes with sheep red blood cells after incubation in the cold decreased, whereas a corresponding increase of cells with receptors for C3, IgG-Fc or surface immunoglobulin was noted. Moreover, after work an increase of cells simultaneously reacting with cell surface markers usually designed as T- or B-cell markers occurred. The reactivity of lymphocytes collected after work in response to Con A, PHA, PWM and PPD was impaired, whereas the slight response to LPS was unchanged. The K-cell cytotoxicity of lymphocytes collected after work increased. The data indicate that physical activity leads to the mobilization of lymphocytes from as yet undetermined sites and with changed composition and reactivity.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson J., Sjöberg O., Möller G. Mitogens as probes for immunocyte activation and cellular cooperation. Transplant Rev. 1972;11:131–177. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1972.tb00048.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentwich Z., Douglas S. D., Siegal F. P., Kunkel H. G. Human lymphocyte-sheep erythrocyte rosette formation: some characteristics of the interaction. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1973 Jul;1(4):511–522. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(73)90007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biberfeld P., Mellstedt H. Selective activation of human B-lymphocytes by suboptimal doses of pokeweed mitogen (PWM). Quantitation and ultrastructure of the stimulated cells. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Dec;89(2):377–388. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90803-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chess L., MacDermott R. P., Schlossman S. F. Immunologic functions of isolated human lymphocyte subpopulations. I. Quantitative isolation of human T and B cells and response to mitogens. J Immunol. 1974 Oct;113(4):1113–1121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickler H. B., Adkinson N. F., Jr, Terry W. D. Evidence for individual human peripheral blood lymphocytes bearing both B and T cell markers. Nature. 1974 Jan 25;247(5438):213–215. doi: 10.1038/247213a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas S. D. Electron microscopic and functional aspects of human lymphocyte response to mitogens. Transplant Rev. 1972;11:39–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1972.tb00045.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedfors E. Activation of peripheral T cells of sarcoidosis patients and healthy controls. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Nov;18(3):379–390. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M. Surface markers on human B and T lymphocytes. III. A marker for lymphoid adherence. Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(3):269–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1974.tb01257.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M. Surface markers on human B and T lymphocytes. IV. Distribution of surface markers on resting and blast-transformed lymphocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(6):739–747. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1974.tb01309.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaur J., Catovsky D., Spiers A. S., Galton D. A. Increase of T lymphocytes in the spleen in chronic granulocytic leukaemia. Lancet. 1974 May 4;1(7862):834–836. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90484-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald H. R., Bonnard G. D. A comparison of the effector cells involved in cell-mediated lympholysis and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity in man. Scand J Immunol. 1975;4(2):129–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1975.tb02609.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellstedt H. In vitro activation of human T and B lymphocytes by pokeweed mitogen. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Jan;19(1):75–82. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E. The glomerular permeability determined by dextran clearance using Sephadex gel filtration. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1968;21(1):77–82. doi: 10.3109/00365516809076979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann P., Perlmann H., Wigzell H. Lymphocyte mediated cytotoxicity in vitro. Induction and inhibition by humoral antibody and nature of effector cells. Transplant Rev. 1972;13:91–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1972.tb00061.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steel C. M., Evans J., Smith M. A. Physiological variation in circulating B cell:T cell ratio in man. Nature. 1974 Feb 8;247(5440):387–389. doi: 10.1038/247387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stobo J. D., Rosenthal A. S., Paul W. E. Functional heterogeneity of murine lymphoid cells. I. Responsiveness to and surface binding of concanavalin A and phytohemagglutinin. J Immunol. 1972 Jan;108(1):1–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxdal M. J., Basham T. Y. B and T-cell stimulatory activities of multiple mitogens from pokeweed. Nature. 1974 Sep 13;251(5471):163–164. doi: 10.1038/251163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


