Abstract
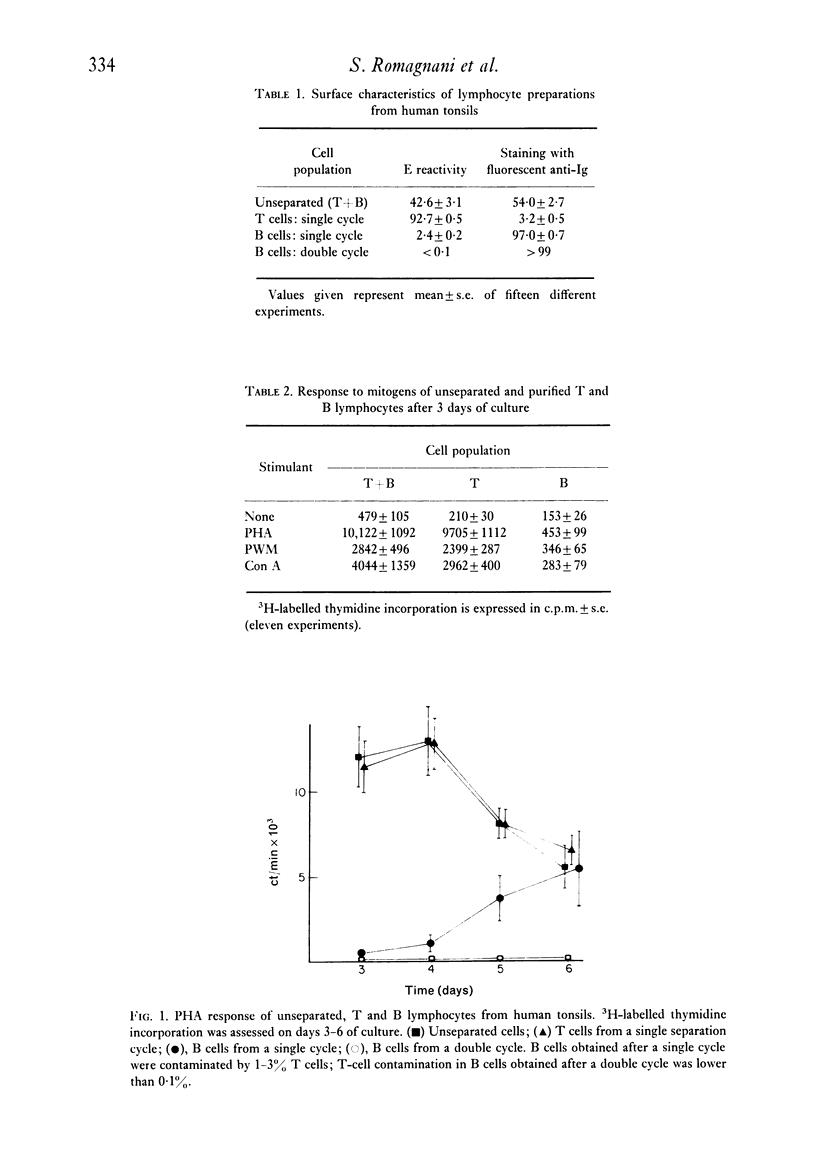
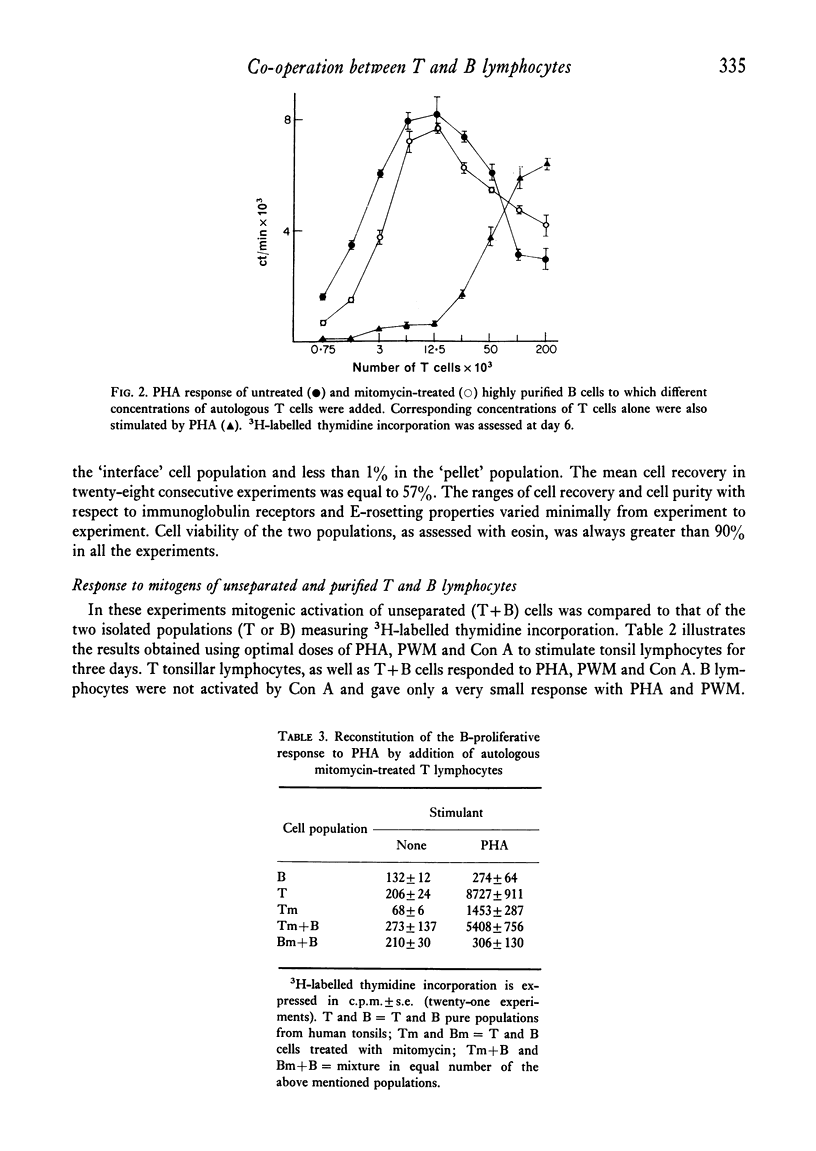
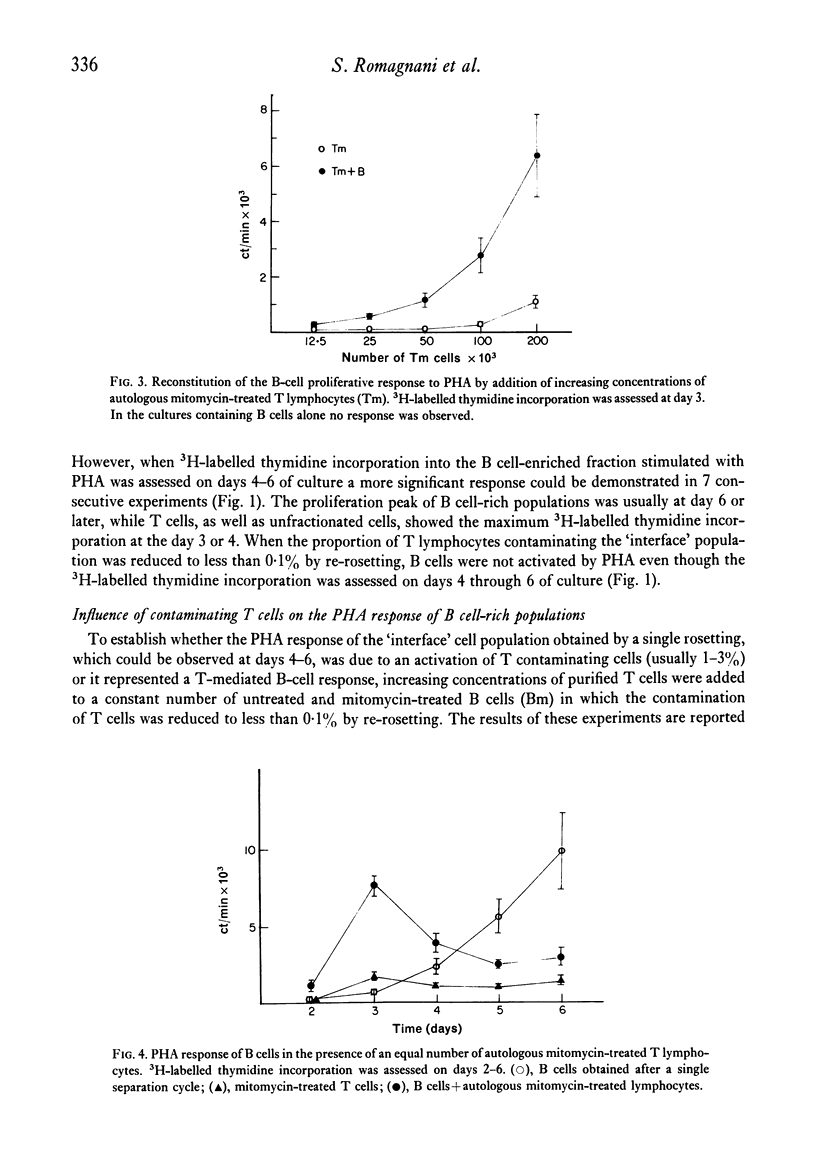
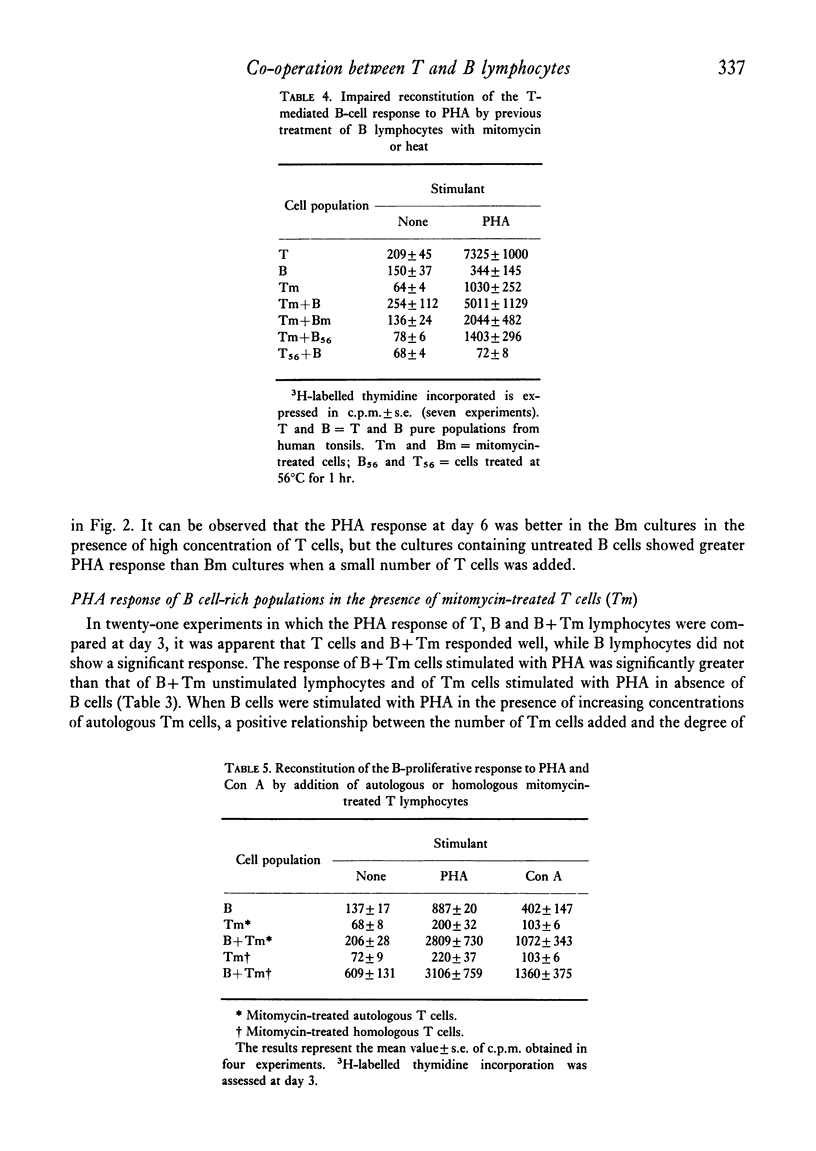
Purified B lymphocytes obtained from human tonsil cell populations by removing E rosette-forming cells by density sedimentation did not proliferate at three days in response to PHA and Con A, but showed a significant 3H-labelled thymidine incorporation when the PHA response was assessed at day 6 of culture. The 6th-day responses, which was completely abolished by the reduction of T-cell contamination to less than 0-1% by re-rosetting and a second separation, was due in part to a direct activation by PHA of contaminating T cells and in part to a T cell-mediated B-cell response. When purified B cells were stimulated for 3 days by PHA in the presence of an equal number of autologous or homologous mitomycin-treated T lymphocytes a highly significant uptake of 3H-labelled thymidine was demonstrated. The majority of blast cells obtained at day 4 in these cultures were unable to form E rosettes and showed surface immunoglobulin by immunofluorescence stain. This response was markedly decreased by previous treatment of B cells with mitomycin C and it was abolished when B cells were killed by heating at 56degrees C for 1 hr. Purified B lymphocytes from human tonsils did not respond in vitro when cultured for 6 days in the presence of soluble antigens (PPD and Candida). However, a highly significant response to the same antigens could be demonstrated when B cells were cultured in the presence of autologous mitomycin-treated T cells. These models of T-B co-operation could provide an interesting tool for studying the differentiation and antibody production in vitro of human B lymphocytes.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brochier J., Samarut C., Gueho J. P., Revillard J. P. T-dependence of human B lymphocyte proliferative response to mitogens. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1976;51(1):101–116. doi: 10.1159/000231582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chess L., MacDermott R. P., Schlossman S. F. Immunologic functions of isolated human lymphocyte subpopulations. I. Quantitative isolation of human T and B cells and response to mitogens. J Immunol. 1974 Oct;113(4):1113–1121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chess L., MacDermott R. P., Schlossman S. F. Immunologic functions of isolated human lymphocyte subpopulations. II. Antigen triggering of T and B cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1974 Oct;113(4):1122–1127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delespesse G., Duchateau J., Gausset P., Govaerts A. In vitro response of subpopulations of human tonsil lymphocytes. I. Cellular collaboration in the proliferative response to PHA and Con A. J Immunol. 1976 Feb;116(2):437–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Rutishauser U., Millette C. F. Cell fractionation and arrangement on fibers, beads, and surfaces. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2153–2157. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galili U., Schlesinger M. The formation of stable E rosettes after neuraminidase treatment of either human peripheral blood lymphocytes or of sheep red blood cells. J Immunol. 1974 May;112(5):1628–1634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geha R. S., Merler E. Response of human thymus-derived (T) and non-thymus-derived (B) lymphocytes to mitogenic stimulation in vitro. Eur J Immunol. 1974 Mar;4(3):193–199. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830040308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M. F., Brown G. Purification of human T and B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1974 Jan;112(1):420–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M. F., Janossy G., Doenhoff M. Activation of human T and B lymphocytes by polyclonal mitogens. Nature. 1974 Apr 19;248(5450):698–701. doi: 10.1038/248698a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips B., Roitt I. M. Evidence for transformation of human B lymphocytes by PHA. Nat New Biol. 1973 Feb 21;241(112):254–256. doi: 10.1038/newbio241254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romagnani S., Amadori A., Biti G., Bellesi G., Ricci M. In vitro lymphocyte response to the phytomitogens in untreated and treated patients with Hodgkin's disease. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1976;51(3):378–389. doi: 10.1159/000231611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romagnani S., Biliotti G., Ricci M. Depression of grass pollen-induced lymphocyte transformation by serum from hyposensitized patients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Jan;19(1):83–91. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlossman S. F., Hudson L. Specific purification of lymphocyte populations on a digestible immunoabsorbent. J Immunol. 1973 Jan;110(1):313–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigzell H., Sundqvist K. G., Yoshida T. O. Separation of cells according to surface antigens by the use of antibody-coated columns. Fractionation of cells carrying immunoglobulins and blood group antigen. Scand J Immunol. 1972;1(1):75–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1972.tb03737.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


