Abstract
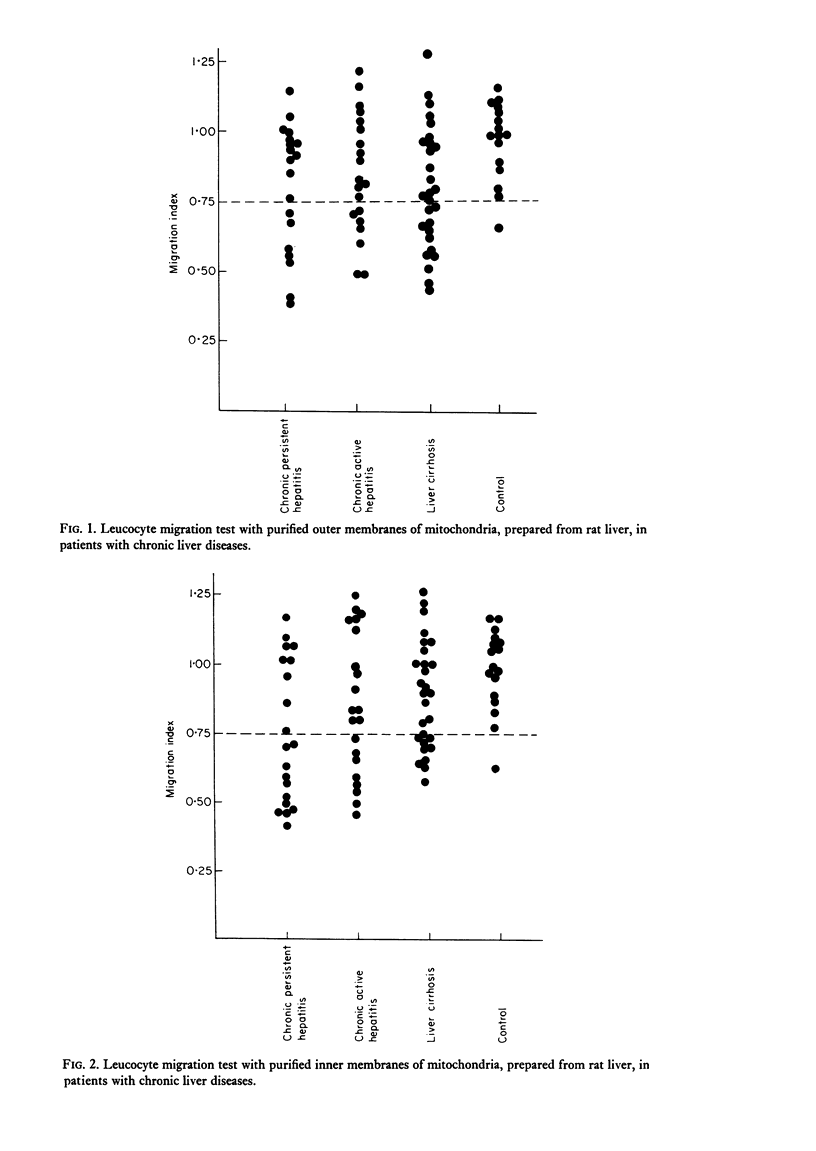
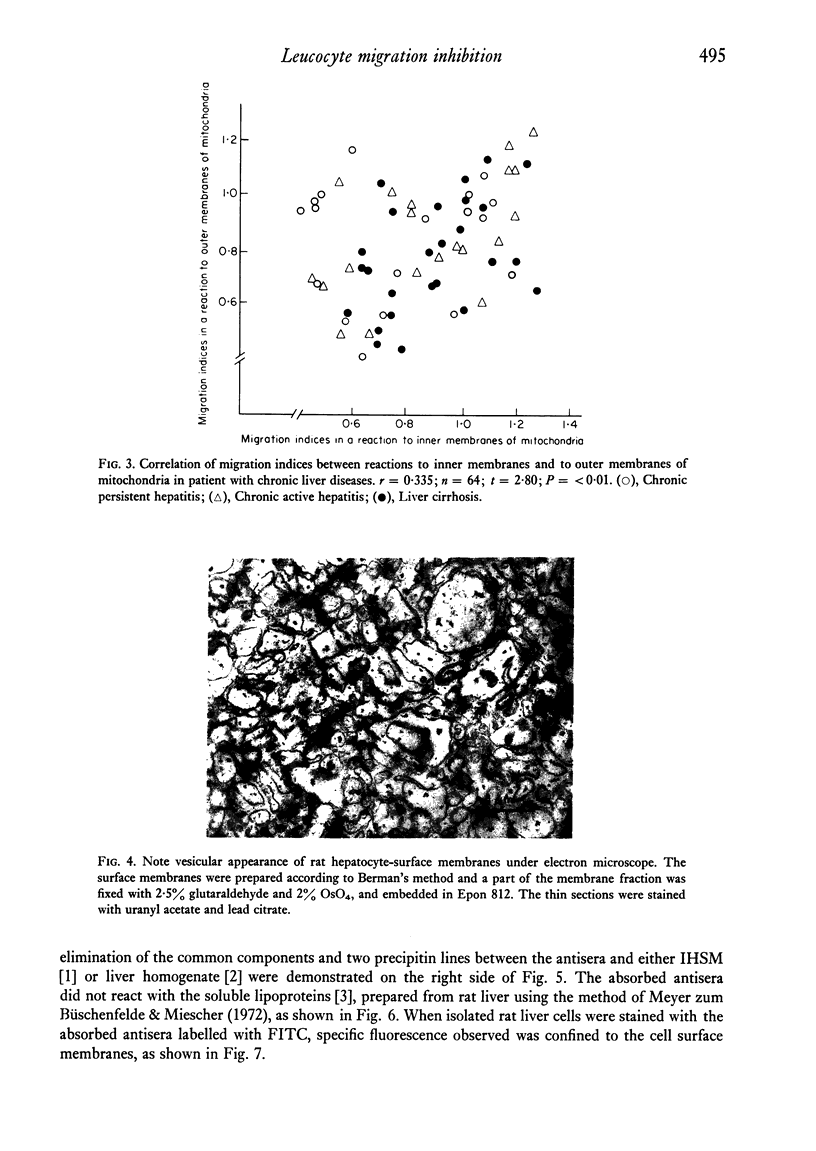
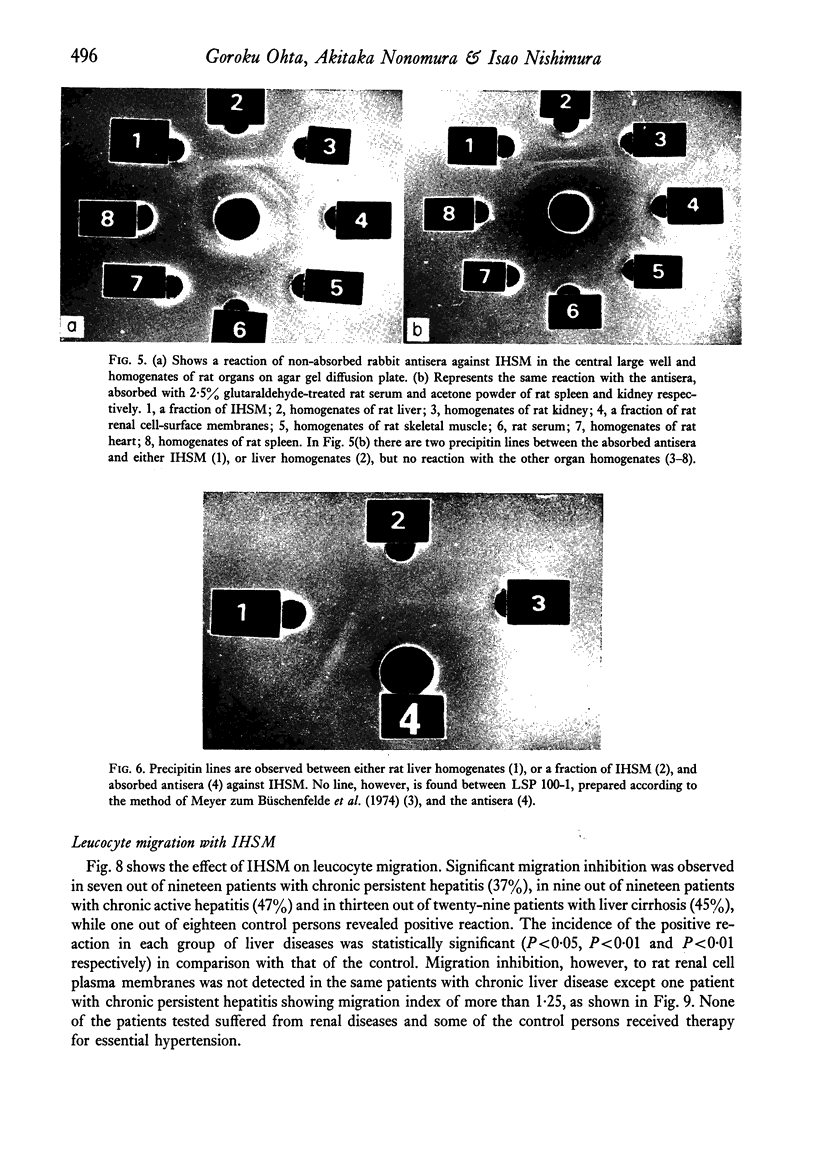
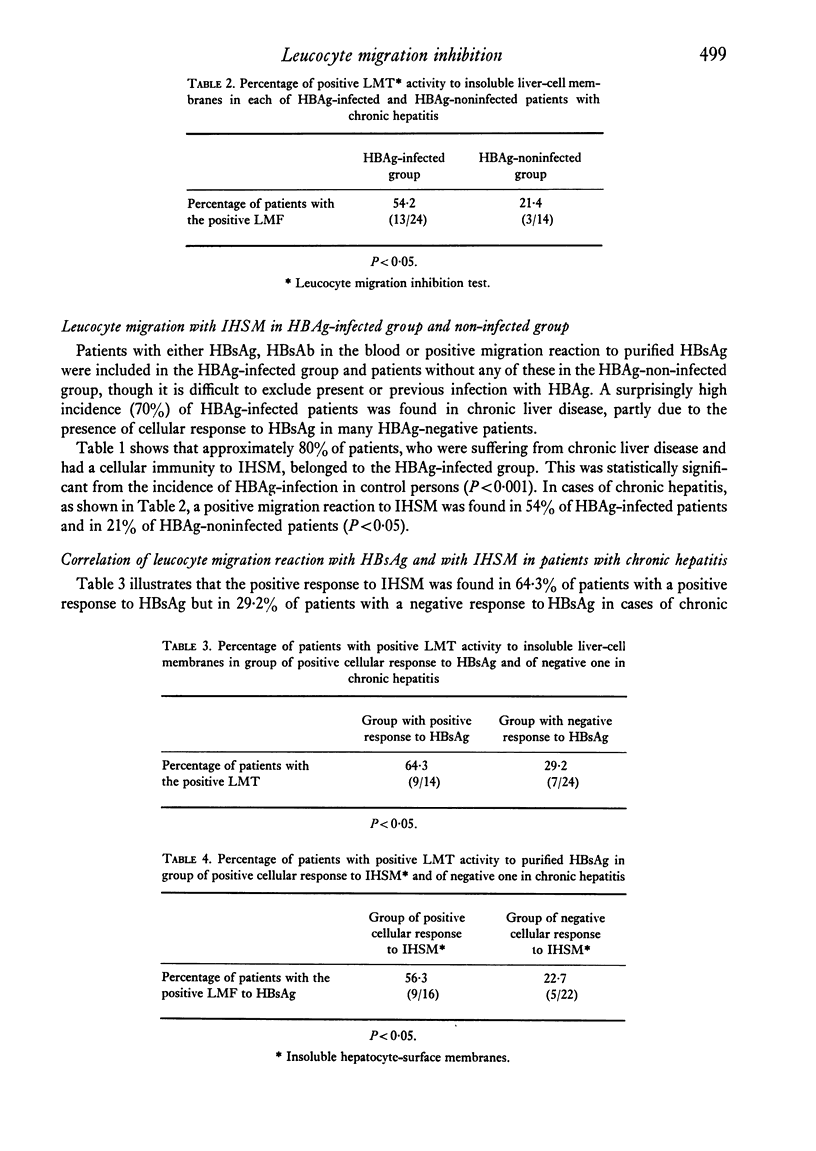
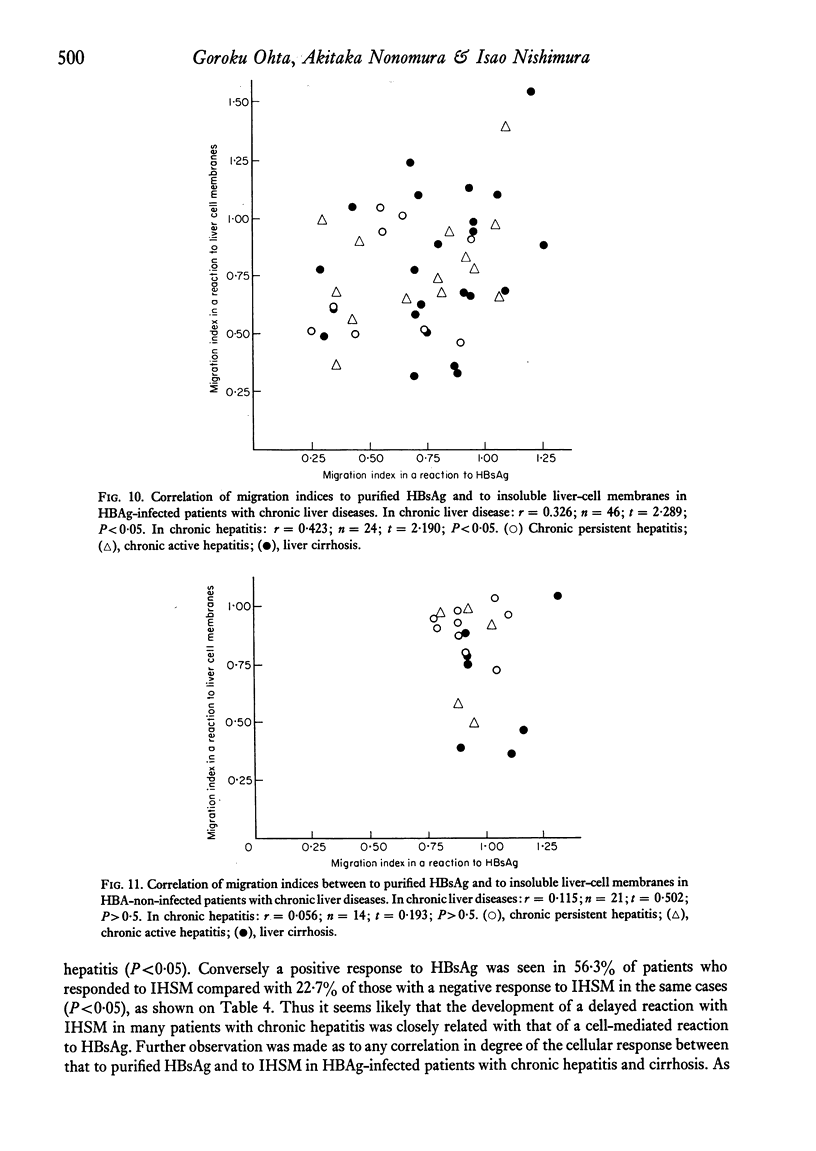
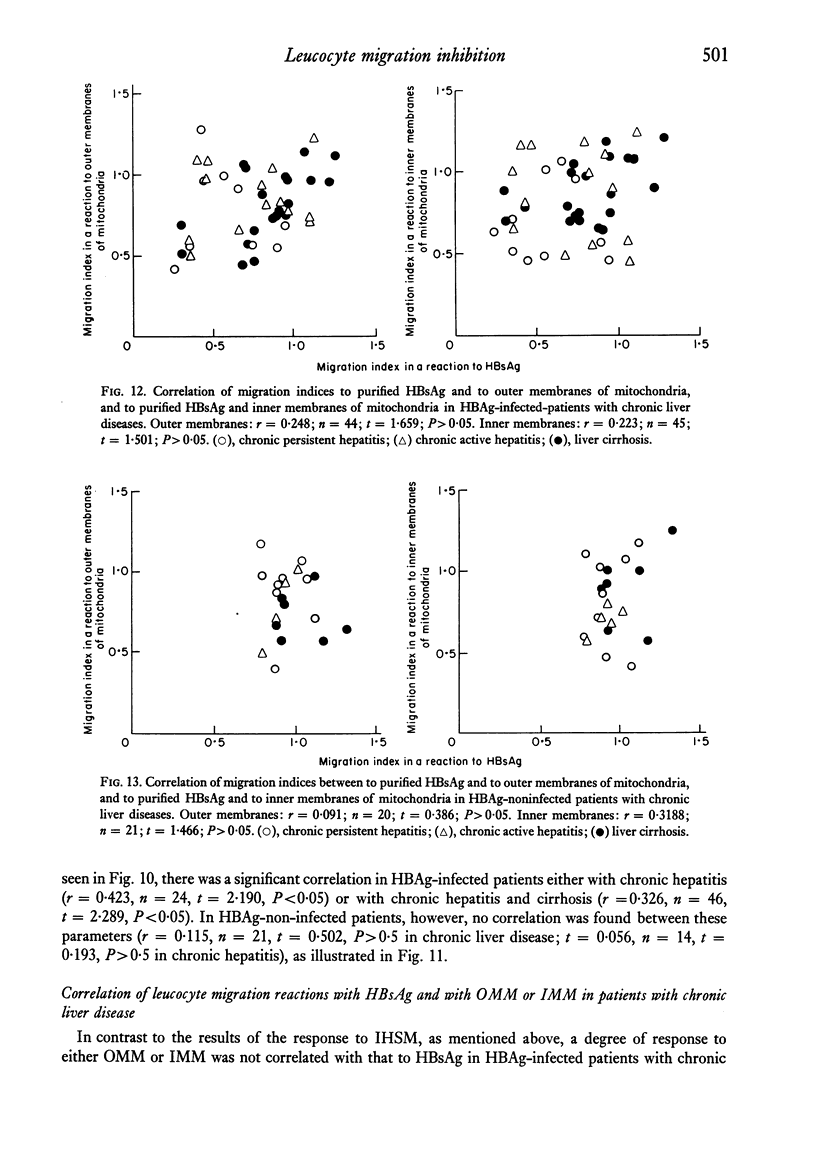
Patients with chronic liver disease were tested for delayed hypersensitivity to the outer and the inner membranes of mitochondria (OMM and IMM) and the insoluble hepatocyte-surface membranes (IHSM), prepared from rat livers, by means of leucocyte migration inhibition technique. Positive reaction to OMM was found in 37% of patients with chronic persistent hepatitis and 35% of those with chronic active hepatitis and 43% of those with liver cirrhosis (P less than 0-05). That to IMM was 55%, 43% and 36% (P less than 0-05) and to IHSM was 37%, 47% and 45% respectively (P less than 0-05). IHSM was found to contain liver-specific components and patients with positive response to IHSM did not reveal at all a positive reaction to rat renal cell-surface membranes. The incidence of positive response to IHSM was significantly higher (54-2%) in patients with the present or previous infection with HBAg than in HBAg-non-infected patients (21-4%) (P less than 0-05). And there seemed to be a good correlation between a degree of cellular response to purified HBsAg and that to IHSM in these HBAg-infected patients. No correlation, however, was found between that to purified HBsAg and that to OMM or IMM in the same patients. This suggested that the cellular response to either HBsAg or IHSM, both related closely, may play a role in the perpetuation of chronic liver disease.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berman H. M., Gram W., Spirtes M. A. An improved, reproducible method opreparing rat liver plasma cell membranes in buffered isotonic sucrose. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jun 3;183(1):10–18. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90124-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostoff J. Migration inhibition studies in human disease. Proc R Soc Med. 1970 Sep;63(9):905–906. doi: 10.1177/003591577006300919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostoff J., Roitt I. M., Doniach D. Leucocyte-migration inhibition in autoimmune diseases. Lancet. 1969 Jun 14;1(7607):1212–1213. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)92192-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büschenfelde K. H., Kössling F. K., Miescher P. A. Experimental chronic active hepatitis in rabbits following immunization with human liver proteins. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 May;11(1):99–108. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calder E. A., McLeman D., Barnes E. W., Irvine W. J. The effect of thyroid antigens on the in vitro migration of leucocytes from patients with Hashimoto thyroiditis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Dec;12(4):429–438. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley F. J., Fox R. A., Sherlock S. Cellular immunity and hepatitis-associated, Australia antigen liver disease. Lancet. 1972 Apr 1;1(7753):723–726. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90234-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Inadequate antibody response to hBAg or suppressor T-cell defect in development of active chronic hepatitis. Lancet. 1974 Dec 28;2(7896):1543–1545. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90287-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstone A. H., Calder E. A., Barnes E. W., Irvine W. J. The effect of gastric antigens on the in vitro migration of leucocytes from patients with atrophic gastritis and pernicious anaemia. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Aug;14(4):501–508. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopf U., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H., Freudenberg J. Liver-specific antigens of different species. II. Localization of a membrane antigen at cell surface of isolated hepatocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Jan;16(1):117–123. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knolle J., Meyer zum Büschenfelde, Bolte J. P., Berger J. Celluläre Immunreaktionen gegenüber dem Hepatitisassoziierten Antigen (HAA) und homologem leberspezifischen Protein (HLP) bei akuten HAA-positiven Hepatitiden. Klin Wochenschr. 1973 Dec 1;51(23):1172–1174. doi: 10.1007/BF01468568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. M., Reed W. D., Mitchell C. G., Galbraith R. M., Eddleston A. L., Zuckerman A. J., Williams R. Cellular and humoral immunity to hepatitis-B surface antigen in active chronic hepatitis. Br Med J. 1975 Mar 29;1(5960):705–708. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5960.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSHALL J. D., EVELAND W. C., SMITH C. W. Superiority of fluorescein isothiocyanate (Riggs) for fluorescent-antibody technic with a modification of its application. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Aug-Sep;98(4):898–900. doi: 10.3181/00379727-98-24222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., Smith M. G., Mitchell C. G., Reed W. D., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Cell-mediated immunity to a human liver-specific antigen in patients with active chronic hepatitis and primary biliary cirrhosis. Lancet. 1972 Aug 12;2(7772):296–297. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92904-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nerup J., Andersen V., Bendixen G. Anti-adrenal cellular hypersensitivity in Addison's disease. IV. In vivo and in vitro investigations on the mitochondrial fraction. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 May;6(5):733–739. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nerup J., Andersen V., Bendixen G. Anti-adrenal, cellular hypersensitivity in Addison's disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 Apr;4(4):355–363. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons D. F., Williams G. R., Chance B. Characteristics of isolated and purified preparations of the outer and inner membranes of mitochondria. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jul 14;137(2):643–666. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb50188.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popper H., Mackay I. R. Relation between Australia antigen and autoimmune hepatitis. Lancet. 1972 May 27;1(7761):1161–1164. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91379-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popper H. The immunologic basis of liver disease. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1975 Apr;51(4):519–527. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richens E. R., Ancill R. J., Gough K. R., Hartog M. Cellular hypersensitivity to mitochondrial antigens in diabetes mellitus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Jan;13(1):1–7. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richens E. R., Irvine W. J., Williams M. J., Hartog M., Ancill R. J. Cellular hypersensitivity to mitochondrial antigens in diabetes mellitus and its relationship to the presence of circulating autoantibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 May;17(1):71–75. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffield J. B., Emmelot P. Studies on plasma membranes. XVI. Tissue specific antigens in the liver cell surface. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Mar;71(1):97–105. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90268-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherlock S. Immunological reactivity and viral hepatitis. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1975 Apr;51(4):528–532. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. G., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Immunological factors in the evolution of active chronic hepatitis and other autoimmune liver diseases. Clin Gastroenterol. 1975 May;4(2):297–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. G., Golding P. L., Eddleston A. L., Mitchell C. G., Kemp A., Williams R. Cell-mediated immune responses in chronic liver diseases. Br Med J. 1972 Feb 26;1(5799):527–530. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5799.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A. D., Cochrane M. A., McFarlane I. G., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Lymphocyte cytotoxicity to isolated hepatocytes in chronic active hepatitis. Nature. 1974 Dec 20;252(5485):721–722. doi: 10.1038/252721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]