Abstract
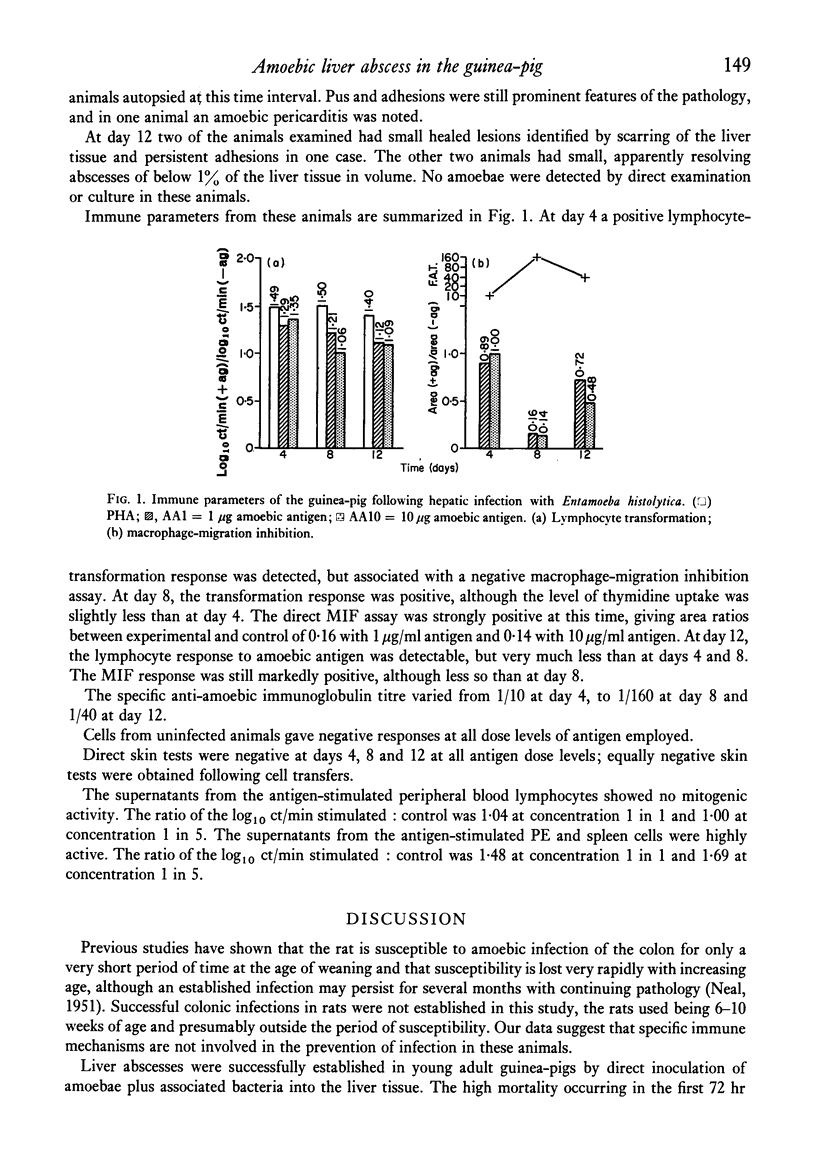
Guinea-pigs infected in the liver with the Biswas strain of Entamoeba histolytica showed no dermal hypersensitivity but showed positive lymphocyte transformation and macrophage-migration inhibition. The time sequence showed an activated response at 4 days after infection, a full response at 8 days when the liver abscesses were resolving and a waning response at 12 days when the abscesses had healed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gögler H., Knight R. The effect of hepatic injury upon the development of amoebic liver abscess in hamsters. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1974 Jun;68(2):177–185. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1974.11686936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris W. G., Bray R. S. Cellular sensitivity in amoebiasis--preliminary results of lymphocytic transformation in response to specific antigen and to mitogen in carrier and disease states. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1976;70(4):340–343. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(76)90095-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healy G. R., Gleason N. N. Studies on the pathogenicity of various strains of Entamoeba histolytica after prolonged cultivation, with observations on strain differences in the rats employed. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1966 May;15(3):294–299. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1966.15.294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarumilinta R. A simple method of inducing amoebic liver abscess in hamsters. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1966 Jun;60(2):139–145. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1966.11686397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane G. J., Matossian R., Batty I. Fluorochrome-labeled anti-immunoglobulin fractions used with stabilized antigen preparations for the assessment of parasitic diseases. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Jun 21;177:134–145. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb35040.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAEGRAITH B. G., HARINASUTA C. Experimental amoebic infection of the liver in guinea-pigs. I. Infection via the mesenteric vein and via the portal vein. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1954 Dec;48(4):421–433. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1954.11685643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAEGRAITH B. G., HARINASUTA C. Experimental amoebic infection of the liver in guinea-pigs. II. Abscess formation in animals with persistent intestinal lesions. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1954 Dec;48(4):434–441. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1954.11685644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEAL R. A. The duration and epidemiological significance of Entamoeba histolytica infections in rats. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1951 Dec;45(3):363–370. doi: 10.1016/s0035-9203(51)80007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEAL R. A., VINCENT P. Strain variation in Entamoeba histolytica. I. Correlation of invasiveness in rats with the clinical history and treatment of the experimental infections. Parasitology. 1955 May;45(1-2):152–162. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000027530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal R. A. Pathogenesis of amoebiasis. Gut. 1971 Jun;12(6):483–486. doi: 10.1136/gut.12.6.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz-Ortiz L., Zamacona-Ravelo G., Capin N. R. Hipersensibilidad celular en amibiasis. III. Efecto in vitro de la concanavalina a y de antígeno amibiano sobre leucocitos periféricos de pacientes con absceso hepático amibiano. Arch Invest Med (Mex) 1974;5(Suppl 2):481–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILLIPS B. P., WOLFE P. A., BARTGIS I. L. Studies on the ameba-bacteria relationship in amebiasis. II. Some concepts on the etiology of the disease. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1958 Jul;7(4):392–399. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1958.7.392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REINERTSON J. W., THOMPSON P. E. Experimental amebic hepatitis in hamsters. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1951 Mar;76(3):518–521. doi: 10.3181/00379727-76-18541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGH B. N., DAS S. R., SAXENA U. VIRULENCE OF STRAINS OF ENTAMOEBA HISTOLYTICA FROM INDIA, WITH AN ACCOUNT OF A METHOD FOR OBTAINING CENT PERCENT INFECTION IN RAT. Ann Biochem Exp Med. 1963 Jul;23:237–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


