Abstract
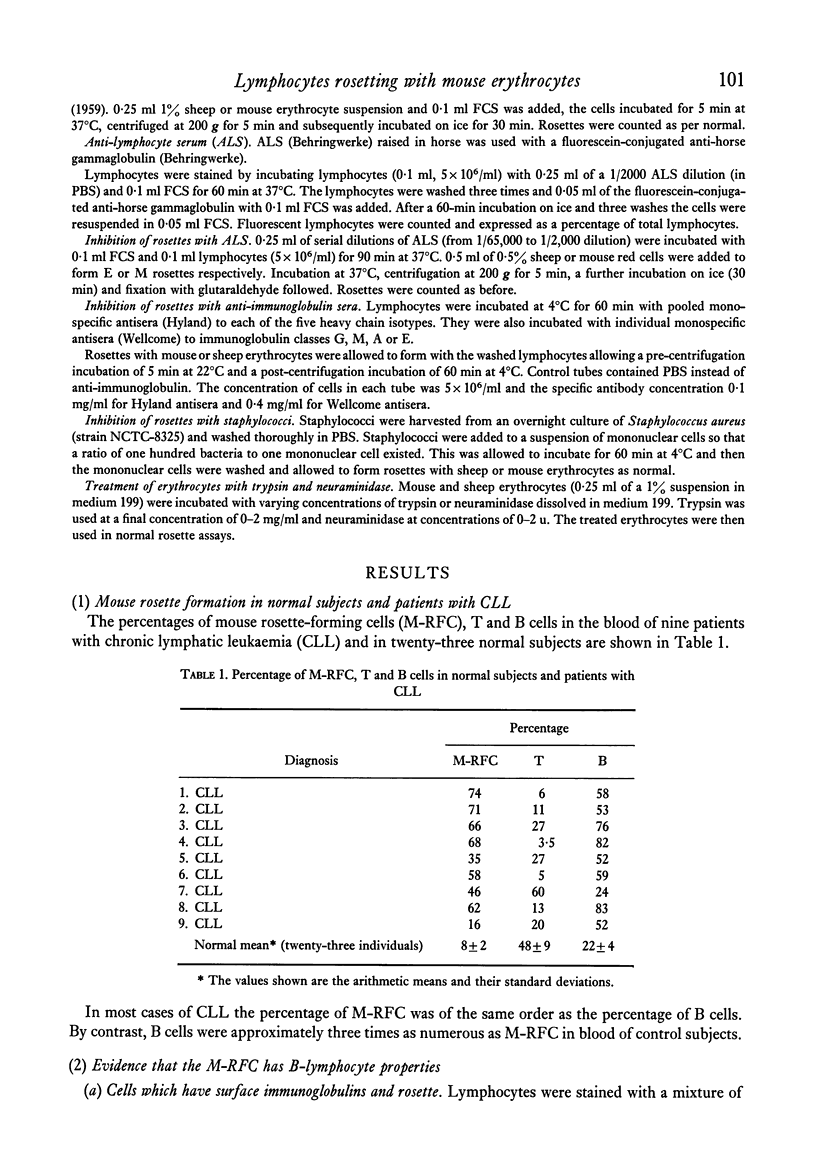
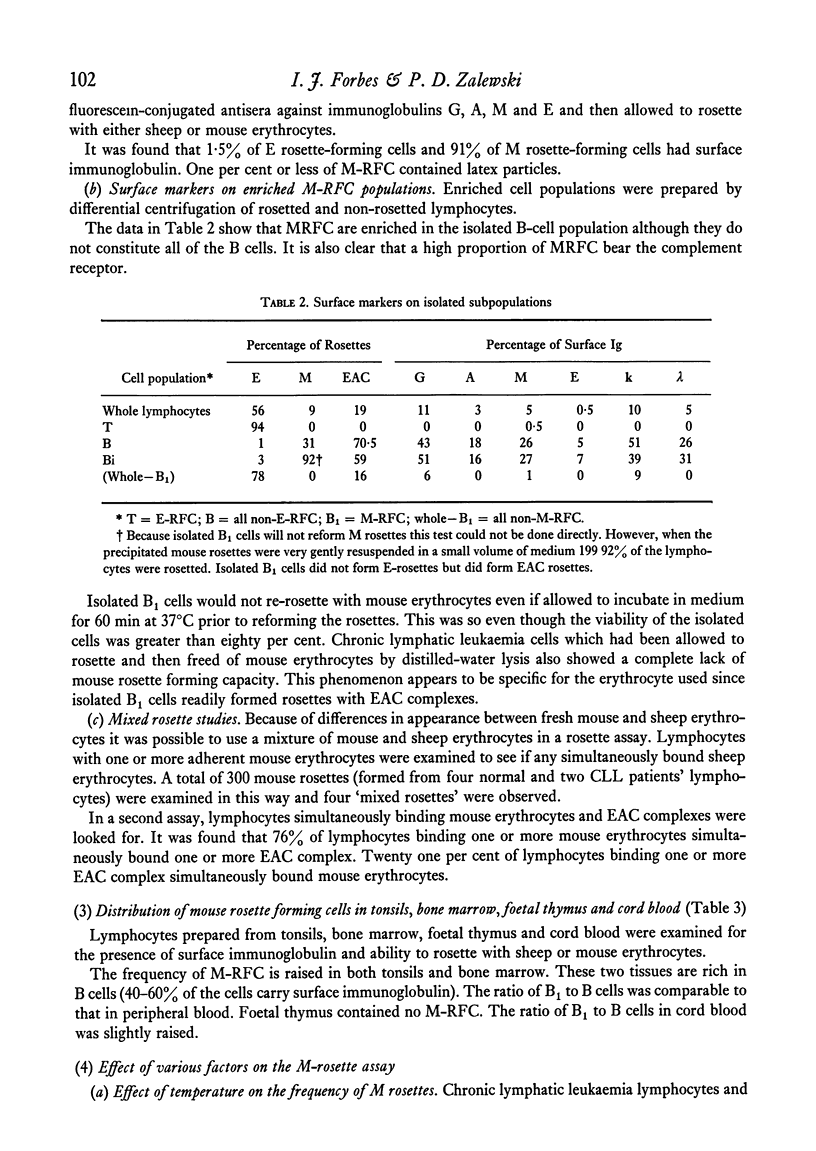
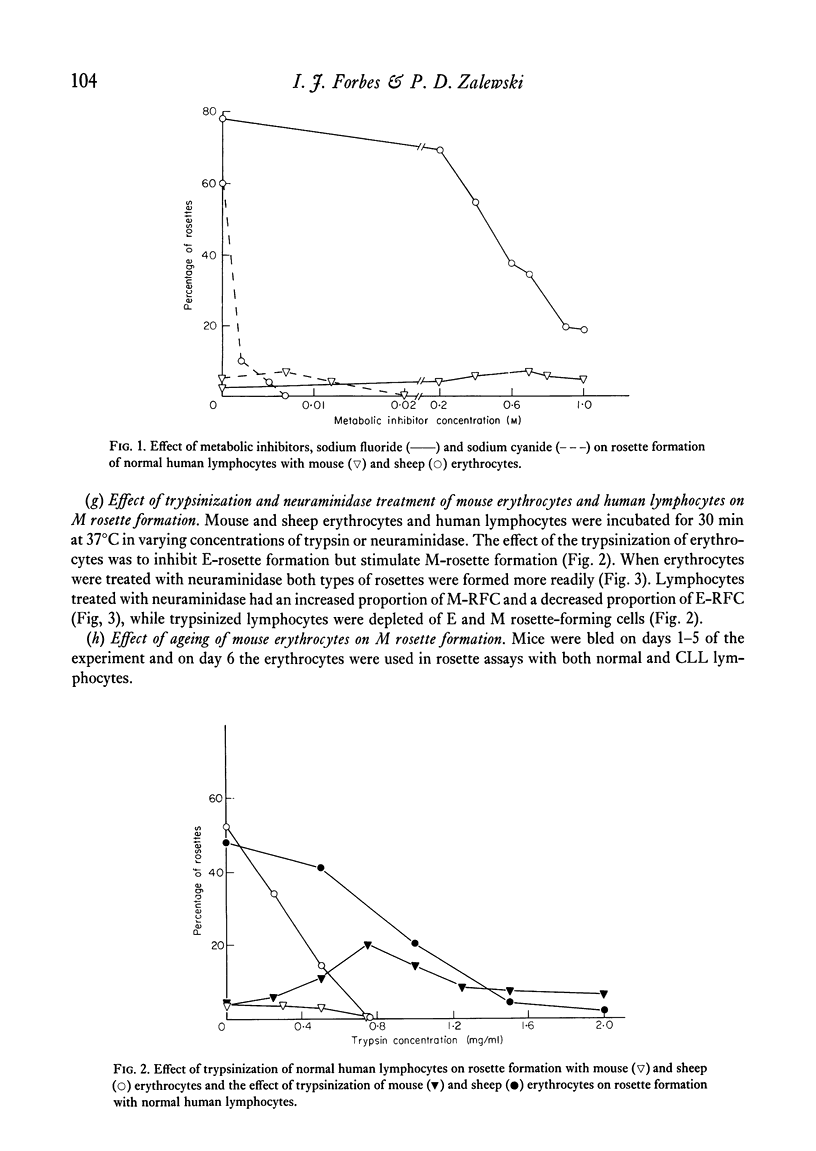
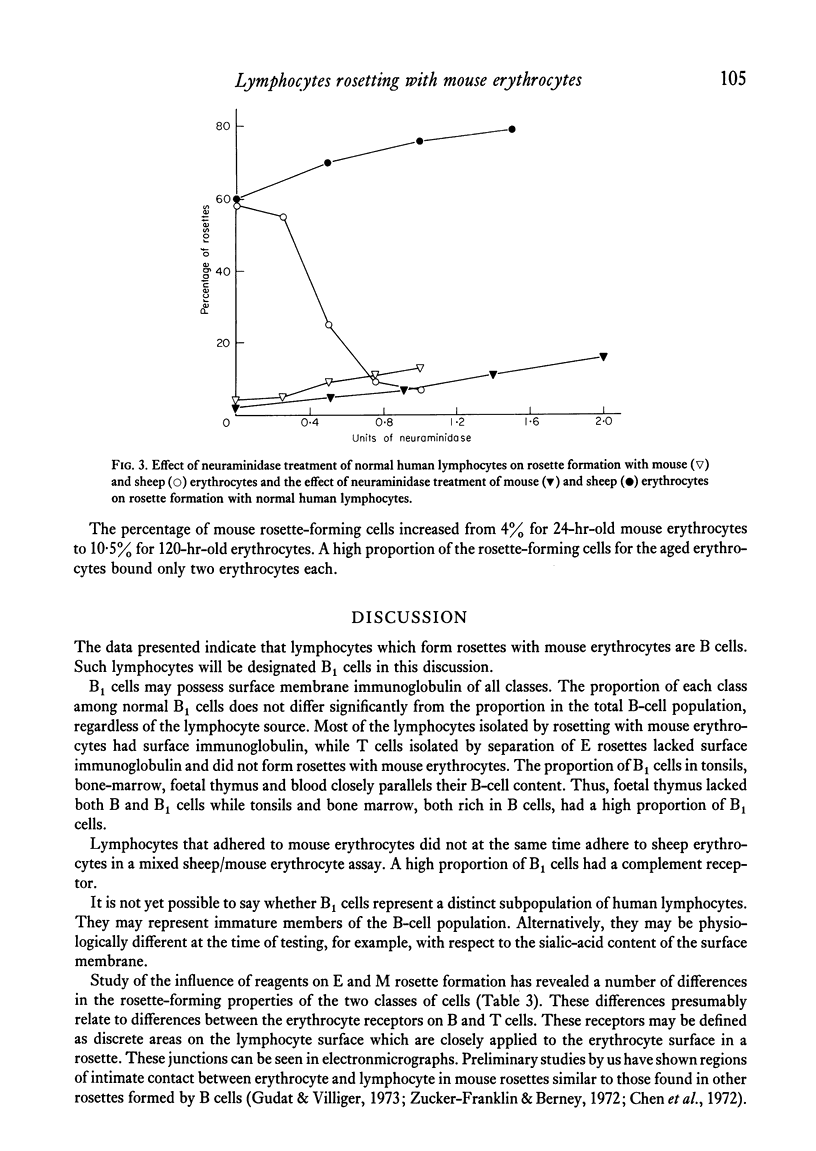
A proportion of human peripheral blood lymphocytes form rosettes with mouse erythrocytes (M-RFC). It is confirmed that the proportion of such rosette-forming cells is high in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL). Analysis of normal lymphocyte populations revealed that M-RFC belong to the B-lymphocyte subclass exclusively. Analysis of their surface markers showed: (a) complement receptors in 50% as compared to 71% of the total B-cell population; (b) a distribution of surface immunoglobulins G, A, M and E typical of the lymphocyte sources; (c) lack of sheep erythrocyte receptor. No differences in the ratio of M-RFC to total B cells was found between lymphocyte population from tonsils, bone marrow and peripheral blood although a significantly higher ratio was seen in cord blood and in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Investigation of the properties of mouse erythrocyte rosette formation revealed the following: (a) incubation of lymphocyte mouse erythrocyte mixtures at 37degreesC before centrifugation inhibited rosette formation when CLL lymphocytes were used; (b) treatment of mouse erythrocytes with neuraminidase or trypsin increased their adhesiveness to lymphocytes; (c) treatment of lymphocytes with neuraminidase promoted M-rosette formation but trypsin treatment had an inhibitory effect; (d) cyanide and fluoride at concentrations which strongly inhibited E-rosette formation had no inhibitory effect on M rosettes; (e) M-rosette formation was inhibited by anti-immunoglobulin serum but not by anti-lymphocyte serum; and (f) M-rosette formation was also inhibited by the presence of staphylococci. E-rosette formation was unaffected. The nature of the bond in mouse rosettes is discussed in the light of these findings. The evidence indicates that the lymphocyte receptor may be a part of an immunoglobulin molecule.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bach J. F., Muller J. Y., Dardenne M. In vivo specific antigen recognition by rosette forming cells. Nature. 1970 Sep 19;227(5264):1251–1252. doi: 10.1038/2271251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catovsky D., Papamichail M., Okos A., Miliani E., Holborow E. J. Formation of mouse red cell rosettes by "hairy" cells. Biomedicine. 1975 Apr 10;23(3):81–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. T., Eden A., Nussenzweig V., Weiss L. Electron microscopic study of the lymphocytes capable of binding antigen-antibody-complement complexes. Cell Immunol. 1972 Jul;4(3):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90031-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudat F. G., Villiger W. A scanning and transmission electron microscope study of antigen-binding sites on rosette-forming cells. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):483–493. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Seal U. S., Finstad J., Williams R. C., Jr Phylogenetic insight into evolution of mammalian Fc fragment of gamma G globulin using staphylococcal protein A. J Immunol. 1970 Jan;104(1):140–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leuchars E., Wallis V. J., Davies A. J. Mode of action for anti-lymphocyte serum. Nature. 1968 Sep 28;219(5161):1325–1328. doi: 10.1038/2191325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClelland D. A., Bridges J. M. The total N-acetyl neuraminic acid content of human normal and lymphatic leukaemic lymphocytes. Br J Cancer. 1973 Feb;27(2):114–119. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1973.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stathopoulos G., Elliott E. V. Formation of mouse or sheep red-blood-cell rosettes by lymphocytes from normal and leukaemic individuals. Lancet. 1974 Apr 6;1(7858):600–601. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92655-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker-Franklin D., Berney S. Electron microscope study of surface immunoglobulin-bearing human tonsil cells. J Exp Med. 1972 Mar 1;135(3):533–548. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.3.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


