Abstract
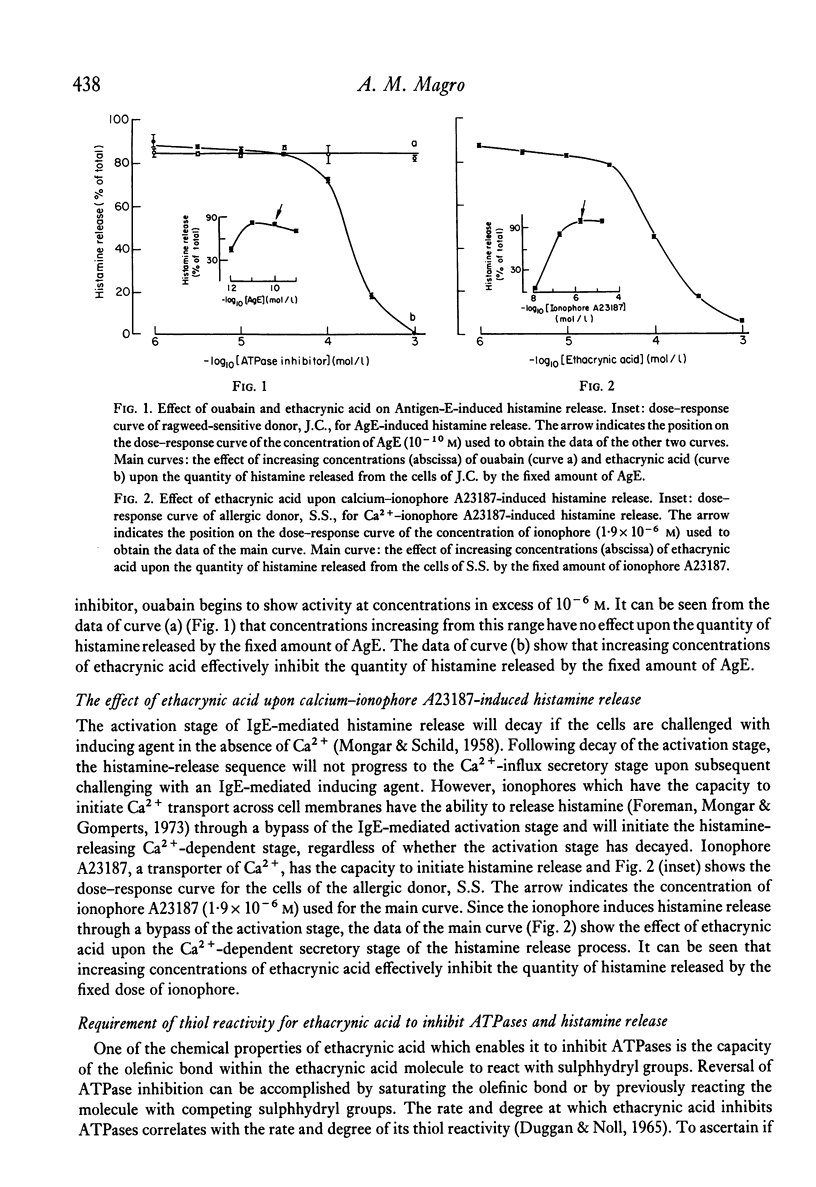
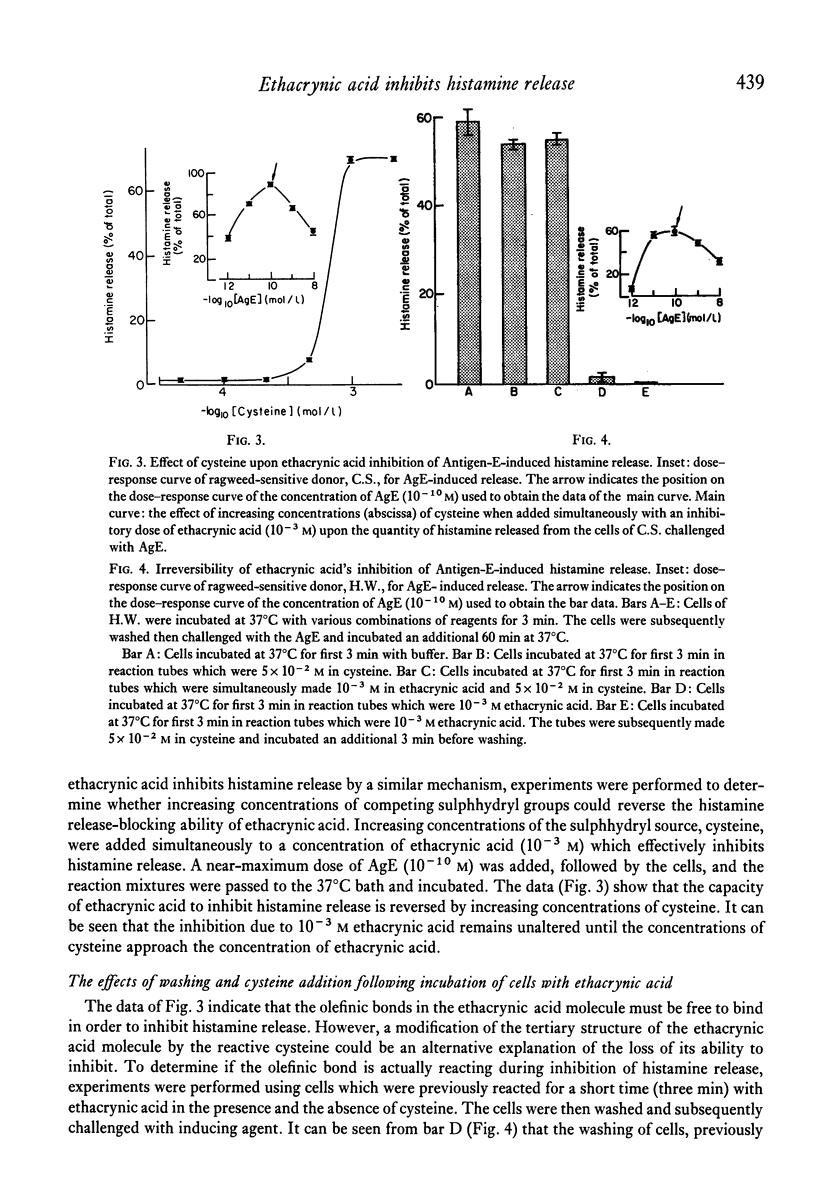
Ethacrynic acid, a known inhibitor of both Na+--K+ and Mg2+-activated ATPases, effectively inhibits histamine release from antigen-challenged human basophils in vitro. Ouabain, an inhibitor specific for Na+--K+-activated ATPases, shows no effect upon the quantity of histamine released from the antigen-challenged basophils. Ethacrynic acid also effectively inhibits Ca2+--ionophore A23187-induced release, implying it inhibits the Ca2+-dependent secretory stage of the histamine-release process. Inhibition of ATPases and histamine release by ethacrynic acid both require the presence of the olefinic bond in the ethacrynic-acid molecule. Possible utilization of analogues of ethacrynic acid as anti-allergic drugs and as a device to investigate the ATPase system of histamine-releasing cells is suggested.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLOCK J. B., BONTING S. L. SODIUM-POTASSIUM ACTIVATED ADENOSINETRIPHOSPHATASE AND CATION TRANSPORT IN NORMAL AND LEUKEMIC HUMAN LEUKOCYTES (STUDIES ON SODIUM-POTASSIUM ACTIVATED ADENOSINETRIPHOSPHATASE. 13). Enzymol Biol Clin (Basel) 1964;41:183–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bicking J. B., Holtz W. J., Watson S., Cragoe E. J., Jr (Vinylaryloxy)acetic acids. A new class of diuretic agents. 1. (Diacylvinylaryloxy)acetic acids. J Med Chem. 1976 Apr;19(4):530–535. doi: 10.1021/jm00226a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bicking J. B., Robb C. M., Watson L. S., Cragoe E. J., Jr (Vinylaryloxy)acetic acids. A new class of diuretic agents. 2. (4-(3-Oxo-1-alkenyl)phenoxy)acetic acids. J Med Chem. 1976 Apr;19(4):544–547. doi: 10.1021/jm00226a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foreman J. C., Mongar J. L., Gomperts B. D. Calcium ionophores and movement of calcium ions following the physiological stimulus to a secretory process. Nature. 1973 Oct 5;245(5423):249–251. doi: 10.1038/245249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka K., Ishizaka T. Identification of gamma-E-antibodies as a carrier of reaginic activity. J Immunol. 1967 Dec;99(6):1187–1198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING T. P., NORMAN P. S. Isolation studies of allergens from regweed pollen. Biochemistry. 1962 Jul;1:709–720. doi: 10.1021/bi00910a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONGAR J. L., SCHILD H. O. Cellular mechanisms in anaphylaxis. Physiol Rev. 1962 Apr;42:226–270. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1962.42.2.226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONGAR J. L., SCHILD H. O. The effect of calcium and pH on the anaphylactic reaction. J Physiol. 1958 Feb 17;140(2):272–284. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed P. W., Lardy H. A. A23187: a divalent cation ionophore. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6970–6977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHULTZ E. M., CRAGOE E. J., Jr, BICKING J. B., BOLHOFER W. A., SPRAGUE J. M. ALPHA, BETA-UNSATURATED KETONE DERIVATIVES OF ARYLOXYACETIC ACIDS, A NEW CLASS OF DIURETICS. J Med Pharm Chem. 1962 May;91:660–662. doi: 10.1021/jm01238a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHORE P. A., BURKHALTER A., COHN V. H., Jr A method for the fluorometric assay of histamine in tissues. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1959 Nov;127:182–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKOU J. C. The influence of some cations on an adenosine triphosphatase from peripheral nerves. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Feb;23(2):394–401. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90343-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz E. M., Bicking J. B., Deana A. A., Gould N. P., Strobauge T. P., Watson L. S., Cragoe E. J., Jr (Vinylaryloxy)acetic acids. A new class of diuretic agents. 3. ((2-Nitro-1-alkenyl)aryloxy)acetic acids. J Med Chem. 1976 Jun;19(6):783–787. doi: 10.1021/jm00228a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siraganian R. P. An automated continuous-flow system for the extraction and fluorometric analysis of histamine. Anal Biochem. 1974 Feb;57(2):383–394. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90093-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woltersdorf O. W., Jr, Robb C. M., Bicking J. B., Watson L. S., Cragoe E. J., Jr (Vinylaryloxy)acetic acids. A new class of diuretic agents. 4. Various ((2-substituted and 2,2-disubstituted vinyl)aryloxy)acetic acids. J Med Chem. 1976 Jul;19(7):972–975. doi: 10.1021/jm00229a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


