Abstract
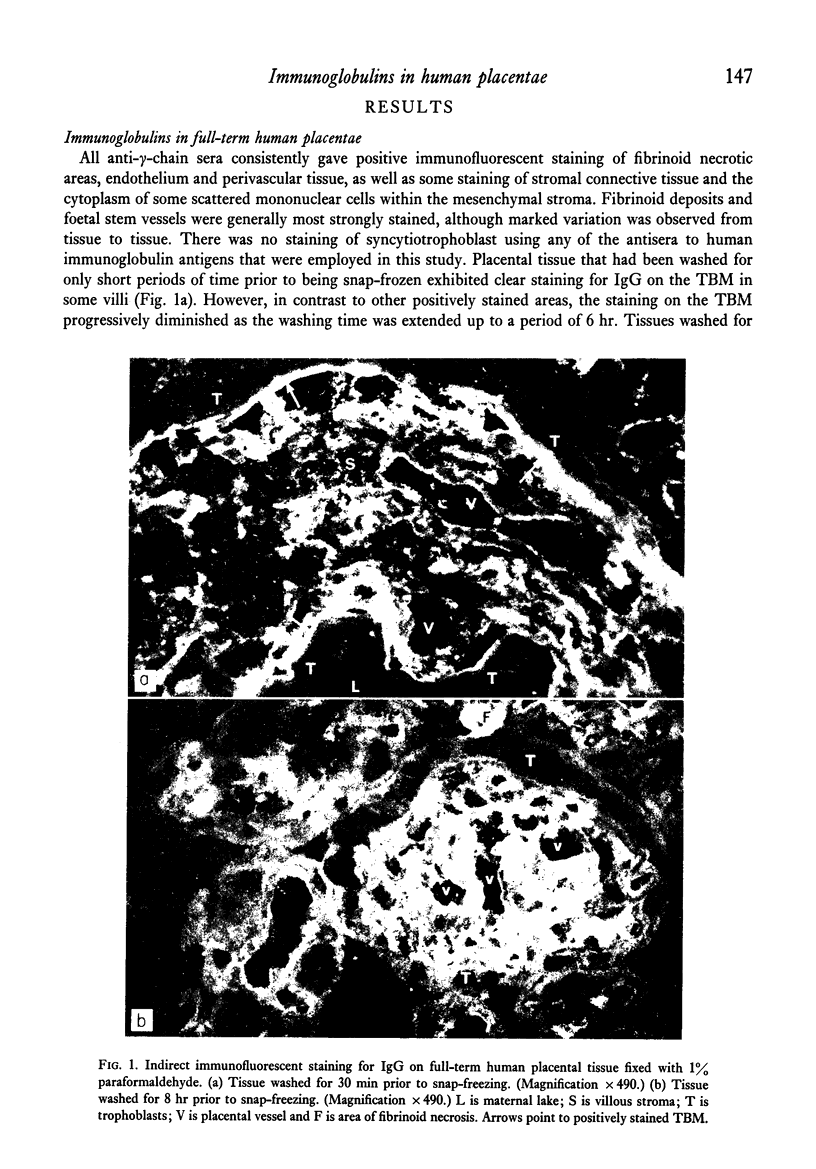
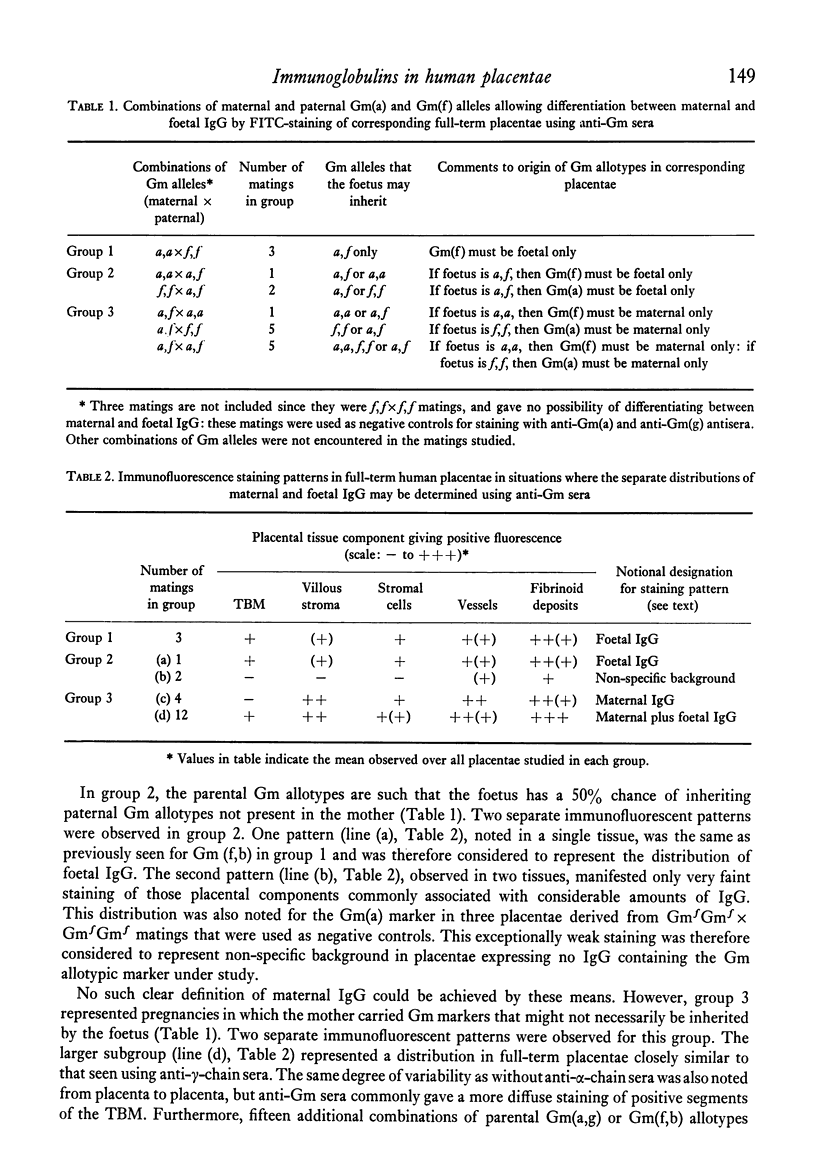
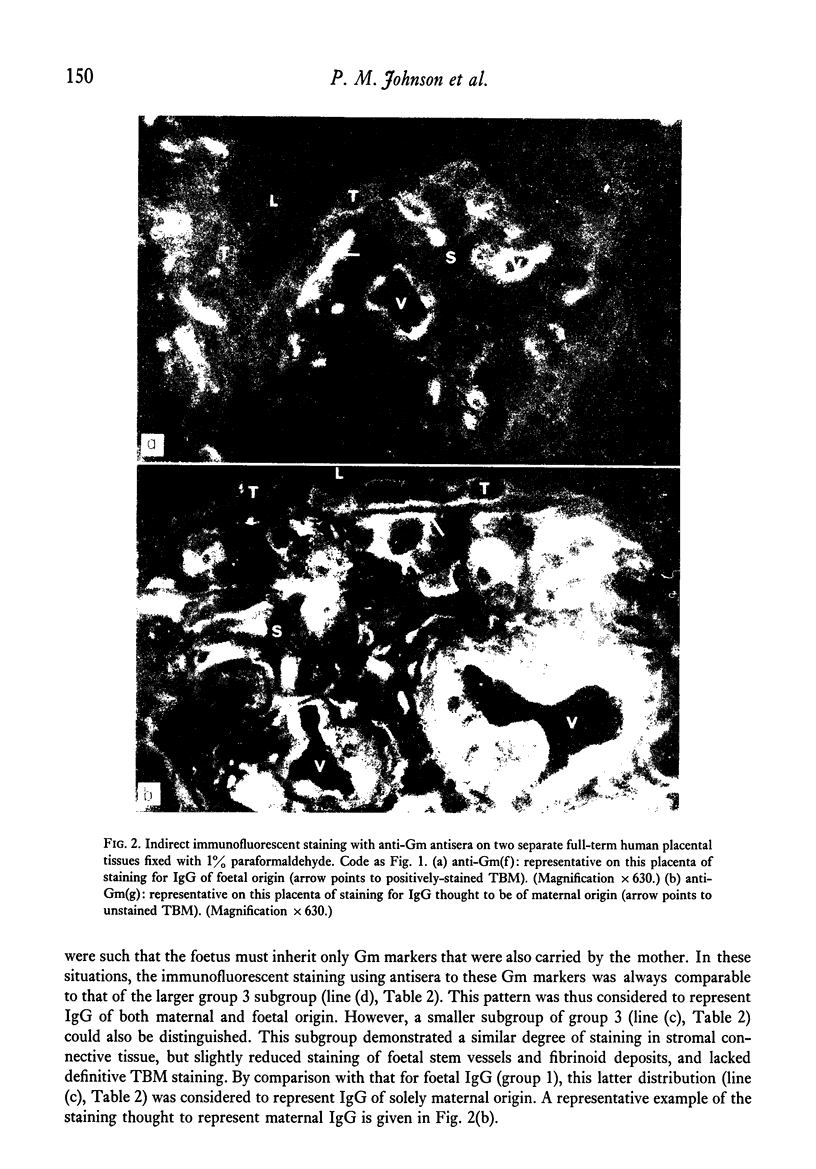
All four human IgG subclasses, and both kappa and lambda light chains, were detected by immunofluorescence in similar distributions in chorionic villi of human placentae. IgG1 and IgG3 were the predominant subclasses. No evidence was obtained for local enzymatic digestion of IgG during placental transfer. Most of the IgG on the trophoblastic basement membrane (TBM) was loosely bound and could be removed by prolonged washing, although some appeared to be more tightly bound to small segments of the TBM. IgM, but not IgA, was present in small amounts in placental villous structures. Immunoglobulin was never observed within the syncytiotrophoblast. Antisera to IgG genetic (Gm) markers were used to locate IgG thought to be of foetal or maternal origin. The presence of paternal Gm markers not carried by the mother was taken as evidence for foetal IgG. Foetal (paternal) Gm markers were observed in placentae, although maternal IgG was the major immunoglobulin present in placental villi. Both maternal and foetal IgG were demonstrated in fibrinoid deposits, vessel walls and the cytoplasm of some stromal cells. Only foetal IgG was definitively observed in the immunoglobulin that is tightly bound to the TBM.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BORSOS T., RAPP H. J. ESTIMATION OF MOLECULAR SIZE OF COMPLEMENT COMPONENTS BY SEPHADEX CHROMATOGRAPHY. J Immunol. 1965 Apr;94:510–513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doughty R. W., Gelsthorpe K. Some parameters of lymphocyte antibody activity through pregnancy and further eluates of placental material. Tissue Antigens. 1976 Jul;8(1):43–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1976.tb00550.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulk W. P., Jeannet M., Creighton W. D., Carbonara A. Immunological studies of the human placenta. Characterization of immunoglobulins on trophoblastic basement membranes. J Clin Invest. 1974 Nov;54(5):1011–1019. doi: 10.1172/JCI107844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulk W. P., Johnson P. M. Immunological studies of human placentae: identification and distribution of proteins in mature chorionic villi. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Feb;27(2):365–375. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulk W. P., Sanderson A. R., Temple A. Distribution of MHC antigens in human placental chorionic villi. Transplant Proc. 1977 Jun;9(2):1379–1384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulk W. P., Temple A. Distribution of beta2 microglobulin and HLA in chorionic villi of human placentae. Nature. 1976 Aug 26;262(5571):799–802. doi: 10.1038/262799a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GITLIN D., KUMATE J., URRUSTI J., MORALES C. THE SELECTIVITY OF THE HUMAN PLACENTA IN THE TRANSFER OF PLASMA PROTEINS FROM MOTHER TO FETUS. J Clin Invest. 1964 Oct;43:1938–1951. doi: 10.1172/JCI105068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitlin D., Biasucci A. Development of gamma G, gamma A, gamma M, beta IC-beta IA, C 1 esterase inhibitor, ceruloplasmin, transferrin, hemopexin, haptoglobin, fibrinogen, plasminogen, alpha 1-antitrypsin, orosomucoid, beta-lipoprotein, alpha 2-macroglobulin, and prealbumin in the human conceptus. J Clin Invest. 1969 Aug;48(8):1433–1446. doi: 10.1172/JCI106109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold E. R., Fudenberg H. H. Chromic chloride: a coupling reagent for passive hemagglutination reactions. J Immunol. 1967 Nov;99(5):859–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeannet M., Werner C., Ramirez E., Vassalli P., Faulk W. P. Anti-HLA, anti-human "Ia-like" and MLC blocking activity of human placental IgG. Transplant Proc. 1977 Jun;9(2):1417–1422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkinson E. J., Billington W. D., Elson J. Detection of receptors for immunoglobulin on human placenta by EA rosette formation. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Mar;23(3):456–461. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. M., Faulk W. P. Immunological studies of human placentae. Lectin binding to villous stroma and to trophoblastic basement membrane. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Jun;24(3):435–440. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. M., Faulk W. P., Wang A. C. Immunological studies of human placentae: subclass and fragment specificity of binding of aggregated IgG by placental endothelial cells. Immunology. 1976 Oct;31(4):659–664. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matre R., Tönder O., Endresen C. Fc receptors in human placenta. Scand J Immunol. 1975;4(7):741–745. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1975.tb02682.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick J. N., Faulk W. P., Fox H., Fudenberg H. H. Immunohistological and elution studies of the human placenta. J Exp Med. 1971 Jan 1;133(1):1–18. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellbye O. J., Natvig J. B. Experimentally produced antibodies to the pepsin site of IgG due to untreated autologous IgG in immune complexes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Aug;7(2):257–267. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellbye O. J., Natvig J. B. Presence and origin of human IgG subclass proteins in newborns. Vox Sang. 1973 Mar;24(3):206–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1973.tb02632.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munthe E., Natvig J. B. Detection of genetic markers of human immunoglobulins by immunofluorescence technique. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Jun 21;177:326–334. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb35061.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natvig J. B., Kunkel H. G. Human immunoglobulins: classes, subclasses, genetic variants, and idiotypes. Adv Immunol. 1973;16:1–59. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60295-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natvig J. B., Turner M. W. Localization of Gm markers to different molecular regions of the Fc fragment. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 May;8(5):685–700. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revillard J. P., Brochier J., Robert M., Bonneau M., Traeger J. Immunologic properties of placental eluates. Transplant Proc. 1976 Jun;8(2):275–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R. J., Wernet P., Kunkel H. G., Dupont B., Jersild C., Fu S. M. Recognition by pregnancy serums of non-HL-A alloantigens selectively expressed on B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1975 Apr 1;141(4):924–929. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Furth R., Schuit H. R., Hijmans W. The immunological development of the human fetus. J Exp Med. 1965 Dec 1;122(6):1173–1188. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.6.1173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


