Abstract
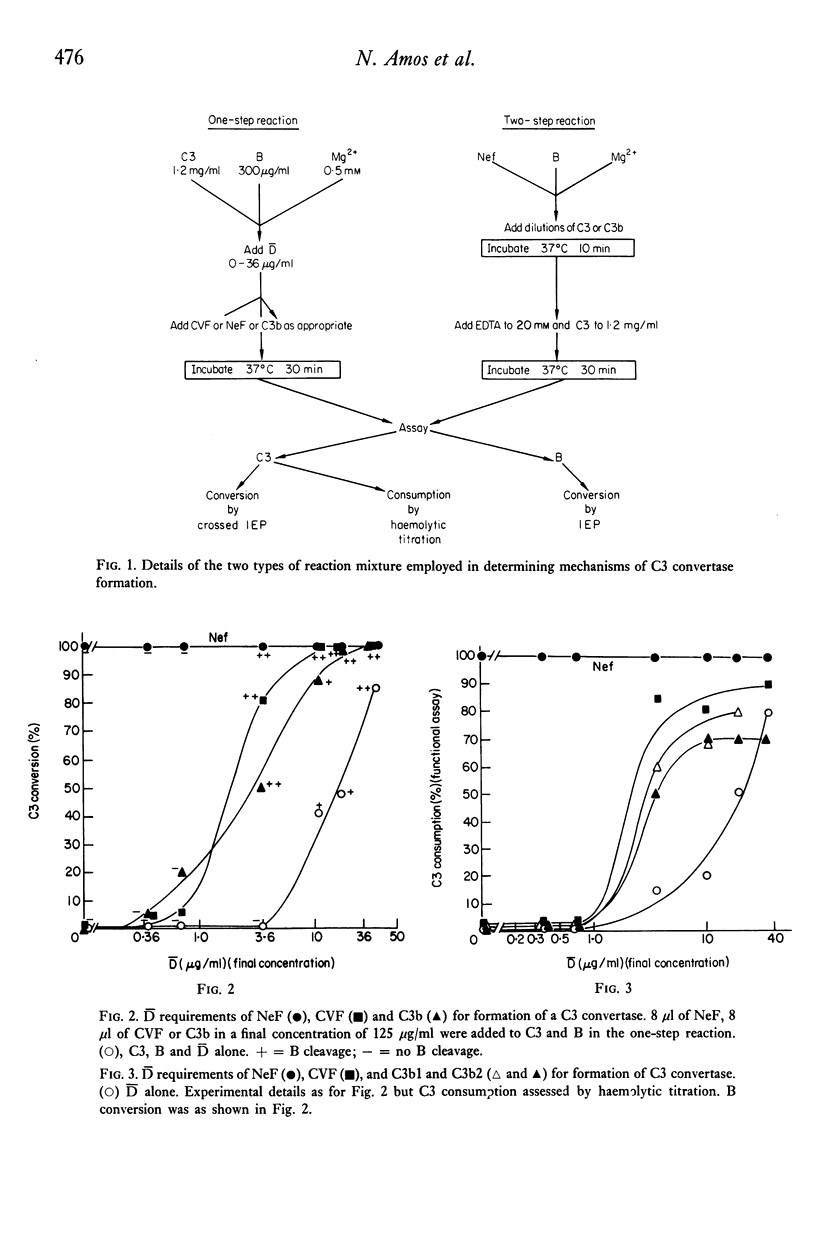
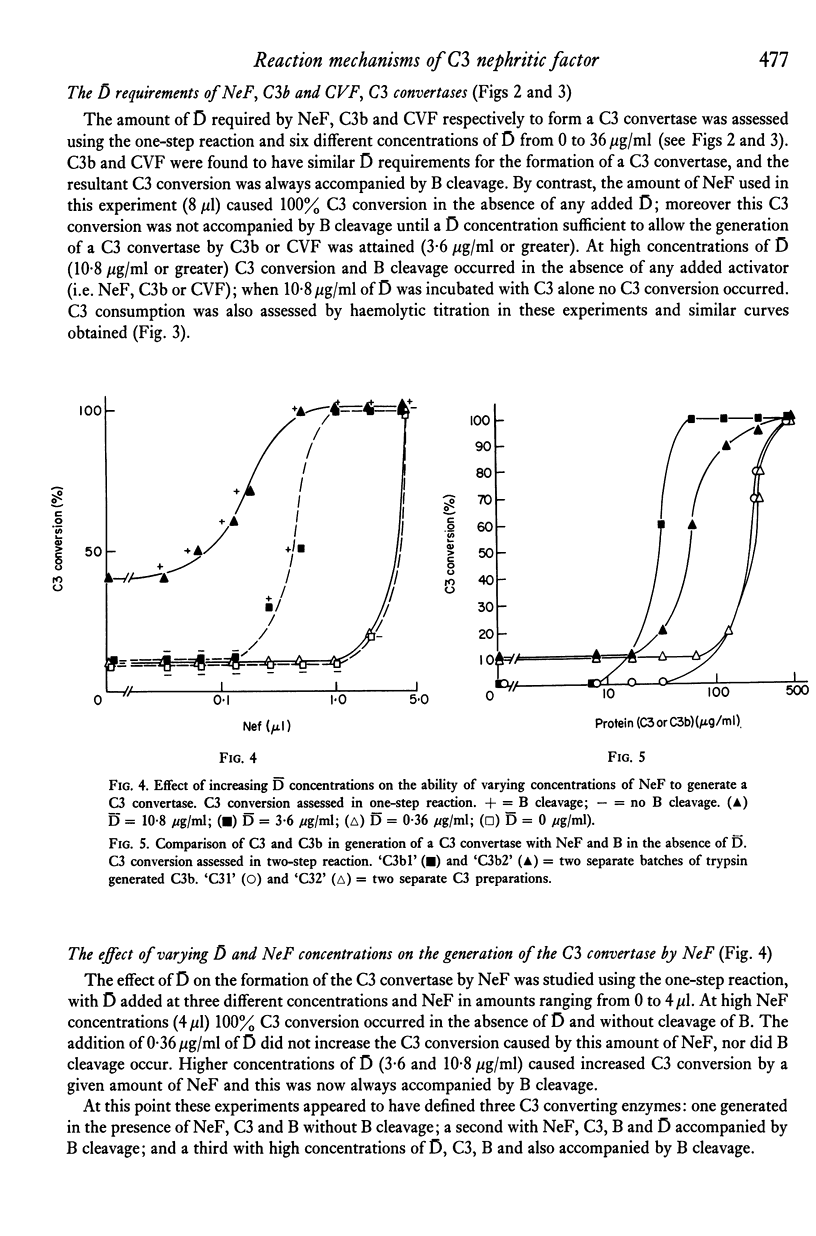
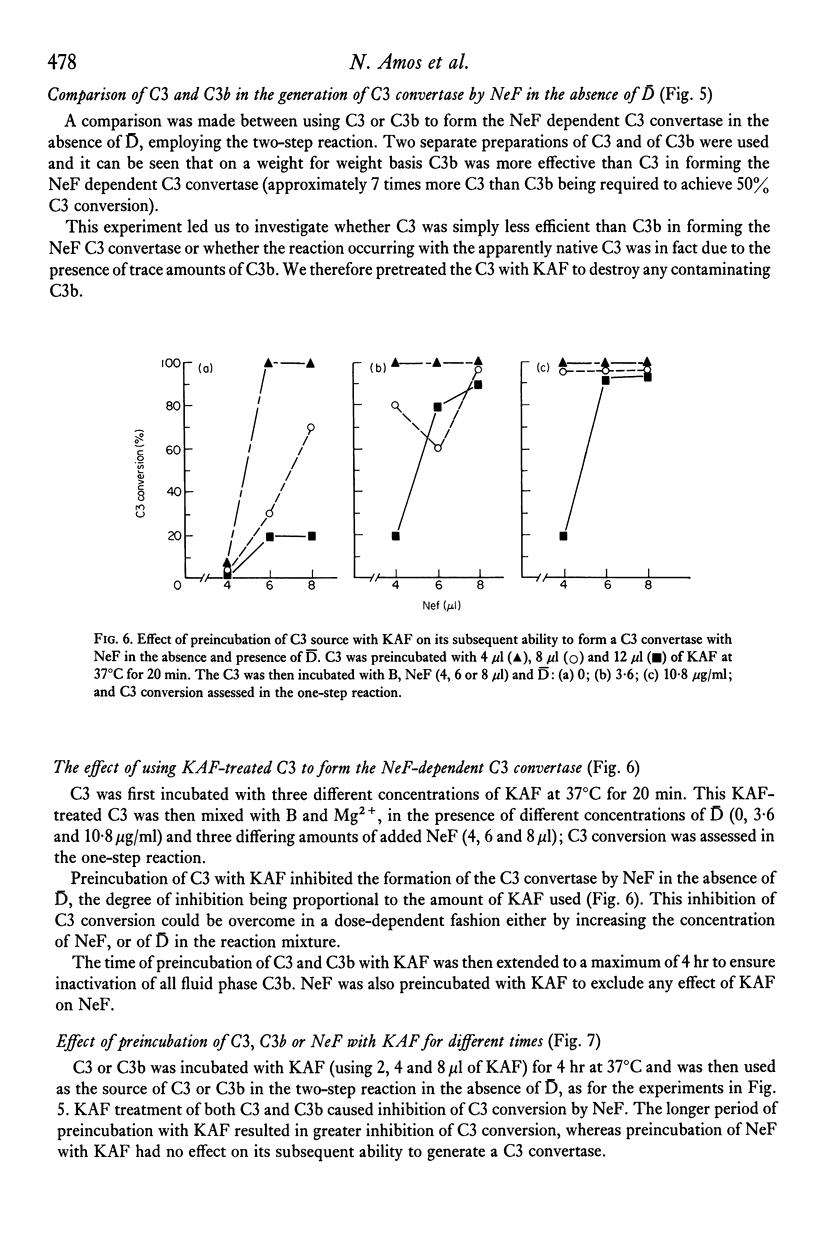
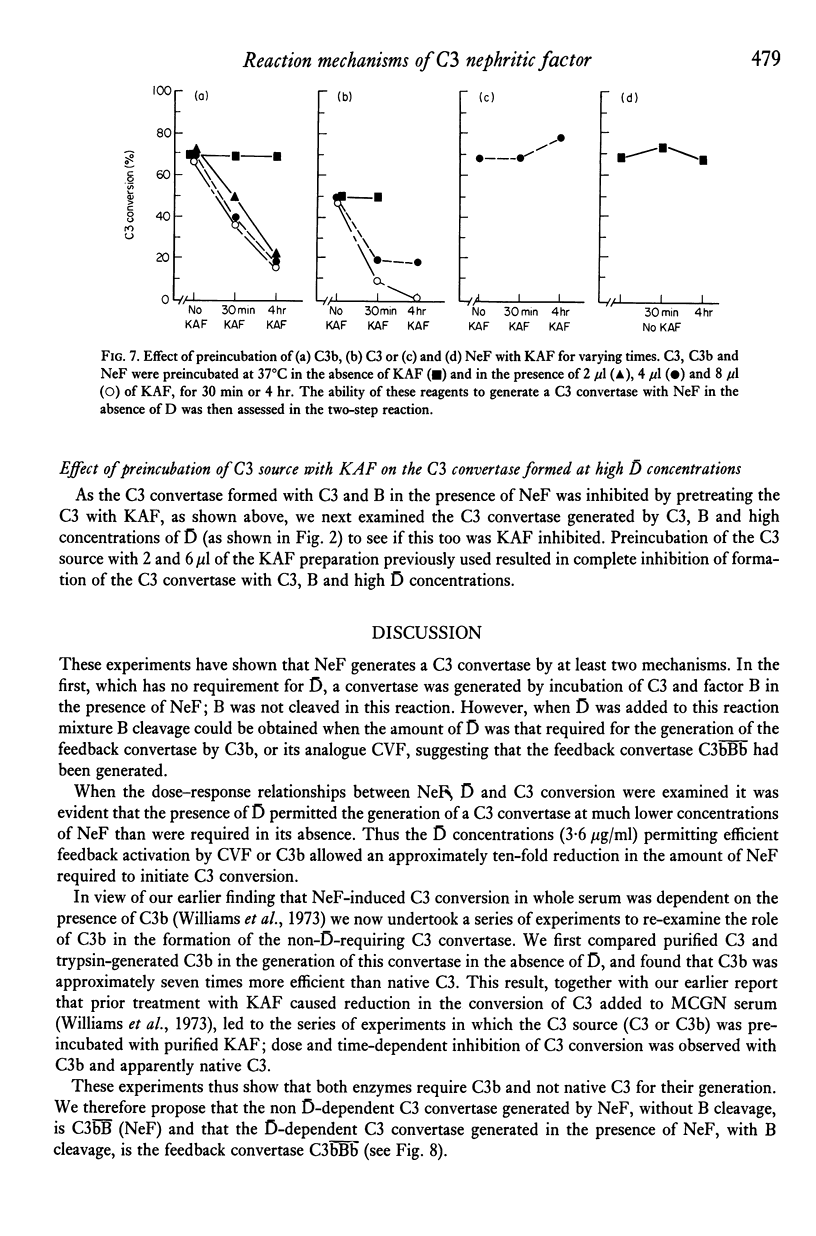
The mechanisms by which a C3 convertase is generated by C3 nephritic factor (NeF) were investigated using purified NeF, C3, C3b, factor B and factor D of the alternative pathway of complement activation. NeF could generate a C3 convertase with C3 and B in the absence of D, and without cleavage of B. At lower concentrations of NeF the addition of D was required to generate a C3 convertase, and B cleavage now occurred. The generation of both the D-independent and D-dependent C3 convertases with NeF was inhibited by preincubation of the C3 source with C3b inactivator (KAF); isolated C3b was more efficient than the C3 preparations used in generating the D-independent C3 convertase with NeF. These experiments indicate that C3b is required for the formation of both convertases, and that the reaction occurring with apparently native C3 is due to trace amounts of C3b. It is concluded that the C3 convertase generated by NeF in the absence of D is C3bB (NeF), and that generated in the presence of D is the feedback convertase C3bBb. The relevance of these experiments to reactions which may occur in vivo is discussed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballow M., Cochrane C. G. Two anticomplementary factors in cobra venom: hemolysis of guinea pig erythrocytes by one of them. J Immunol. 1969 Nov;103(5):944–952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlesworth J. A., Williams D. G., Sherington E., Lachmann P. J., Peters D. K. Metabolic studies of the third component of complement and the glycine-rich beta glycoprotein in patients with hypocomplementemia. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jun;53(6):1578–1587. doi: 10.1172/JCI107708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Götze O., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The C3-activator system: an alternate pathway of complement activation. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 2):90s–108s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURELL C. B. ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY CROSSED ELECTROPHORESIS. Anal Biochem. 1965 Feb;10:358–361. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J., Nicol P. Reaction mechanism of the alternative pathway of complement fixation. Lancet. 1973 Mar 3;1(7801):465–467. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91886-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters D. K., Martin A., Weinstein A., Cameron J. S., Barratt T. M., Ogg C. S., Lachmann P. J. Complement studies in membrano-proliferative glomerulonephritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Jul;11(3):311–320. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber R. D., Medicus R. G., Gïtze O., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Properdin- and nephritic factor-dependent C3 convertases: requirement of native C3 for enzyme formation and the function of bound C3b as properdin receptor. J Exp Med. 1975 Sep 1;142(3):760–772. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.3.760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitzer R. E., Vallota E. H., Forristal J., Sudora E., Stitzel A., Davis N. C., West C. D. Serum C'3 lytic system in patients with glomerulonephritis. Science. 1969 Apr 25;164(3878):436–437. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3878.436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitzel A. E., Spitzer R. E. The utilization of properdin in the alternate pathway of complement activation: isolation of properdin convertase. J Immunol. 1974 Jan;112(1):56–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallota E. H., Forristal J., Spitzer R. E., Davis N. C., West C. D. Characteristics of a non-complement-dependent C3-reactive complex formed form factors in nephritic and normal serum. J Exp Med. 1970 Jun 1;131(6):1306–1324. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.6.1306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallota E. H., Götze O., Spiegelberg H. L., Forristal J., West C. D., Müller-Eberhard H. J. A serum factor in chronic hypocomplementemic hephritis distinct from immunoglobulins and activating the alternate pathway of complement. J Exp Med. 1974 May 1;139(5):1249–1261. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.5.1249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. G., Lachmann P. J., Charlesworth J. A., Peters D. K. Role of C3b in the breakdown of C3 in hypocomplementaemic mesangiocapillary glomerulonephritis. Lancet. 1973 Mar 3;1(7801):447–449. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91877-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. G., Peters D. K., Fallows J., Petrie A., Kourilsky O., Morel-Maroger L., Cameron J. S. Studies of serum complement in the hypocomplementaemic nephritides. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Nov;18(3):391–405. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


