Abstract
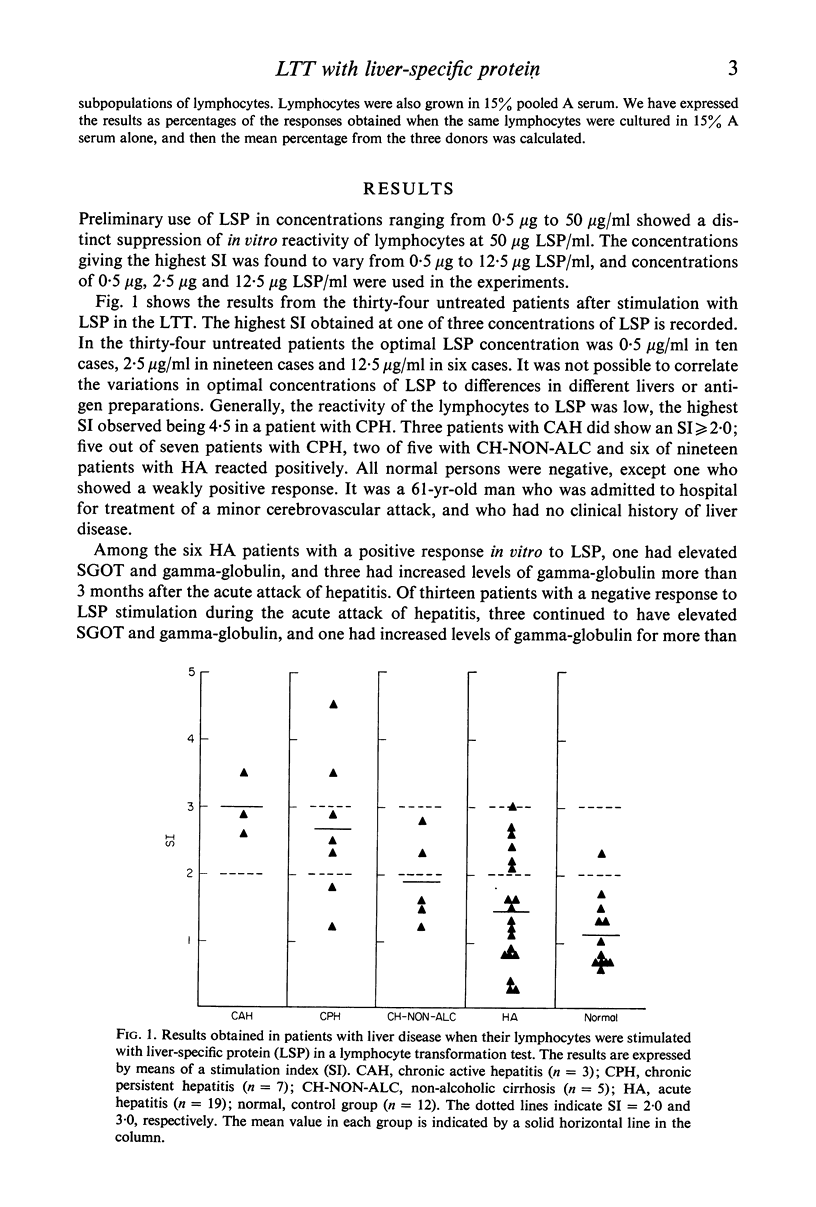
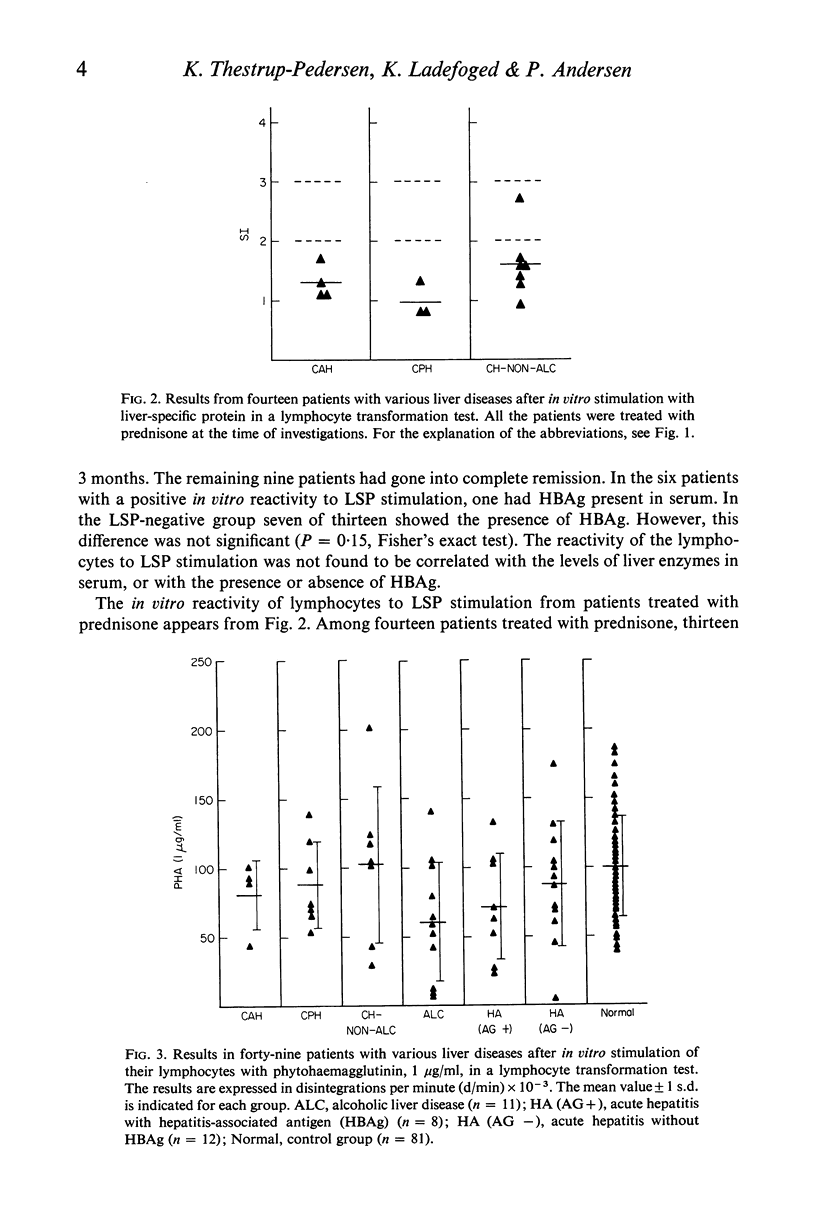
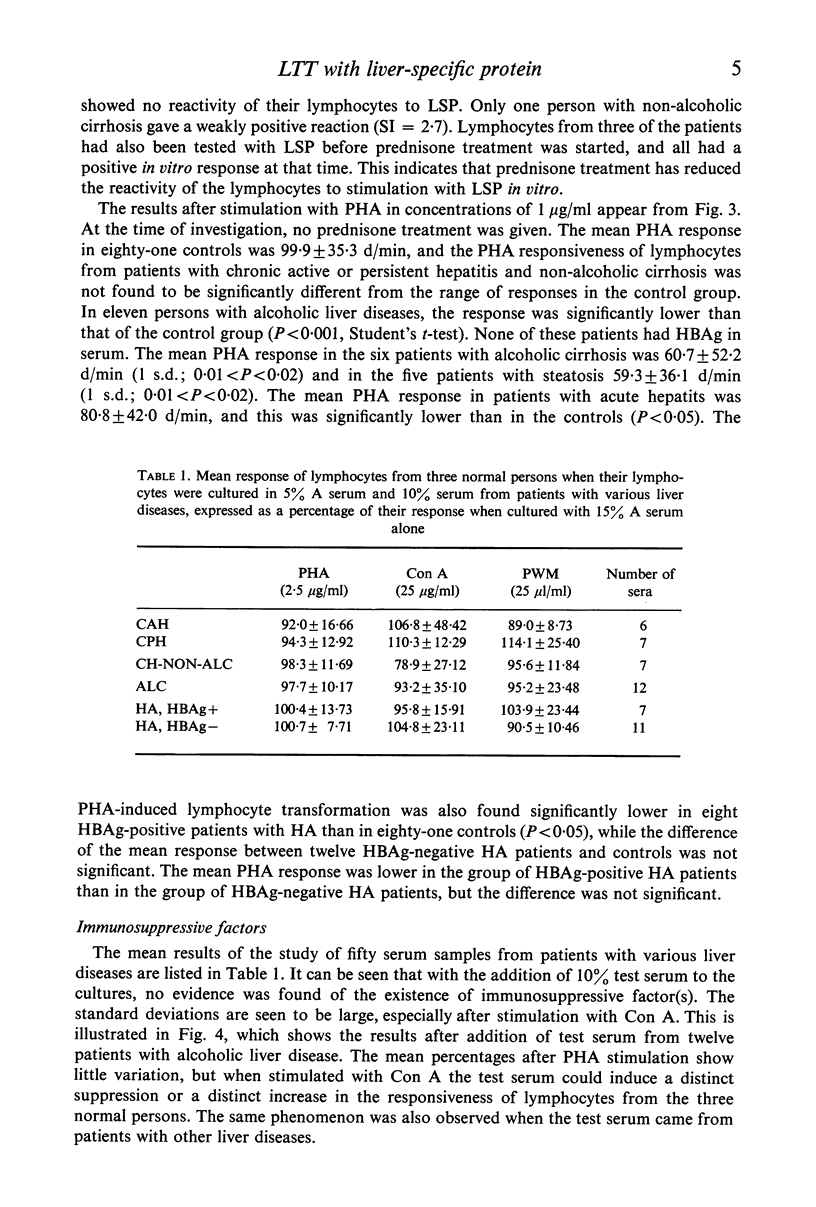
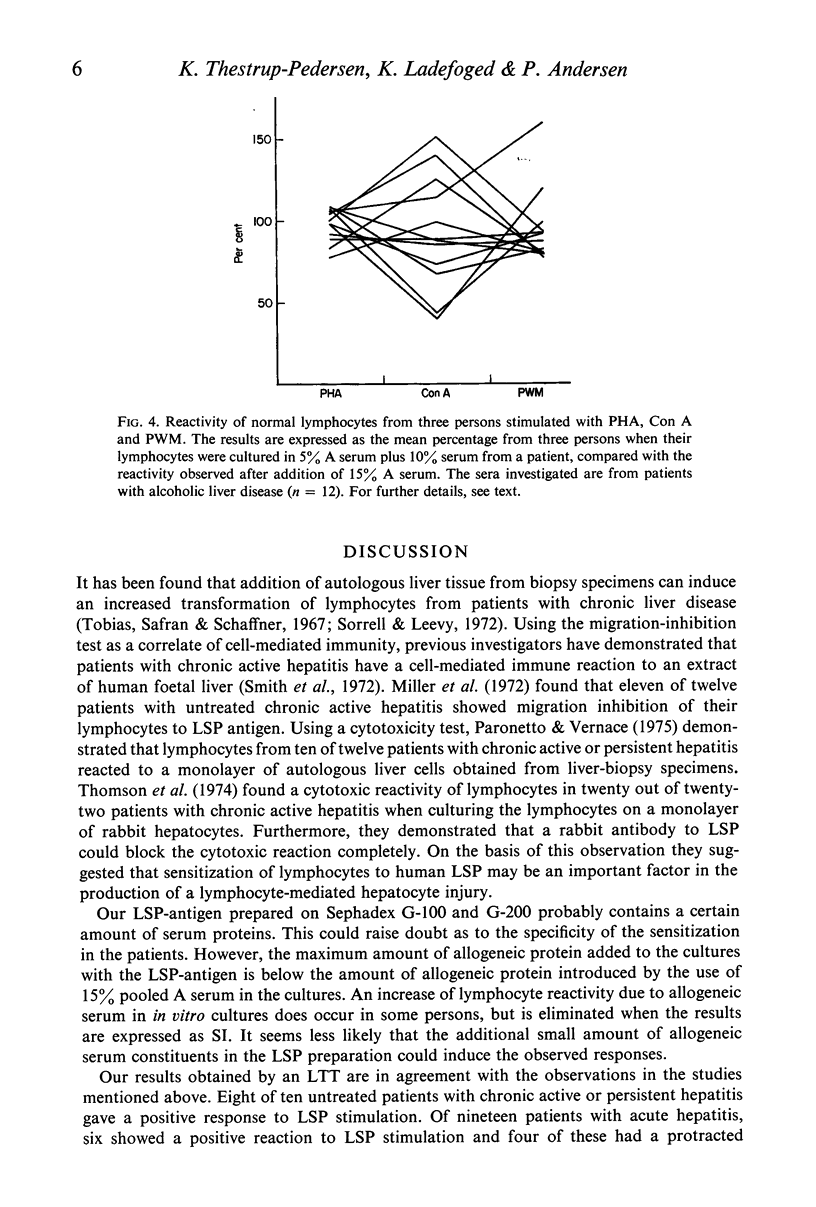
Lymphocytes from thirty-four untreated patients with various liver diseases were stimulated in a lymphocyte transformation test with liver-specific protein (LSP). Eight of ten patients with chronic active or persistent hepatitis, two of five patients with non-alcoholic cirrhosis and six of nineteen patients with acute hepatitis showed a positive in vitro reactivity to LSP. In a control group of twelve persons without evidence of liver disease, eleven gave a negative response to LSP stimulation, whereas one person showed a positive response. Among fourteen patients with chronic hepatitis or non-alcoholic cirrhosis treated with prednisone at the time of the investigation, only one showed reactivity to LSP stimulation. Three patients in this group had previously had a positive reaction before prednisone was given. There was no statistically significant correlation between the reactivity to LSP stimulation and the presence or absence of hepatitis-associated antigen (HBAg) in serum, or with the biochemical liver parameters. The response to in vitro stimulation with phytohaemagglutinin (PHA) was found to be significantly lower as compared with the control group in eleven patients with alcoholic liver disease and in the patients with acute hepatitis who had HBAg in serum. This decrease in reactivity could apparently not be ascribed to immuno-suppressive factors in the patients' sera.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agarwal S. S., Blumberg B. S., Gerstley B. J., London W. T., Millman I., Sutnick A. I., Loeb L. A. Lymphocyte transformation and hepatitis. I. Impairment of thymidine incorporation and DNA polymerase activity. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Sep;137(4):1498–1502. doi: 10.3181/00379727-137-35818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein I. M., Webster K. H., Williams R. C., Jr, Strickland R. G. Reduction in circulating T lymphocytes in alcoholic liver disease. Lancet. 1974 Aug 31;2(7879):488–490. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92015-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clot J., Mathieu O., Elharrar S., Robinet-Levy M., Lemaire J. M. Inhibitory effect of Australia-positive sera on in-vitro-stimulated T lymphocytes. Lancet. 1973 Sep 8;2(7828):576–577. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92407-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giustino V., Dudley F. J., Sherlock S. Thymus-dependent lymphocyte function in patients with hepatitis-associated antigen. Lancet. 1972 Oct 21;2(7782):850–853. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92212-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu C. C., Leevy C. M. Inhibition of PHA-stimulated lymphocyte transformation by plasma from patients with advanced alcoholic cirrhosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 May;8(5):749–760. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangi R. J., Dwyer J. M., Kantor F. S. The effect of plasma upon lymphocyte response in vitro. Demonstration of a humoral inhibitor in patients with sarcoidosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Dec;18(4):519–528. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., Smith M. G., Mitchell C. G., Reed W. D., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Cell-mediated immunity to a human liver-specific antigen in patients with active chronic hepatitis and primary biliary cirrhosis. Lancet. 1972 Aug 12;2(7772):296–297. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92904-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray-Lyon I. M., Stern R. B., Williams R. Controlled trial of prednisone and azathioprine in active chronic hepatitis. Lancet. 1973 Apr 7;1(7806):735–737. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92125-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newberry W. M., Shorey J. W., Sanford J. P., Combes B. Depression of lymphocyte reactivity to phytohemagglutinin by serum from patients with liver disease. Cell Immunol. 1973 Jan;6(1):87–97. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newble D. I., Holmes K. T., Wangel A. G., Forbes I. J. Immune reactions in acute viral hepatitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Apr;20(1):17–28. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paronetto F., Vernace S. Immunological studies in patients with chronic active hepatitis. Cytotoxic activity of lymphocytes to autochthonous liver cells grown in tissue culture. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Jan;19(1):99–104. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. G., Golding P. L., Eddleston A. L., Mitchell C. G., Kemp A., Williams R. Cell-mediated immune responses in chronic liver diseases. Br Med J. 1972 Feb 26;1(5799):527–530. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5799.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorrell M. F., Leevy C. M. Lymphocyte transformation and alcoholic liver injury. Gastroenterology. 1972 Dec;63(6):1020–1025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thestrup-Pedersen K. Temporary suppression of lymphocyte transformation after tuberculin skin testing. Immunology. 1974 Dec;27(6):965–971. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A. D., Cochrane M. A., McFarlane I. G., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Lymphocyte cytotoxicity to isolated hepatocytes in chronic active hepatitis. Nature. 1974 Dec 20;252(5485):721–722. doi: 10.1038/252721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobias H., Safran A. P., Schaffner F. Lymphocyte stimulation and chronic liver disease. Lancet. 1967 Jan 28;1(7483):193–195. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91830-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


