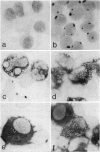
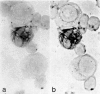
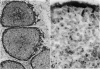
Abstract
Histochemical staining for alpha-naphthyl (non-specific) esterase has been employed to define subpopulations of human peripheral blood lymphocytes and monocytes. To define optimal conditions for staining, various fixatives, incubation times and cell preparations were compared. The great majority of human blood lymphocytes were found to have discrete granules of reaction product. More than 80% of T lymphocytes separated by E rosetting are esterase-positive whereas non-T lymphocytes are esterase-negative. Lymphocytes transformed by polyclonal mitogens lose their esterase-staining granules, which suggests that immature T cells are esterase-negative. Most blood monocytes show a diffuse cytoplasmic esterase reaction product and are phagocytic. However, about 20% of diffusely stained cells are not phagocytic. When leucocytes are cultured for 24 to 48 hr, the total number of esterase-positive cells increases and the great majority are phagocytic. This is interpreted as maturation of precursors into mature esterase-positive phagocytic monocytes. When cultured for longer periods, some lose phagocytic capacity and acquire the characteristics of secretory cells. Esterase-staining of lymph node sections allowed the identification of T- and B-dependent areas as well as macrophages related to sinuses. The esterase-staining technique could play a useful role in clinical and experimental immunology.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown G., Greaves M. F. Enumeration of absolute numbers of T and B lymphocytes in human blood. Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(2):161–172. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1974.tb01244.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrarini M., Moretta L., Abrile R., Durante M. L. Receptors for IgG molecules on human lymphocytes forming spontaneous rosettes with sheep red cells. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Jan;5(1):70–72. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froland S. S., Natvig J. B. Identification of three different human lymphocyte populations by surface markers. Transplant Rev. 1973;16:114–162. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1973.tb00119.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz D. A., Garrett M. A., Craig A. H. Serum effects of mitogenic reactivity in subjects with systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis and scleroderma. Technical considerations and lack of correlation with anti-lymphocyte antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Jan;27(1):100–110. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz D. A., Lobo P. I. Characterizaiton of two populations of human lymphocytes bearing easily detectable surface immunoglobulin. J Clin Invest. 1975 Dec;56(6):1464–1472. doi: 10.1172/JCI108227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz D. A. The development of macrophages from large mononuclear cells in the blood of patients with inflammatory disease. J Clin Invest. 1972 Apr;51(4):760–768. doi: 10.1172/JCI106870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller J., Brun del Re G., Buerki H., Keller H. U., Hess M. W., Cottier H. Nonspecific acid esterase activity: a criterion for differentiation of T and B lymphocytes in mouse lymph nodes. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Apr;5(4):270–274. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller J., Keller H. U., Brun del Re G., Buerki H., Hess M. W. Nonspecific esterase activity in T cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1976;66:117–122. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-4355-4_17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranki A., Tötterman T. H., Häyry P. Identification of resting human T and B lymphocytes by acid alpha-naphthyl acetate esterase staining combined with rosette formation with Staphylococcus aureus strain Cowan 1. Scand J Immunol. 1976;5(10):1129–1138. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1976.tb00254.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmalzl F., Braunsteiner H. Cytochemische Darstellung von Esteraseaktivitäten in Blut- und Knochenmarkszellen. Klin Wochenschr. 1968 Jun 15;46(12):642–650. doi: 10.1007/BF01727733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker S. B., Pierre R. V., Jordon R. E. Rapid identification of monocytes in a mixed mononuclear cell preparation. J Immunol Methods. 1977;14(3-4):267–269. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90137-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yam L. T., Li C. Y., Crosby W. H. Cytochemical identification of monocytes and granulocytes. Am J Clin Pathol. 1971 Mar;55(3):283–290. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/55.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]