Abstract
The development of T- or B-membrane determinants on human foetal lymphoid cells was studied by the direct immunofluorescence technique, using a tetramethyl rhodamine isothiocyanate (TRITC) labelled horse antihuman T-cell conjugate (ATC) for the detection of T lymphocytes and a fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) labelled goat antihuman Fab conjugate for the demonstration of Ig-bearing B lymphocytes. Human foetal lymphocytes were also tested for spontaneous rosette formation with sheep red blood cells (SRBC).
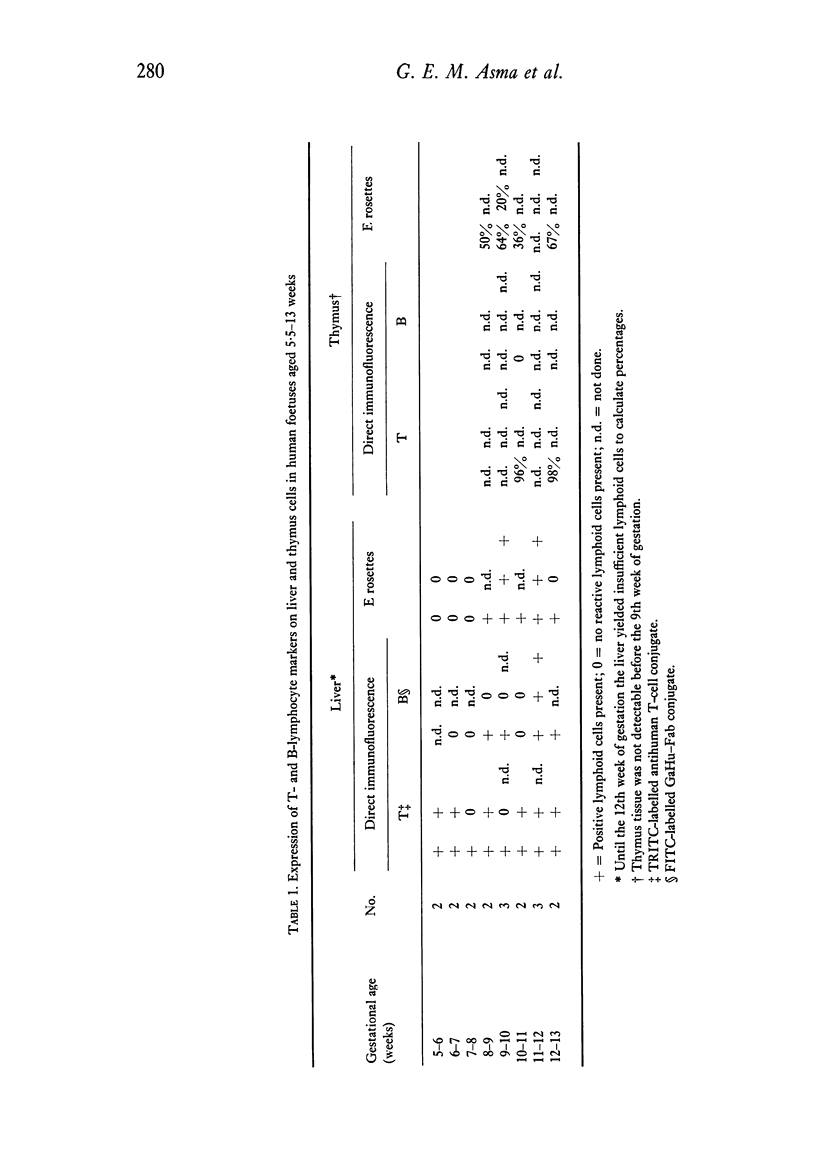
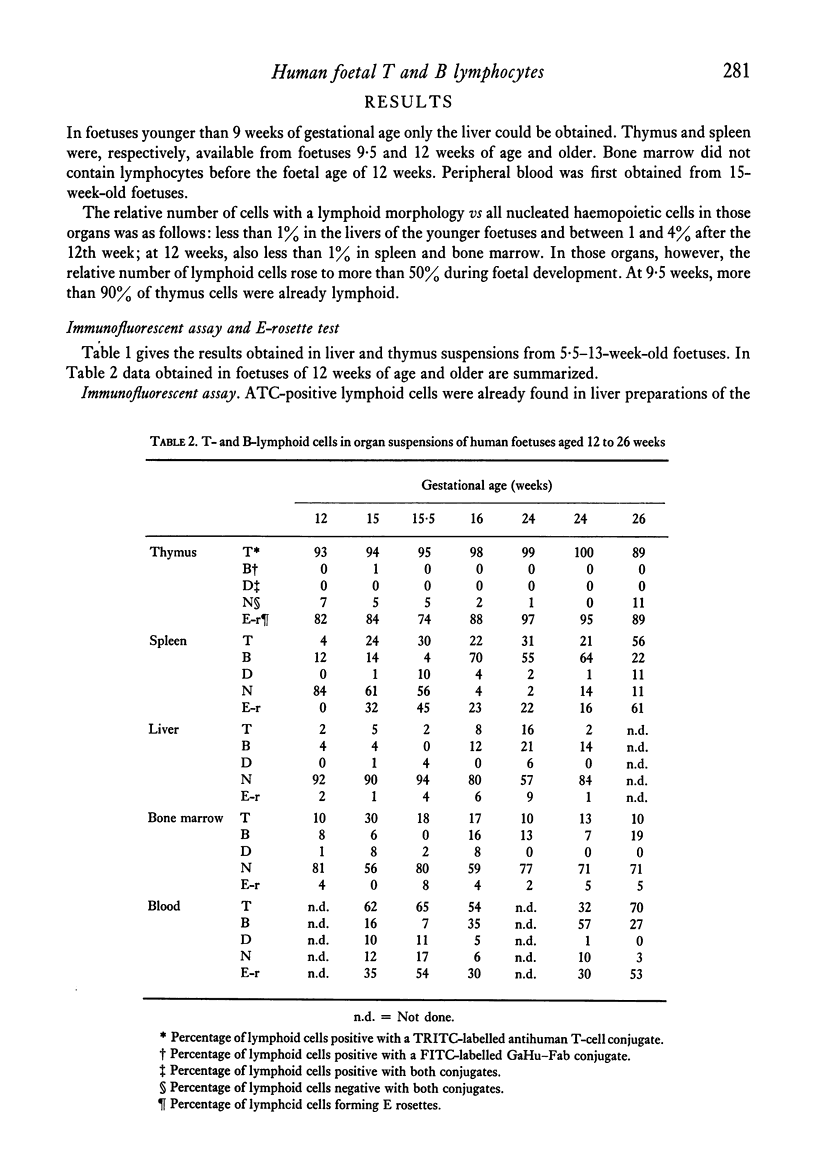
Cell suspensions of liver, spleen, thymus, bone marrow and blood of twenty-five human foetuses of 5·5–26 weeks of gestational age have been investigated. ATC-positive lymphoid cells were first seen in the liver at 5·5 weeks; E rosette-forming cells (ERFC) and Ig-bearing lymphoid cells were first found at 9 weeks. ERFC were also present in the thymus at 9 weeks. By 12 weeks, fluorescent B and T lymphocytes were found in bone marrow and spleen. ERFC were also found in bone marrow at this age, but not in spleen. At 15 weeks, more than 80% of blood lymphoid cells had T or B determinants.
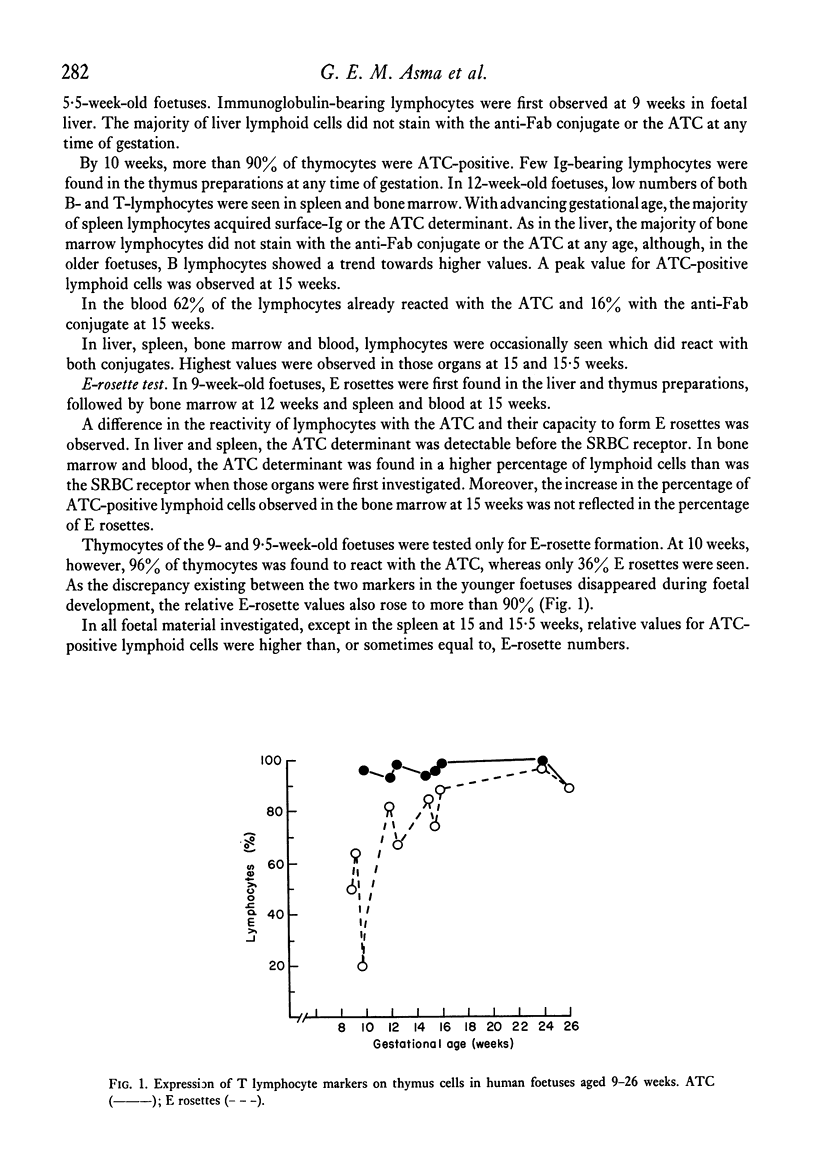
A difference in the reactivity of lymphoid cells with the ATC and their capacity to form E rosettes was observed. In liver and spleen, the ATC determinant was detectable before the SRBC receptor. In bone marrow, blood and thymus the ATC determinant was found on a higher percentage of lymphoid cells than was the SRBC receptor when those organs were first investigated. During the entire investigated period of gestation, the majority of lymphoid cells in liver and bone marrow did not react with either of the conjugates, nor did they form E rosettes. In all organs investigated, except in the thymus, lymphoid cells were occasionally seen which reacted with both conjugates. By the 16th week of foetal age, more than 90% of lymphoid cells in thymus, spleen and blood had acquired T- or B-membrane determinants.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiuti F., Wigzell H. Function and distribution pattern of human T lymphocytes. I. Production of anti-T lymphocyte specific sera as estimated by cytotoxicity and elimination of function of lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Feb;13(2):171–181. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asma G. E., Schuit H. R., Hijmans W. The determination of numbers of T and B lymphocytes in the blood of children and adults by the direct immunofluorescence technique. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Aug;29(2):286–294. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach J. F. Evaluation of T-cells and thymic serum factors in man using the rosette technique. Transplant Rev. 1973;16(0):196–217. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1973.tb00121.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyse E. A., Abbott J. Surface reorganization as initial inductive event in the differentiation of prothymocytes to thymocytes. Fed Proc. 1975 Jan;34(1):24–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr M. C., Stites D. P., Fudenberg H. H. The numerical development of lymphoid cells during human embryogenesis. Transplantation. 1975 Nov;20(5):410–413. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197511000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gattringer C., Wick G. Relationship between E receptors and a T-specific surface antigen on human T cells. Immunology. 1977 Feb;32(2):199–205. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand M. C., Asofsky R., Paul W. E. Ontogeny of B lymphocytes. I. In vitro appearance of Ig-bearing lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1974 Dec;14(3):460–469. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(74)90197-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward A. R., Ezer G. Development of lymphocyte populations in the human foetal thymus and spleen. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 May;17(1):169–178. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Holm G., Wigzell H. Surface markers on human T and B lymphocytes. I. A large population of lymphocytes forming nonimmune rosettes with sheep red blood cells. J Exp Med. 1972 Aug 1;136(2):207–215. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonsson V. Technical aspects of the rosette technique for detecting human circulating B and T lymphocytes. Normal values and some remarks on null lymphocytes. Scand J Haematol. 1974;13(5):361–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamelin J. P., Lisowska-Bernstein B., Matter A., Ryser J. E., Vassalli P. Mouse thymus-independent and thymus-derived lymphoid cells. I. Immunofluorescent and functional studies. J Exp Med. 1972 Nov 1;136(5):984–1007. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.5.984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchalonis J. J., Cone R. E., Boehmer H. V. Surface immunoglobulins of peripheral thymus-derived lymphocytes. Immunochemistry. 1974 May;11(5):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(74)90206-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuwissen H. J., Bach F. H., Hong R., Good R. A. Lymphocyte studies in congenital thymic dysplasia: The one-way stimulation test. J Pediatr. 1968 Feb;72(2):177–185. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(68)80306-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroz C., Hahn Y. Cell-surface immunoglobulin human thymus cells and its biosynthesis in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3716–3720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen F. L., Fanger M. W. Studies on the human T-lymphocyte population - IV. The isolation of T-lymphocyte antigens from peripheral lymphocytes. Immunochemistry. 1976 Feb;13(2):121–127. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(76)90279-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen F. L., Fanger M. W. Studies on the human T-lymphocyte population. I. The development and characterization of a specific anti-human T-cell antibody. J Immunol. 1974 Oct;113(4):1128–1137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen J. J., Cooper M. D., Raff M. C. In vitro generation of B lymphocytes in mouse foetal liver, a mammalian 'bursa equivalent'. Nature. 1974 May 24;249(455):361–363. doi: 10.1038/249361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLAYFAIR J. H., WOLFENDALE M. R., KAY H. E. The leucocytes of peripheral blood in the human foetus. Br J Haematol. 1963 Jul;9:336–344. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1963.tb06558.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prindull G. Maturation of cellular and humoral immunity during human embryonic development. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1974 Jul;63(4):607–615. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1974.tb04855.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato V. L., Waksal S. D., Herzenberg L. A. Identification and separation of pre T-cells from nu/nu mice: differentiation by preculture with thymic reticuloepithelial cells. Cell Immunol. 1976 Jun 1;24(1):173–185. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90142-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stites D. P., Carr M. C., Fudenberg H. H. Ontogeny of cellular immunity in the human fetus: development of responses to phytohemagglutinin and to allogeneic cells. Cell Immunol. 1974 Mar 30;11(1-3):257–271. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(74)90026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutman O., Good R. A. Immunocompetence of embryonic hemopoietic cells after traffic to thymus. Transplant Proc. 1971 Mar;3(1):923–925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touraine J. L., Touraine F., Kiszkiss D. F., Choi Y. S., Good R. A. Heterologous specific antiserum for identification of human T lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Apr;16(4):503–520. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vossen J. M. Membrane-associated immunoglobulin determinants on bone marrow and blood lymphocytes in the pediatric age group and on fetal tissues. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 30;254:262–279. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb29176.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wybran J., Carr M. C., Fudenberg H. H. The human rosette-forming cell as a marker of a population of thymus-derived cells. J Clin Invest. 1972 Oct;51(10):2537–2543. doi: 10.1172/JCI107069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Furth R., Schuit H. R., Hijmans W. The immunological development of the human fetus. J Exp Med. 1965 Dec 1;122(6):1173–1188. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.6.1173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


