Abstract
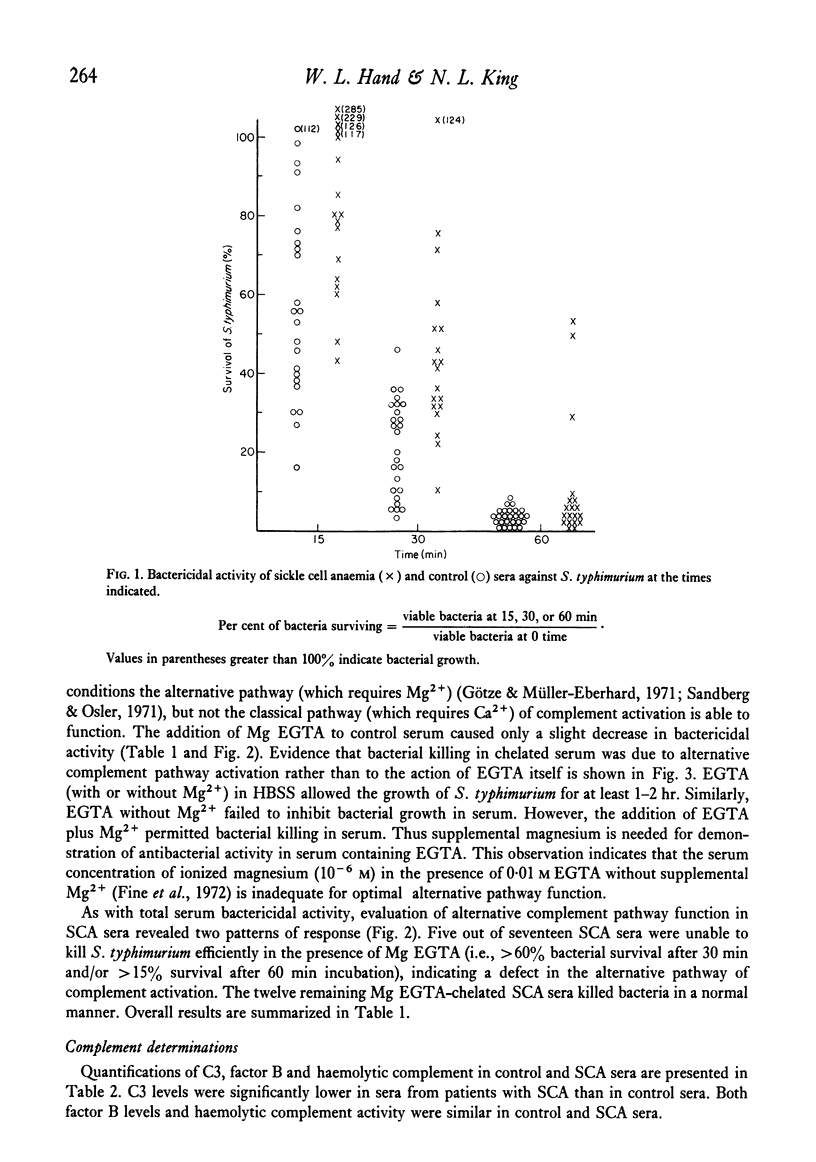
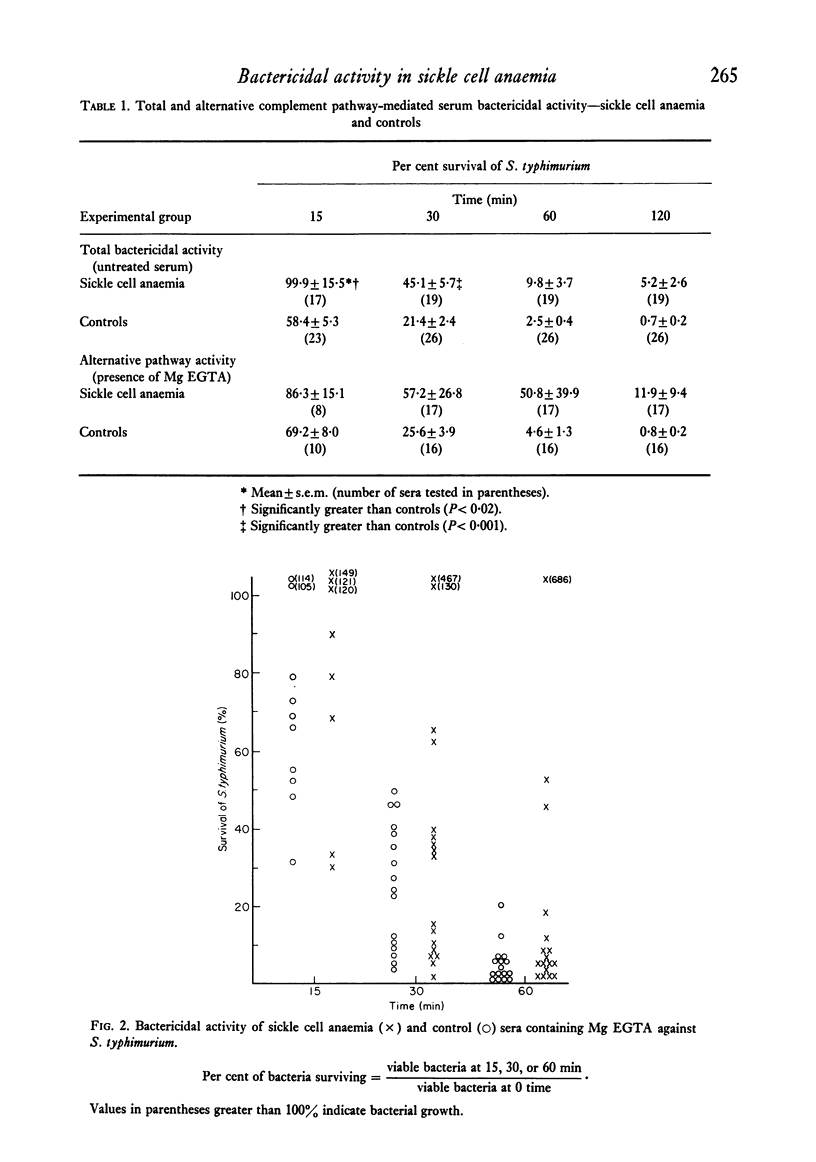
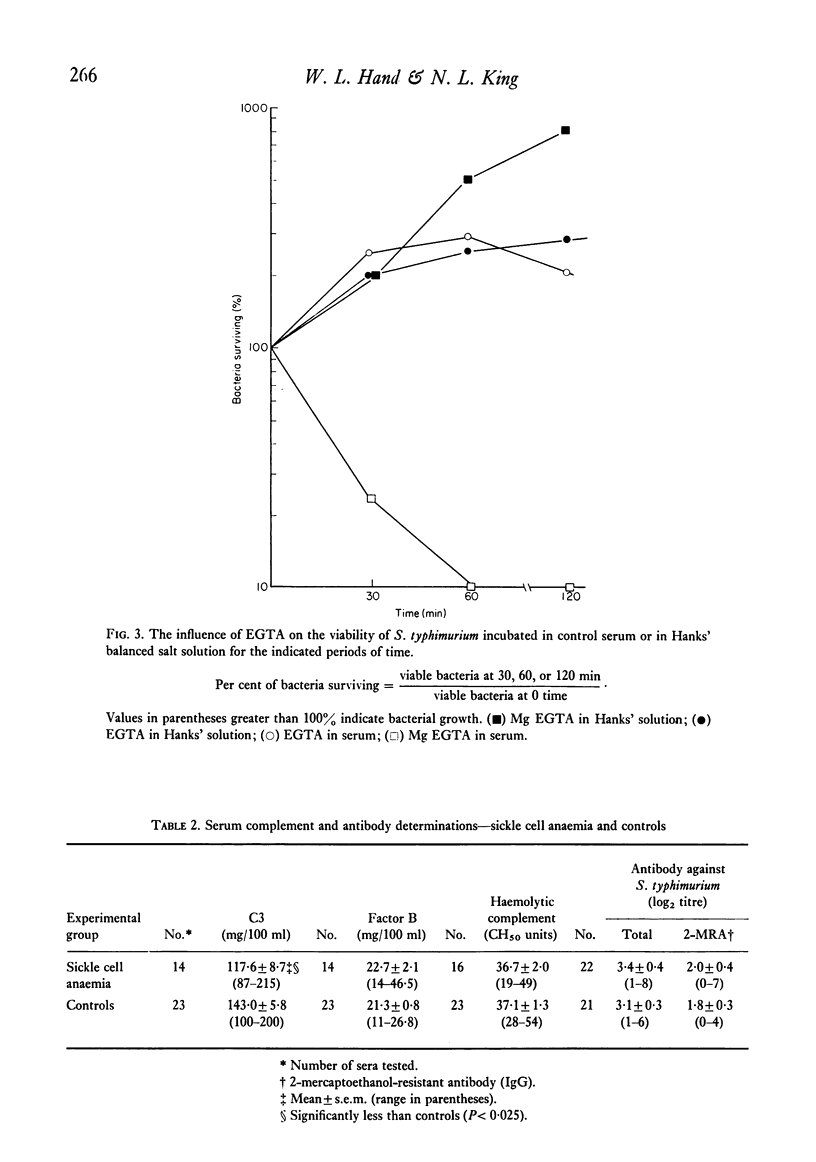
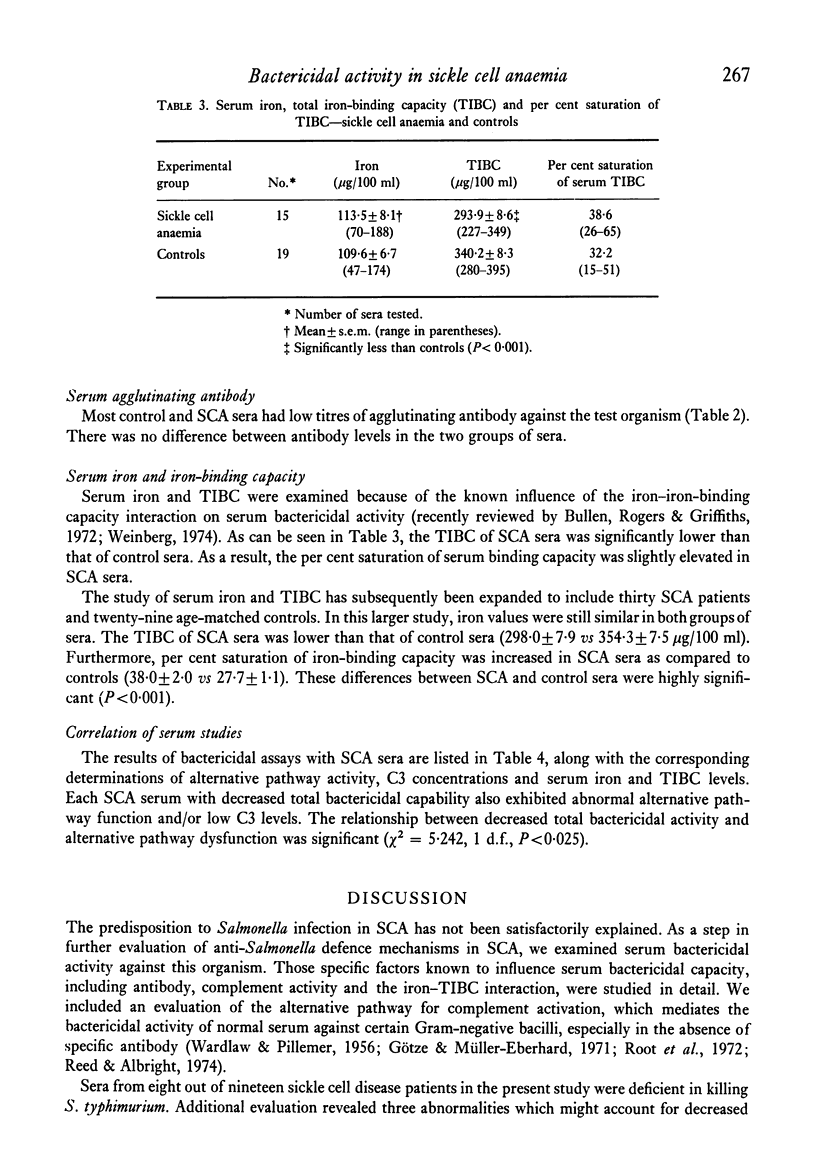
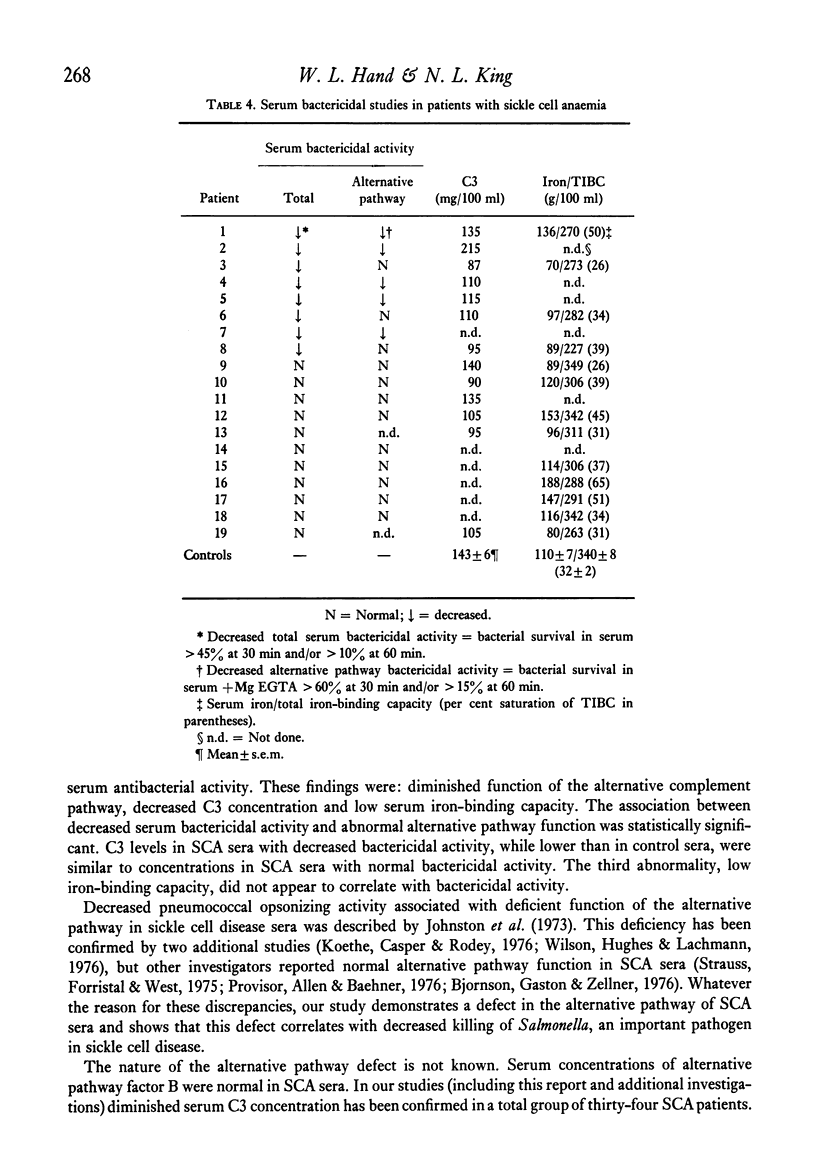
Systemic salmonellosis is a recognized complication of sickle cell anemia (SCA). In our initial study of SCA host defences against salmonella, we evaluated the bactericidal activity of serum against Salmonella typhimurium. When compared to controls, sera from eight out of nineteen SCA patients were deficient in bactericidal function. Levels of factor B, haemolytic complement and agglutinating antibody were similar in SCA and control sera. However, abnormalities that might theoretically account for the decreased antibacterial activity were observed in many SCA sera. These abnormal findings included: (a) defective function of the alternative complement pathway (decreased bacterial killing in the presence of Mg EGTA); (b) low serum C3 concentration; and (c) decreased total iron-binding capacity (TIBC), with a resultant increase in per cent saturation of iron-binding capacity. Of these deficiencies only the abnormal alternative pathway function was significantly associated with decreased serum bactericidal activity. A suggested function of serum bactericidal activity is prevention of bacteraemia by susceptible organisms. Thus diminished serum bactericidal capacity may increase the risk of Salmonella bacteraemia in some individuals with sickle cell disease.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alper C. A., Johnson A. M., Birtch A. G., Moore F. D. Human C'3: evidence for the liver as the primary site of synthesis. Science. 1969 Jan 17;163(3864):286–288. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3864.286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullen J. J., Rogers H. J., Griffiths E. Iron binding proteins and infection. Br J Haematol. 1972 Oct;23(4):389–392. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1972.tb07073.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS S. D., WEDGWOOD R. J. KINETICS OF THE BACTERICIDAL ACTION OF NORMAL SERUM ON GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA. J Immunol. 1965 Jul;95:75–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine D. P., Marney S. R., Jr, Colley D. G., Sergent J. S., Des Prez R. M. C3 shunt activation in human serum chelated with EGTA. J Immunol. 1972 Oct;109(4):807–809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOOK E. W. Salmonellosis: certain factors influencing the interaction of Salmonella and the human host. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1961 Jul;37:499–512. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haurani F. I., Meyer A., O'Brien R. Production of transferrin by the macrophage. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1973 Sep;14(3):309–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeejeebhoy K. N., Ho J., Greenberg G. R., Phillips M. J., Bruce-Robertson A., Sodtke U. Albumin, fibrinogen and transferrin synthesis in isolated rat hepatocyte suspensions. A model for the study of plasma protein synthesis. Biochem J. 1975 Jan;146(1):141–155. doi: 10.1042/bj1460141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. B., Jr, Newman S. L., Struth A. G. An abnormality of the alternate pathway of complement activation in sickle-cell disease. N Engl J Med. 1973 Apr 19;288(16):803–808. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197304192881601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabins S. A., Lerner C. Fulminant pneumococcemia and sickle cell anemia. JAMA. 1970 Jan 19;211(3):467–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye D., Gill F. A., Hook E. W. Factors influencing host resistance to Salmonella infections: the effects of hemolysis and erythrophagocytosis. Am J Med Sci. 1967 Aug;254(2):205–215. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196708000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koethe S. M., Casper J. T., Rodey G. E. Alternative complement pathway activity in sera from patients with sickle cell disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Jan;23(1):56–60. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann J. D., Smith J. W., Miller T. E., Barnett J. A., Sanford J. P. Local immune response in experimental pyelonephritis. J Clin Invest. 1969 Nov;47(11):2541–2550. doi: 10.1172/JCI105936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson H. A., Spencer R. P., Cornelius E. A. Functional asplenia in sickle-cell anemia. N Engl J Med. 1969 Oct 23;281(17):923–926. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196910232811703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persijn J. P., van der Slik W., Riethorst A. Determination of serum iron and latent iron-binding capacity (LIBC). Clin Chim Acta. 1971 Nov;35(1):91–98. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(71)90298-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed W. P., Albright E. L. Serum factors responsible for killing of Shigella. Immunology. 1974 Jan;26(1):205–215. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringelhann B., Konotey-Ahulu F. I. Immunological studies in sickle cell crisis in Ghana. Afr J Med Sci. 1973 Jan;4(1):17–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roantree R. J., Rantz L. A. A STUDY OF THE RELATIONSHIP OF THE NORMAL BACTERICIDAL ACTIVITY OF HUMAN SERUM TO BACTERIAL INFECTION. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jan;39(1):72–81. doi: 10.1172/JCI104029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson M. G., Watson R. J. Pneumococcal meningitis in sickle-cell anemia. N Engl J Med. 1966 May 5;274(18):1006–1008. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196605052741806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root R. K., Ellman L., Frank M. M. Bactericidal and opsonic properties of C4-deficient guinea pig serum. J Immunol. 1972 Sep;109(3):477–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddy S., Gigli I., Austen K. F. The complement system of man (second of four parts). N Engl J Med. 1972 Sep 14;287(11):545–549. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197209142871106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg A. L., Osler A. G. Dual pathways of complement interaction with guinea pig immunoglobulins. J Immunol. 1971 Nov;107(5):1268–1273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simberkoff M. S., Ricupero I., Rahal J. J., Jr Host resistance to Serratia marcescens infection: serum bactericidal activity and phagocytosis by normal blood leukocytes. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Feb;87(2):206–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stecher V. J., Thorbecke G. J. Sites of synthesis of serum proteins. OI. Serum proteins produced by macrophages in vitro. J Immunol. 1967 Oct;99(4):643–652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vosti K. L., Randall E. Sensitivity of serologically classified strains of escherichia coli of human origin to the serum bactericidal system. Am J Med Sci. 1970 Feb;259(2):114–119. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197002000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARDLAW A. C., PILLEMER L. The properdin system and immunity. V. The bactericidal activity of the properdin system. J Exp Med. 1956 May 1;103(5):553–575. doi: 10.1084/jem.103.5.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Iron and susceptibility to infectious disease. Science. 1974 May 31;184(4140):952–956. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4140.952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkelstein J. A., Drachman R. H. Deficiency of pneumococcal serum opsonizing activity in sickle-cell disease. N Engl J Med. 1968 Aug 29;279(9):459–466. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196808292790904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



