Abstract
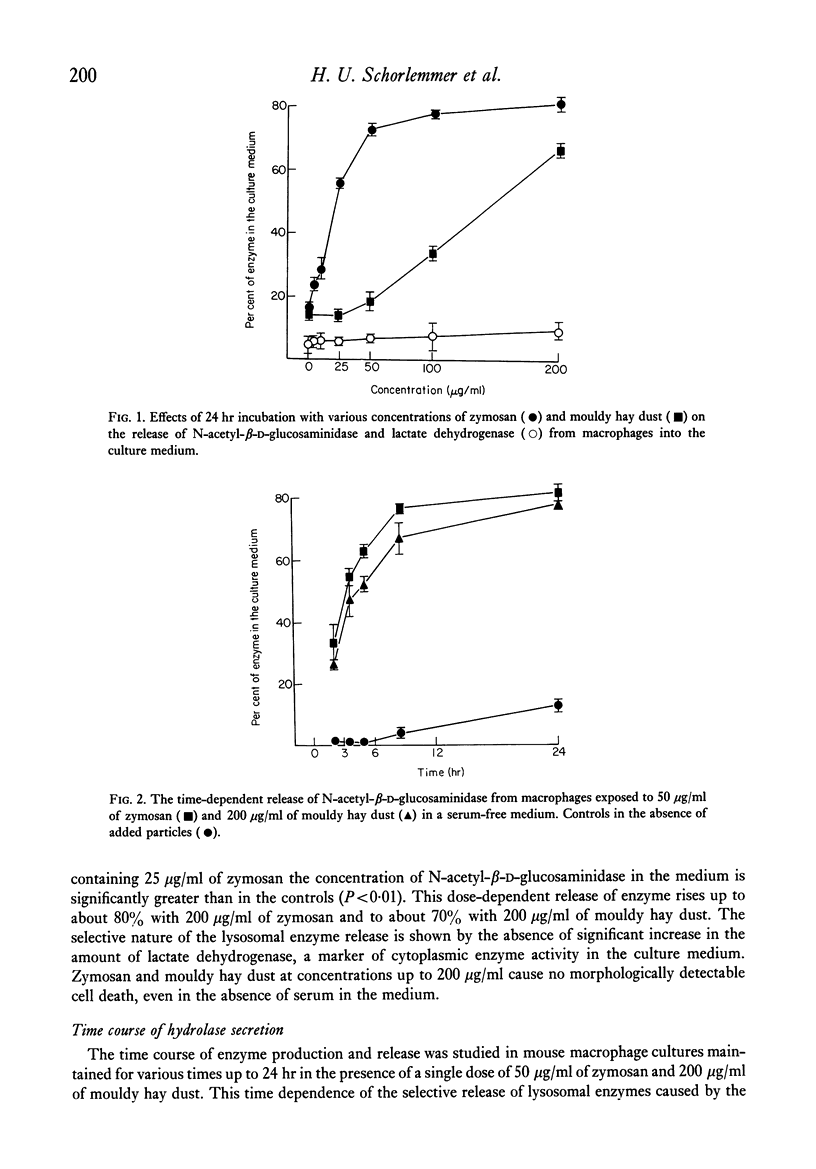
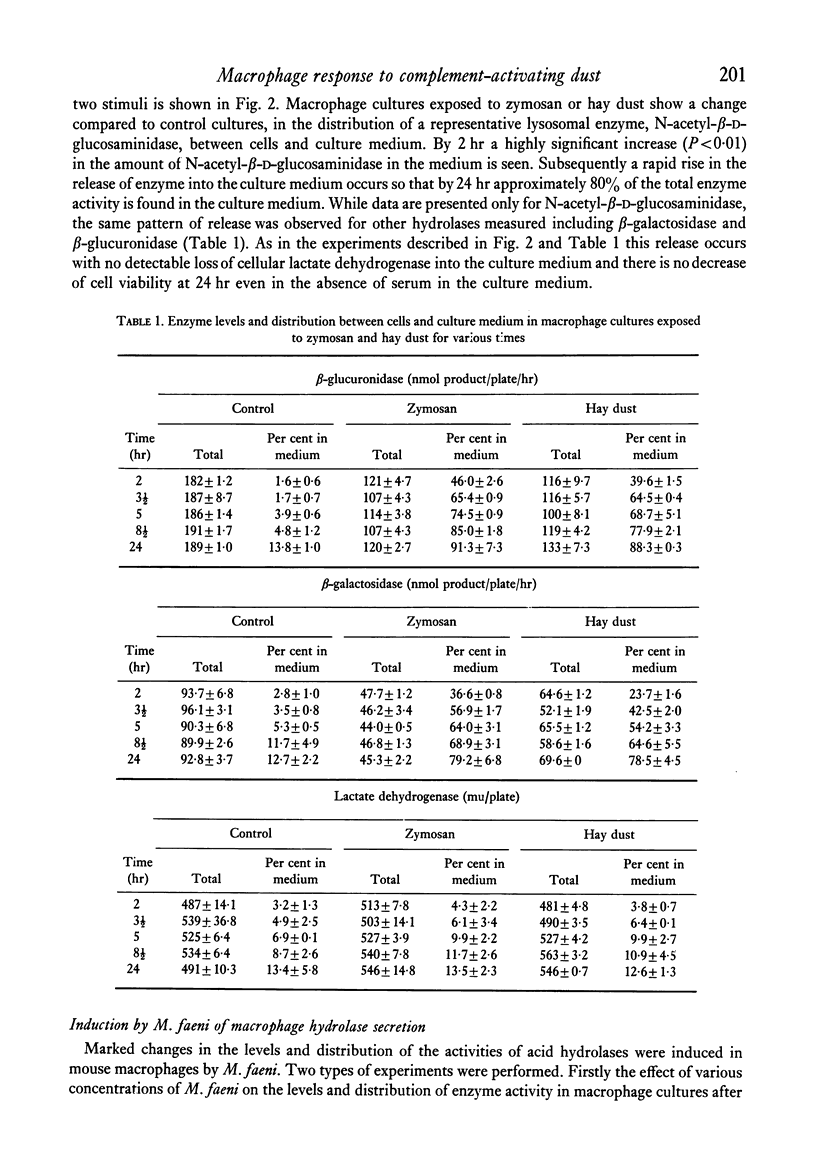
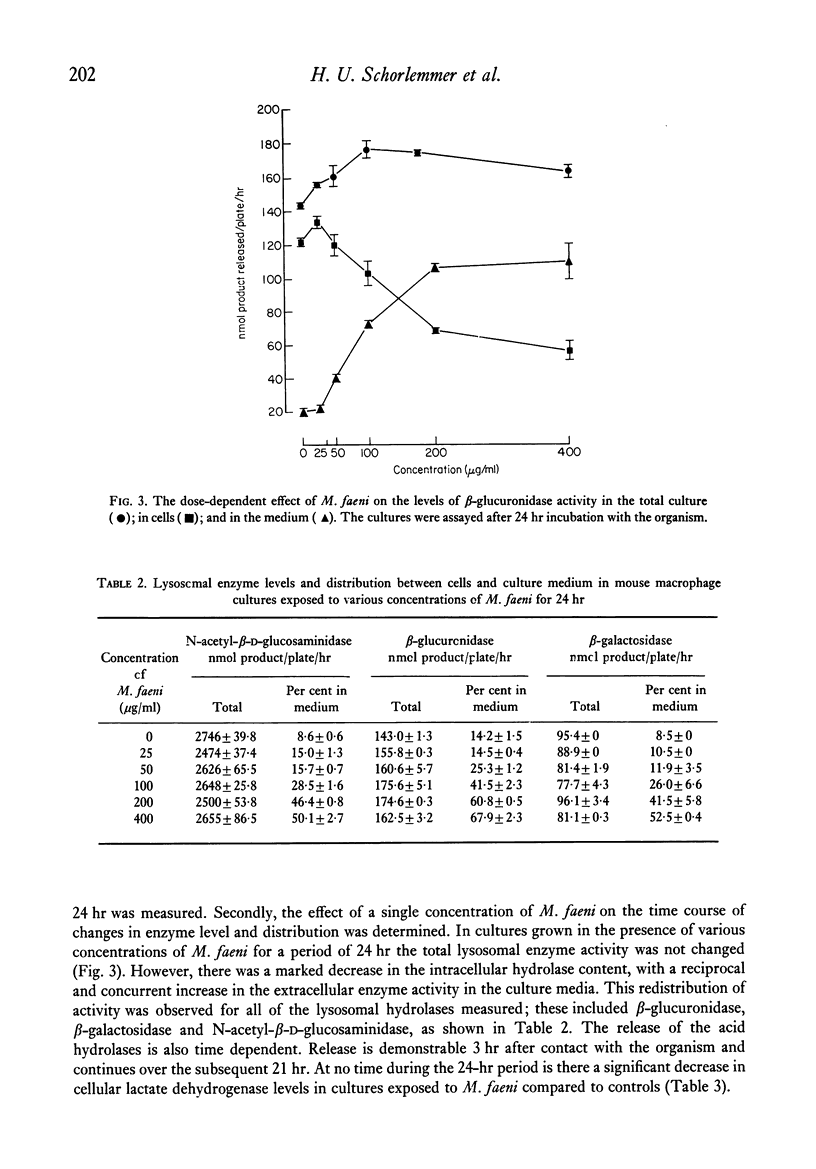
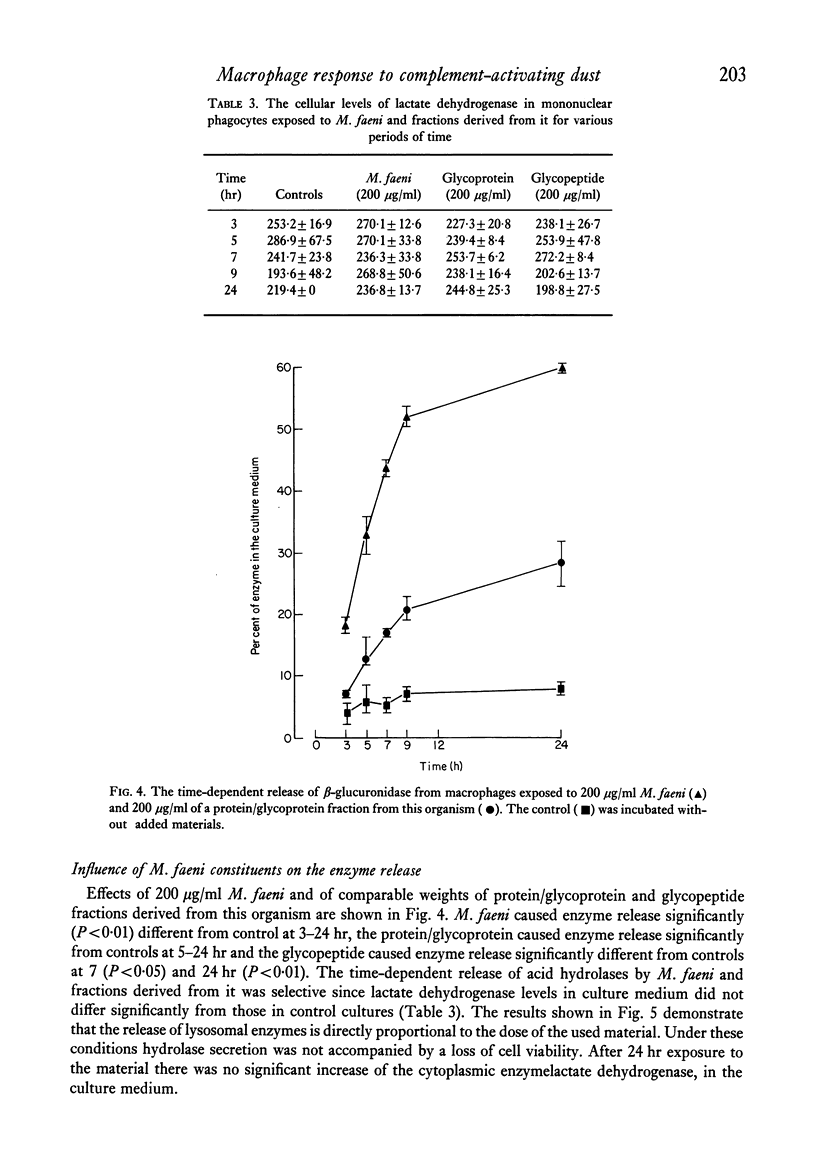
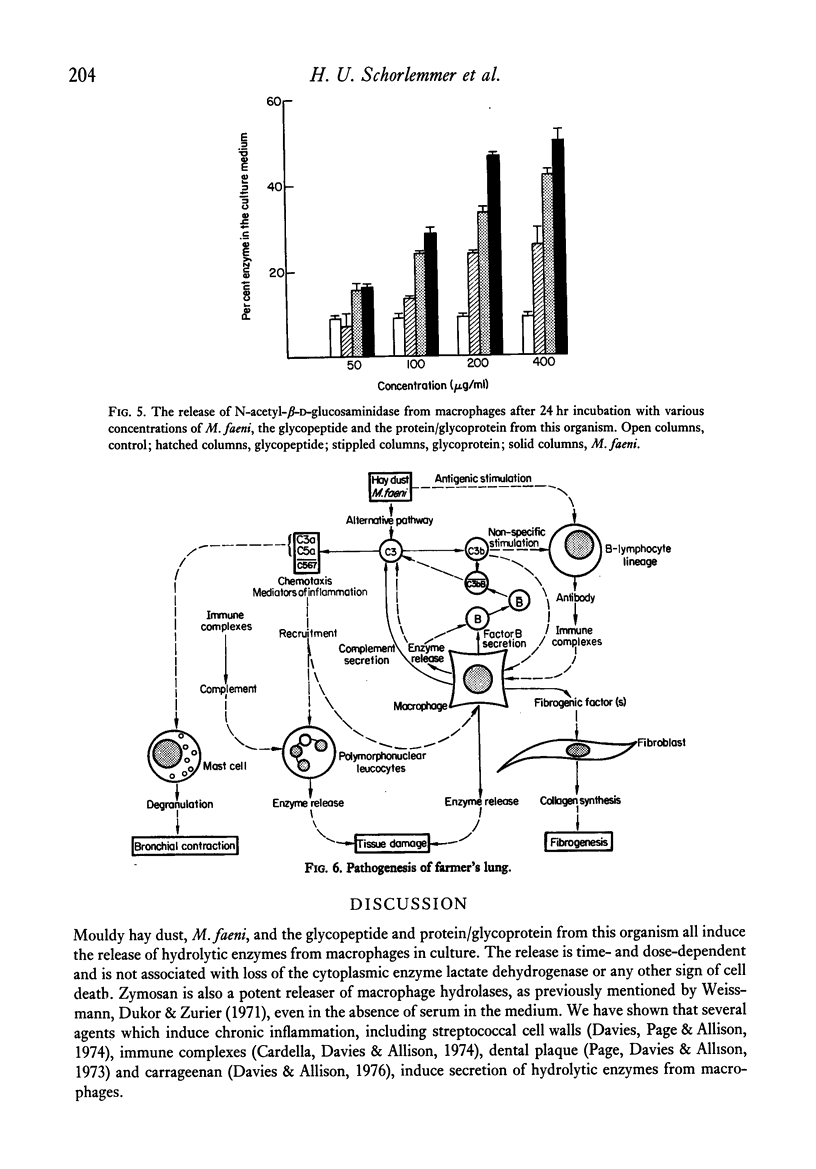
Mouse peritoneal macrophages in culture exposed to mouldy hay dust, Micropolyspora faeni or glycopeptide or protein/glycoprotein fractions from this organism show marked biochemical changes. For comparison the interaction of cultured macrophages with zymosan has been investigated. All these agents induce the release of hydrolytic enzymes from macrophages, even in the absence of serum in the medium. The release is time- and dose-dependent and is not associated with loss of the cytoplasmic enzyme lactate dehydrogenase or any other sign of cell death. The parallelism between the capacity of these agents to activate the complement system via the alternative pathway and to induce inflammatory responses in vivo and selective lysosomal enzyme secretion from cultures of macrophages is discussed. The in vitro phenomena seen with mouldy hay dust, M. faeni, the protein/glycoprotein and the glycopeptide derived from it, may be relevant to understanding the role of mononuclear phagocytes in the disease farmer's lung and other inflammatory reactions.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bentley C., Bitter-Suermann D., Hadding U., Brade V. In vitro synthesis of factor B of the alternative pathway of complement activation by mouse peritoneal macrophages. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Jun;6(6):393–398. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitter-Suermann D., Hadding U., Schorlemmer H. U., Limbert M., Dierich M., Dukor P. Activation by some T-independent antigens and B cell mitogens of the alternative pathway of the complement system. J Immunol. 1975 Aug;115(2):425–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokisch V. A., Müller-Eberhard H. J., Cochrane C. G. Isolation of a fragment (C3a) of the third component of human complement containing anaphylatoxin and chemotactic activity and description of an anaphylatoxin inactivator of human serum. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):1109–1130. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONCHIE J., FINDLAY J., LEVVY G. A. Mammalian glycosidases; distribution in the body. Biochem J. 1959 Feb;71(2):318–325. doi: 10.1042/bj0710318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardella C. J., Davies P., Allison A. C. Immune complexes induce selective release of lysosomal hydrolases from macrophages. Nature. 1974 Jan 4;247(5435):46–48. doi: 10.1038/247046a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P., Page R. C., Allison A. C. Changes in cellular enzyme levels and extracellular release of lysosomal acid hydrolases in macrophages exposed to group A streptococcal cell wall substance. J Exp Med. 1974 May 1;139(5):1262–1282. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.5.1262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dukor P., Hartmann K. U. Hypothesis. Bound C3 as the second signal for B-cell activation. Cell Immunol. 1973 Jun;7(3):349–356. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90199-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. H. A quantitative study on the activation of the alternative pathway of complement by mouldy hay dust and thermophilic actinomycetes. Clin Allergy. 1976 Jan;6(1):19–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1976.tb01408.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gery I., Waksman B. H. Potentiation of the T-lymphocyte response to mitogens. II. The cellular source of potentiating mediator(s). J Exp Med. 1972 Jul 1;136(1):143–155. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. M., Weissmann G. Generation of C5-derived lysosomal enzyme-releasing activity (C5a) by lysates of leukocyte lysosomes. J Immunol. 1974 Nov;113(5):1583–1588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The demonstration in human serum of "conglutinogen-activating factor" and its effect on the third component of complement. J Immunol. 1968 Apr;100(4):691–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahav M., Ne'eman N., Adler E., Ginsburg I. Effect of leukocyte hydrolases on bacteria. I. Degradation of 14C-labeled Streptococcus and Staphylococcus by leukocyte lysates in vitro. J Infect Dis. 1974 May;129(5):528–537. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.5.528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai A Fat R. F., van Furth R. In vitro synthesis of some complement components (C1q, C3 and C4) by lymphoid tissues and circulating leucocytes in man. Immunology. 1975 Feb;28(2):359–368. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson A., Brade V., Schorlemmer H. U., Burger R., Bitter-Suermann D., Hadding U. Interaction of C3b, B, and D in the alternative pathway of complement activation. J Immunol. 1975 Oct;115(4):1108–1113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page R. C., Davies P., Allison A. C. Effects of dental plaque on the production and release of lysosomal hydrolases by macrophages in culture. Arch Oral Biol. 1973 Dec;18(12):1481–1495. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(73)90124-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schorlemmer H. U., Allison A. C. Effects of activated complement components on enzyme secretion by macrophages. Immunology. 1976 Nov;31(5):781–788. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schorlemmer H. U., Davies P., Allison A. C. Ability of activated complement components to induce lysosomal enzyme release from macrophages. Nature. 1976 May 6;261(5555):48–49. doi: 10.1038/261048a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyderman R., Shin H., Dannenberg A. M., Jr Macrophage proteinase and inflammation: the production of chemotactic activity from the fifth complement by macrophage proteinase. J Immunol. 1972 Oct;109(4):896–898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura N., Nelson R. A., Jr Three naturally-occurring inhibitors of components of complement in guinea pig and rabbit serum. J Immunol. 1967 Sep;99(3):582–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WENZEL F., EMANUEL D. A., LAWTON B. R., MAGNIN G. E. ISOLATION OF THE CAUSATIVE AGENT OF FARMER'S LUNG. Ann Allergy. 1964 Oct;22:533–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Cochrane C. G., Muller-Eberhard H. J. Further studies on the chemotactic factor of complement and its formation in vivo. Immunology. 1966 Aug;11(2):141–153. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann G., Dukor P., Zurier R. B. Effect of cyclic AMP on release of lysosomal enzymes from phagocytes. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 2;231(22):131–135. doi: 10.1038/newbio231131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie B., Pauli B., Gygax M. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: experimental production in guinea pigs with antigens of Micropolyspora faeni. Pathol Microbiol (Basel) 1973;39(6):393–411. doi: 10.1159/000162686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


