Abstract
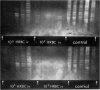
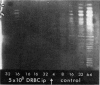
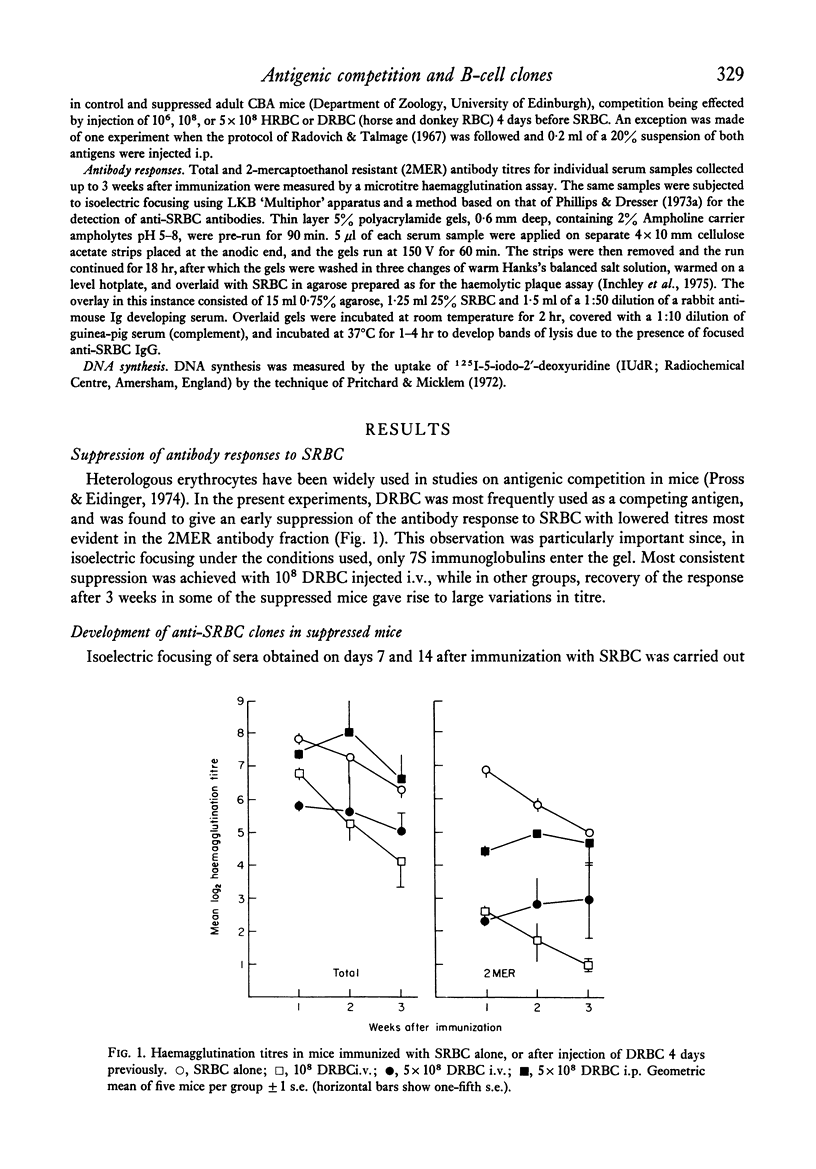
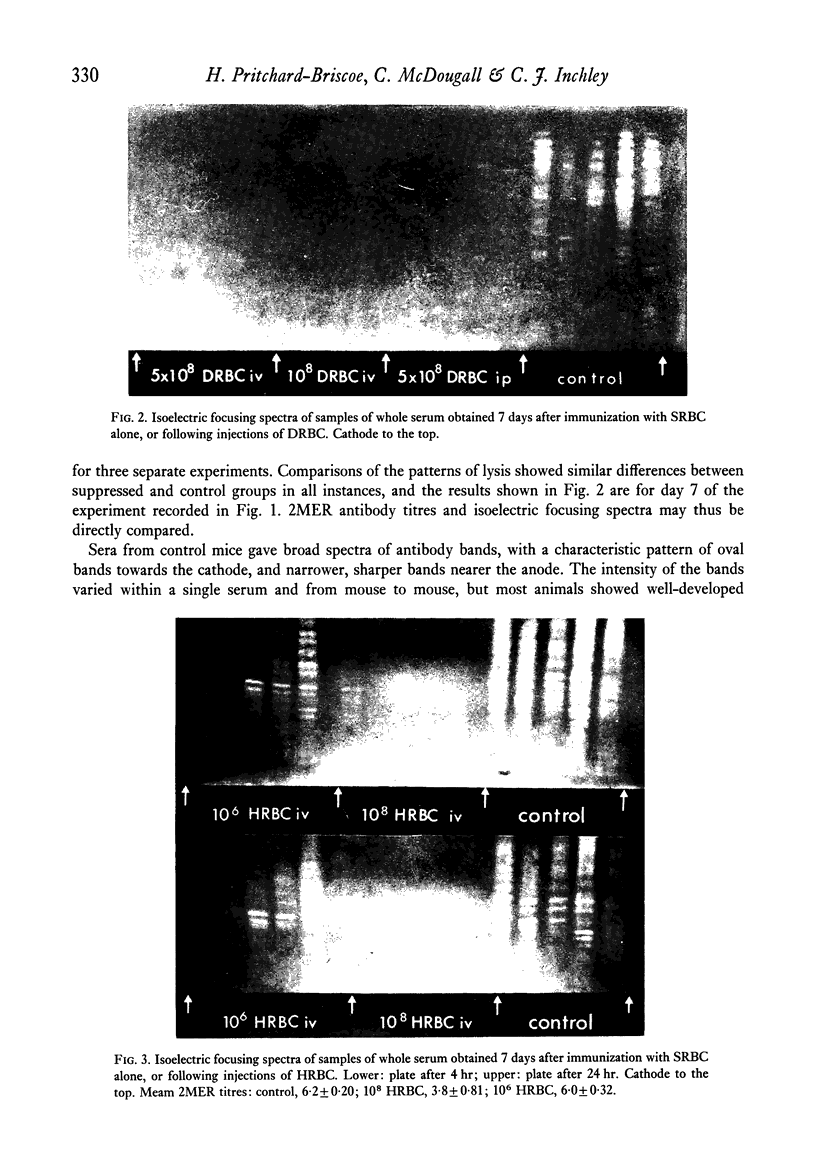
Isoelectric focusing in polyacrylamide gels was used to investigate the anti-sheep red blood cell antibody responses of mice subjected to antigenic competition. A reduction in the number and intensity of antibody bands was found, even in situations where the suppression of IgG antibody titres was minimal, while with large reductions in titre, antibody bands were rarely seen. It thus appeared that the output of individual B-cell clones was severely depressed during competition. It was concluded that inhibition of clonal expansion is an important feature of competition, and that this may reflect a normal regulatory activity which acts to limit cellular proliferation during immune responses. This conclusion was supported by observations on the level of DNA synthesis, following immunization with sheep red cells, in the spleens of normal and suppressed mice.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bash J. A., Waksman B. H. The suppressive effect of immunization on the proliferative responses of rat T cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 2):782–787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black S. J. Antigen-induced changes in lymphocyte circulatory patterns. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Mar;5(3):170–175. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black S. J., Inchley C. J. Characteristics of immunological memory in mice. I. Separate early generation of cells mediating IgM and IgG memory to sheep erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1974 Aug 1;140(2):333–348. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.2.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies A. J., Carter R. L., Leuchars E., Wallis V., Koller P. C. The morphology of immune reactions in normal, thymectomized and reconstituted mice. I. The response to sheep erythrocytes. Immunology. 1969 Jan;16(1):57–69. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eidinger D., Pross H. F., Kerbel R. S., Baines M. G., Ackerman A., Khan S. A. Further studies of competition of antigens. I. Variation in immunosuppression induced by alterations of dosage, route of injection, nature of antigen, and immunological status of host. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Jun;17(6):803–812. doi: 10.1139/m71-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann M., Schrader J. W. Mechanism of antigenic competition. II. Induction by specific T cell products. Cell Immunol. 1974 Nov;14(2):255–269. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(74)90210-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon R. K., Gery I., Waksman B. H. Suppressive effects of in vivo immunization on PHA responses in vitro. J Immunol. 1974 Jan;112(1):215–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon R. K., Kondo K. Antigenic competition between heterologous erythrocytes. I. Thymic dependency. J Immunol. 1971 Jun;106(6):1524–1531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inchley C. J., Black S. J., Mackay E. A. Characteristics of immunological memory in mice. II. Resistance of nonrecirculating memory cells to antigen-mediated suppression of the secondary antibody response. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Feb;5(2):100–104. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janossy G., Greaves M. Functional analysis of murine and human B lymphocyte subsets. Transplant Rev. 1975;24:177–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1975.tb00169.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. T., Merrifield N., Zarchy T., Brody N. I., Siskind G. W. Studies on antigenic competition. 3. Effect on antigenic competition on antibody affinity. Immunology. 1974 May;26(5):943–955. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menkes J. S., Hencin R. S., Gershon R. K. The infectiousness of antigenic competition: conferrability of nonreactivity upon allogeneic T-cells. J Immunol. 1972 Nov;109(5):1052–1057. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J. M., Dresser D. W. Antibody isoelectric spectra visualized by antigen-coated erythrocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Nov;3(11):738–740. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J. M., Dresser D. W. Isoelectric spectra of different classes of anti-erythrocyte antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Aug;3(8):524–527. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830030816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J. M., Dresser D. W. The clonal origin of cells contributing to successive phases of a cyclical immune response. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Oct;5(10):684–689. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830051007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard H., Micklem H. S. Immune responses in congenitally thymus-less mice. I. Absence of response to oxazolone. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Jan;10(1):151–161. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pross H. F., Eidinger D. Antigenic competition: a review of nonspecific antigen-induced suppression. Adv Immunol. 1974;18:133–168. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60309-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radovich J., Talmage D. W. Antigenic competition: cellular or humoral. Science. 1967 Oct 27;158(3800):512–514. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3800.512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrader J. W., Feldmann M. The mechanism of antigenic competition. I. The macrophage as a site of a reversible block of T-B lymphocyte collaboration. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Nov;3(11):711–717. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. W., Roberts W. K., Talmage D. W. Regulation of the immune response: production of a soluble suppressor by immune spleen cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1975 May;114(5):1616–1622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]