Abstract
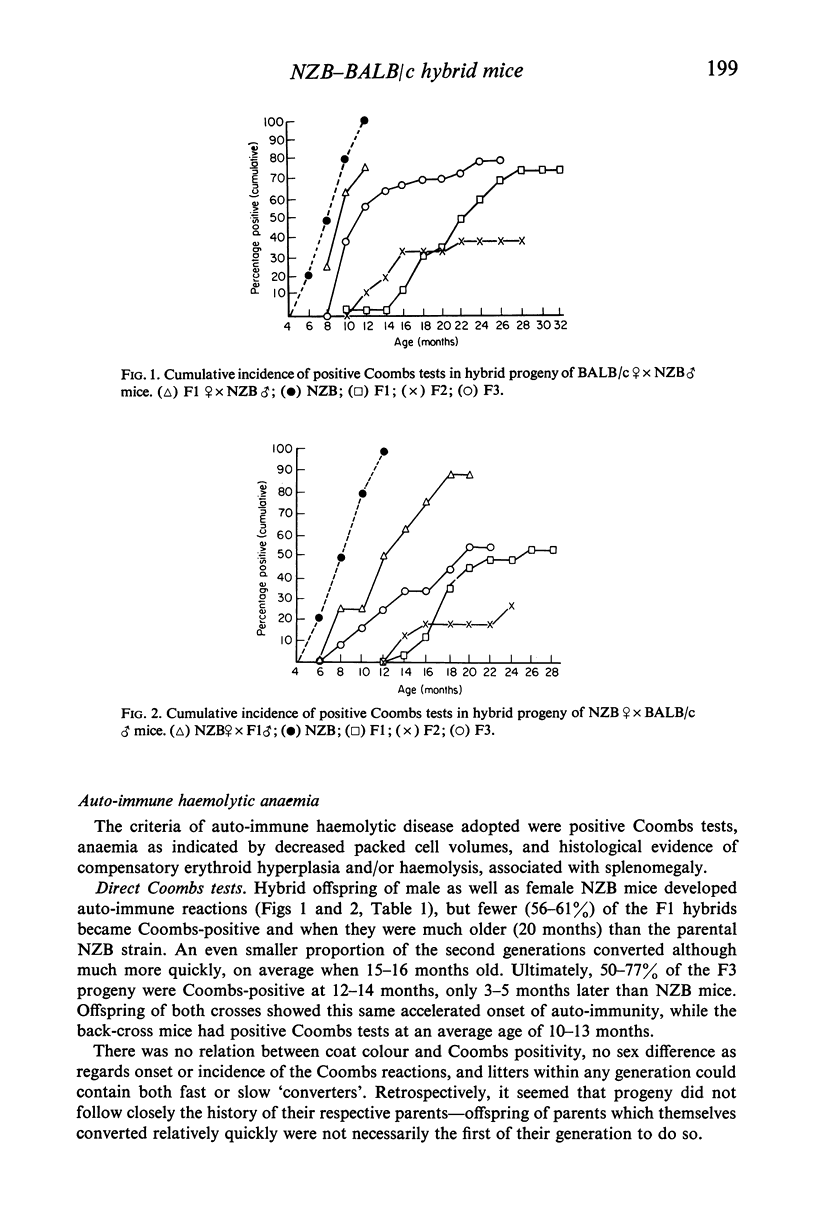
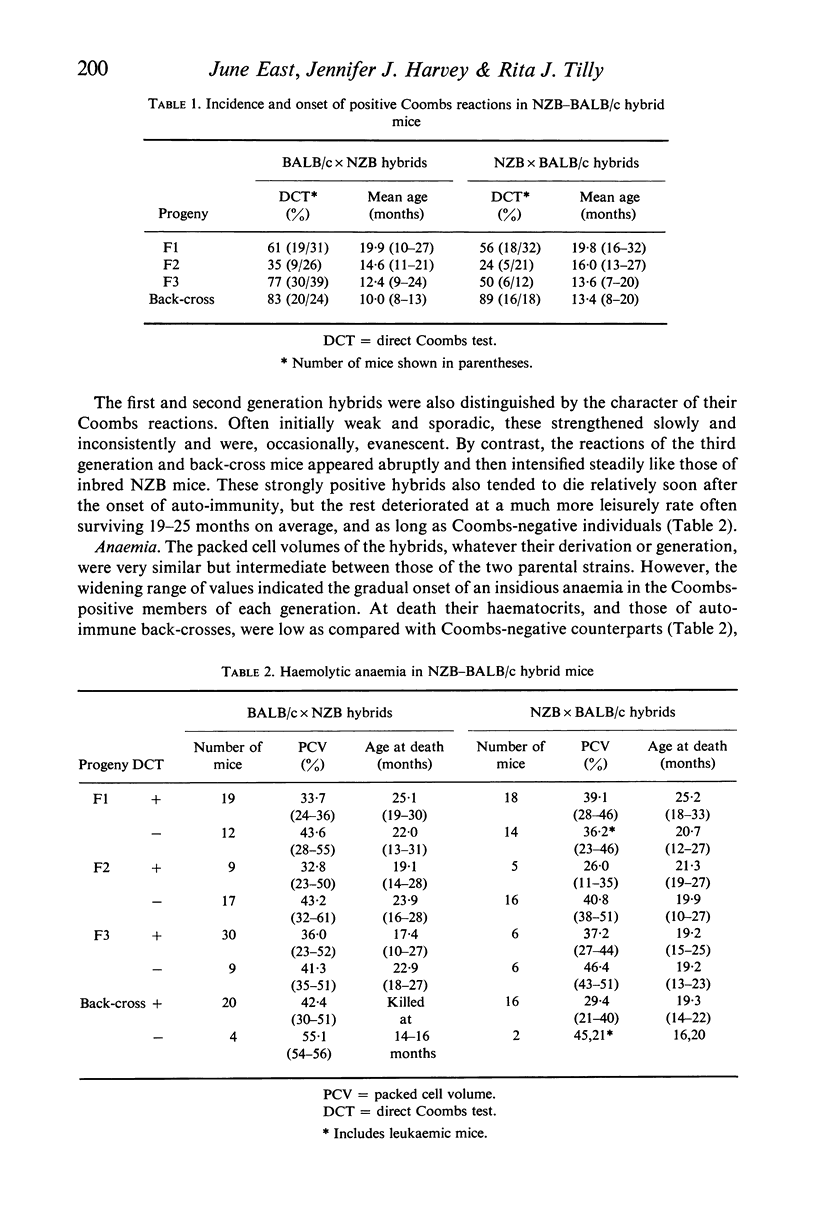
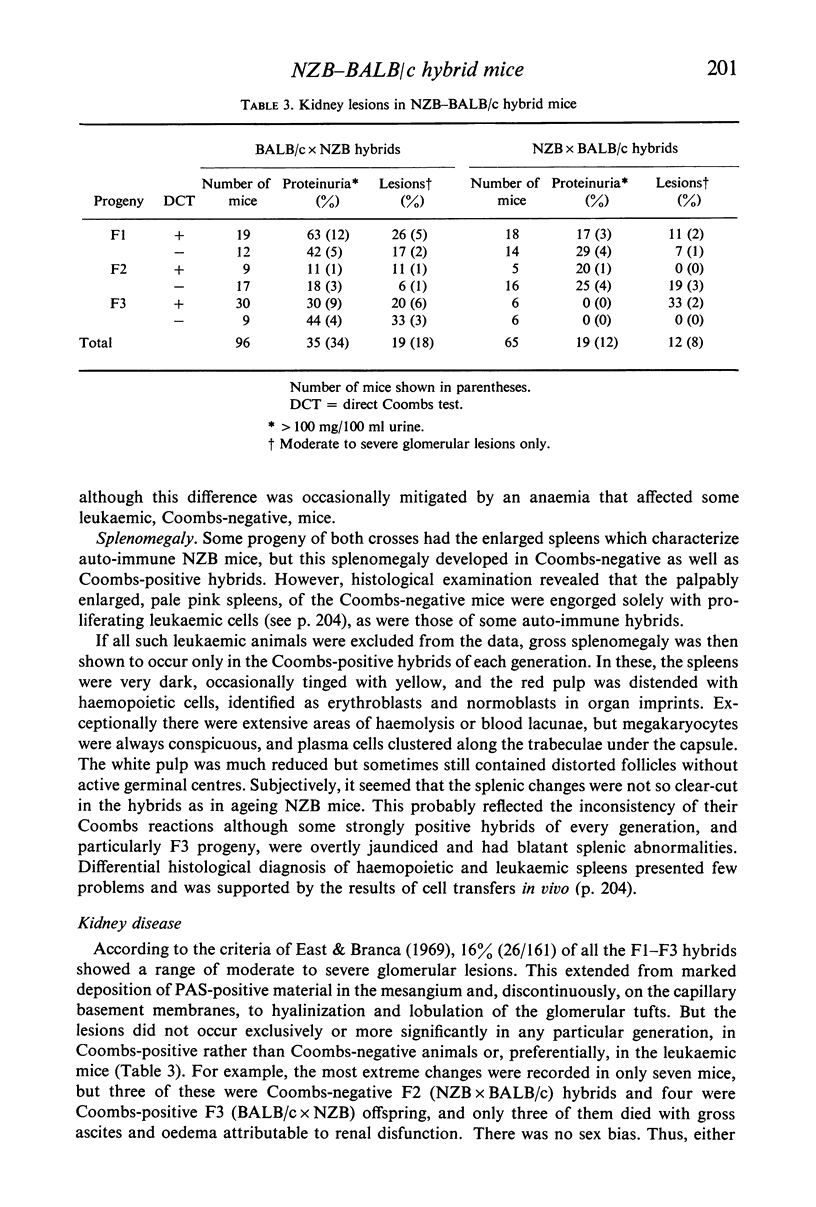
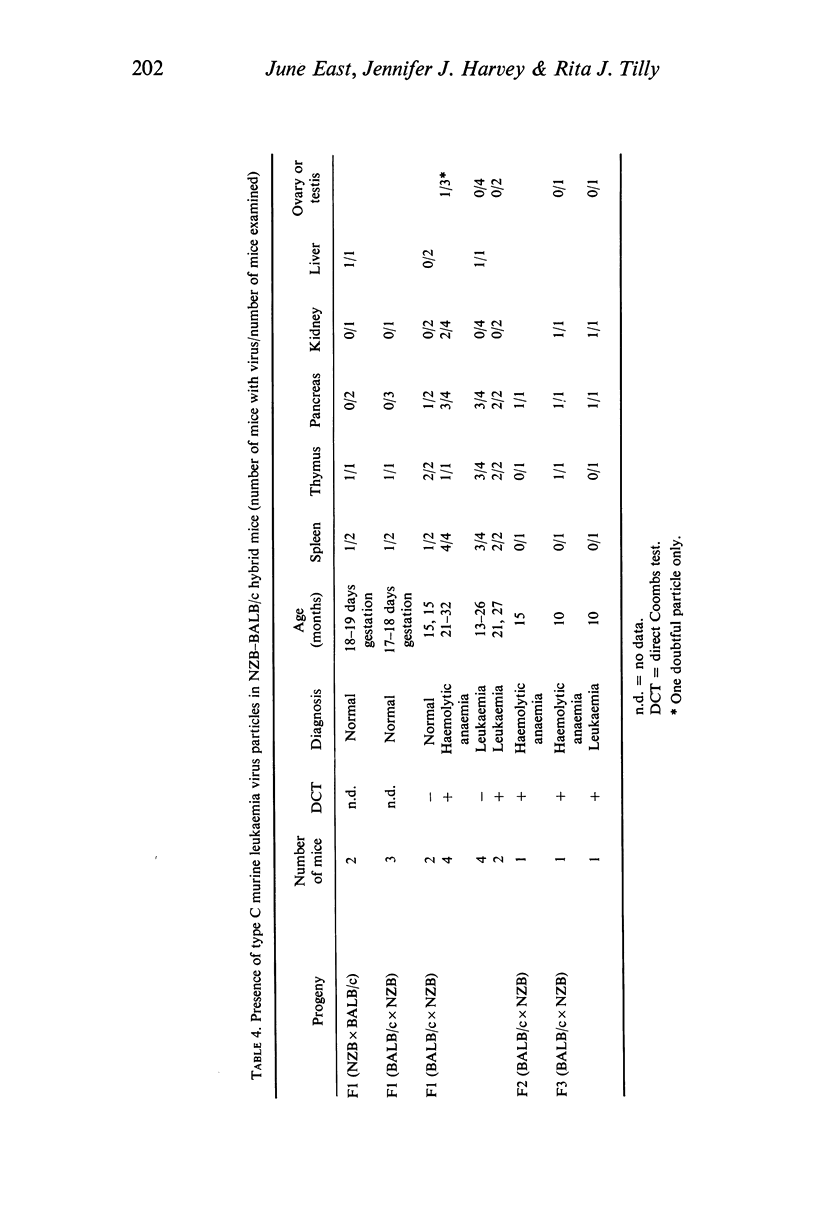
When mated to normal BALB/c partners, male and female NZB mice transmitted auto-immune haemolytic anaemia to three generations of their hybrid progeny. Red cell auto-antibodies (positive Coombs tests) were detected, on average, 11 months later in the F1 hybrids than in the parental strain, and the course of the disease was protracted. In explicably, the auto-immune reactions then appeared progressively earlier in successive generations of both croses. The Coombs reactions of the F1 and F2 hybrids were often weak and inconsistent, while those of F3 offspring showed the strong and stable picture typical of NZB mice. The incidence of auto-immune disease in each generation, although similar in the reciprocal crosses, indicated that the pattern of inheritance was very complex. The hybrids did not develop the lymphoid type B reticulum cell neoplasia which characterizes auto-immune NZB mice. Instead, and irrespective of Coombs status, they had lymphocytic leukaemias, lung adenomas, hepatomas and type A reticulum cell neoplasms of the liver. Murine leukaemia virus was identified electronmicroscopically in F1 embryos, and in all the adults examined. It was also isolated from leukaemic spleen cells passaged briefly in vivo, and from malignant hepatic (reticulum) cells maintained in vitro. These isolated were leukaemogenic in newborn BALB/c, NZB, and F1 hybrid recipients, but did not induce or accelerate positive Coombs reactions. Only a small proportion of the hybrids had significant glomerulonephritis, and overt kidney disease was minimal. The lesions were not confined to Coombs-positive mice. Possible links between auto-immunity, malignancy, and virus infection in NZB mice are discussed in the light of these results.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoki T., Boyse E. A., Old L. J., De Harven E., Hämmerling U., Wood H. A. G (Gross) and H-2 cell-surface antigens: location on Gross leukemia cells by electron microscopy with visually labeled antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Mar;65(3):569–576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.3.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERNHARD W. The detection and study of tumor viruses with the electron microscope. Cancer Res. 1960 Jun;20:712–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIELSCHOWSKY M., BIELSCHOWSKY F. OBSERVATIONS ON NZB/B1 MICE; DIFFERENTIAL FERTILITY IN RECIPROCAL CROSSES AND THE TRANSMISSION OF THE AUTO-IMMUNE HAEMOLYTIC ANAEMIA TO NZB/B1 X NZC/B1 HYBRIDS. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1964 Aug;42:561–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes R. D., Tuffrey M. A., Berry C. L. Auto-immune disease in (NZB x CFW) F1 mice. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(2):391–403. doi: 10.1002/path.1700950206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes R. D., Tuffrey M. Serum antinuclear factor and the influence of environment in mice. Nature. 1967 Jun 10;214(5093):1136–1138. doi: 10.1038/2141136a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braverman I. M. Study of autoimmune disease in New Zealand mice. I. Genetic features and natural history of NZB, NZY and NZW strains and NZB-NZW hybrids. J Invest Dermatol. 1968 Jun;50(6):483–499. doi: 10.1038/jid.1968.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnet F. M., Holmes M. C. The natural history of the NZB/NZW F1 hybrid mouse: a laboratory model of systemic lupus erythematosus. Australas Ann Med. 1965 Aug;14(3):185–191. doi: 10.1111/imj.1965.14.3.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnet M., Holmes M. C. Genetic investigations of autoimmune disease in mice. Nature. 1965 Jul 24;207(995):368–371. doi: 10.1038/207368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croker B. P., Jr, del Villano B. C., Jensen F. C., Lerner R. A., Dixon F. J. Immunopathogenicity and oncogenicity of murine leukemia viruses. I. Induction of immunologic disease and lymphoma in (BALB-c times NZB)F1 mice by Scripps leukemia virus. J Exp Med. 1974 Oct 1;140(4):1028–1048. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.4.1028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUNN T. B. Normal and pathologic anatomy of the reticular tissue in laboratory mice, with a classification and discussion of neoplasms. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1954 Jun;14(6):1281–1433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- East J., Branca M. Autoimmune reactions and malignant changes in germ-free New Zealand Black mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 Jun;4(6):621–635. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- East J., De Sousa M. A., Prosser P. R., Jaquet H. Malignant changes in New Zealand black mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1967 Jul;2(4):427–443. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- East J., De Sousa M. A. The thymus autoimmunity and malignancy in New Zealand black mice. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1966 Sep;22:605–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- East J. Immunopathology and neoplasms in New Zealand black (NZB) and SJL-J mice. Prog Exp Tumor Res. 1970;13:84–134. doi: 10.1159/000386038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- East J., de Sousa M. A., Parrott D. M. Immunopathology of New Zealand black (NZB) mice. Transplantation. 1965 Nov;3(6):711–729. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196511000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghaffar A., Playfair J. H. The genetic basis of autoimmunity in NZB mice studied by progeny-testing. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Mar;8(3):479–490. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleichmann H., Gleichmann E., André-Schwartz J., Schwartz R. S. Chronic allogeneic disease. 3. Genetic requirements for the induction of glomerulonephritis. J Exp Med. 1972 Mar 1;135(3):516–532. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.3.516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELYER B. J., HOWIE J. B. Renal disease associated with positive lupus erythematosus tests in a cross-bred strain of mice. Nature. 1963 Jan 12;197:197–197. doi: 10.1038/197197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELYER B. J., HOWIE J. B. Spontaneous auto-immune disease in NZB/BL mice. Br J Haematol. 1963 Apr;9:119–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1963.tb05450.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLMES M. C., BURNET F. M. THE INHERITANCE OF AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE IN MICE: A STUDY OF HYBRIDS OF THE STRAINS NZB AND C3H. Heredity (Edinb) 1964 Aug;19:419–434. doi: 10.1038/hdy.1964.52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. H., Dixon F. J. Genesis of antinuclear antibody in NZB-W mice: role of genetic factors and of viral infections. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Jun;6(6):829–839. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. H., Dixon F. J. Pathogenesis of the glomerulonephritis of NZB/W mice. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):507–522. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner R. A., Jensen F., Kennel S. J., Dixon F. J., Des Roches G., Francke U. Karyotypic, virologic, and immunologic analyses of two continuous lymphocyte lines established from New Zealand black mice: possible relationship of chromosomal mosaicism to autoimmunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2965–2969. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A., Pincus T. Demonstration of biological activity of a murine leukemia virus of New Zealand black mice. Science. 1970 Oct 16;170(3955):326–327. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3955.326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A. Xenotropic viruses: murine leukemia viruses associated with NIH Swiss, NZB, and other mouse strains. Science. 1973 Dec 14;182(4117):1151–1153. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4117.1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison R. M., Rabstein L. S., Bryan W. R. Mortality rate and spontaneous lesions found in 2,928 untreated BALB/cCr mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Apr;40(4):683–685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markham R. V., Jr, Sutherland J. C., Mardiney M. R., Jr The ubiquitous occurrence of immune complex localization in the renal glomeruli of normal mice. Lab Invest. 1973 Jul;29(1):111–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellors R. C., Aoki T., Huebner R. J. Further implication of murine leukemia-like virs in the disorders of NZB mice. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):1045–1062. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.1045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellors R. C. Autoimmune disease in NZB-Bl mice. II. Autoimmunity and malignant lymphoma. Blood. 1966 Apr;27(4):435–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellors R. C., Huang C. Y. Immunopathology of NZB/BL mice. V. Viruslike (filtrable) agent separable from lymphoma cells and identifiable by electron microscopy. J Exp Med. 1966 Dec 1;124(6):1031–1038. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.6.1031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowinski R. C., Old L. J., Boyse E. A., de Harven E., Geering G. Group-specific viral antigens in the milk and tissues of mice naturally infected with mammary tumor virus or Gross leukemia virus. Virology. 1968 Apr;34(4):617–629. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90083-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prosser P. R. Particles resembling murine leukaemia virus in New Zealand black mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1968 Mar;3(3):213–226. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P. J., Hicks J. D., Boston L. E., Abbott A. Failure to transfer haemolytic anaemia or glomerulonephritis with cell-free material from NZB mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Feb;6(2):227–239. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanford B. H., Kohn H. I., Daly J. J., Soo S. F. Long-term spontaneous tumor incidence in neonatally thymectomized mice. J Immunol. 1973 May;110(5):1437–1439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel B. V., Brown M., Morton J. I. Detection of antinuclear antibodies in NZB and other mouse strains. Immunology. 1972 Mar;22(3):457–463. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner N. L. Genetic control of spontaneous and induced antierythrocyte autoantibody production in mice. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1973 Apr;1(3):353–363. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(73)90052-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


