Abstract
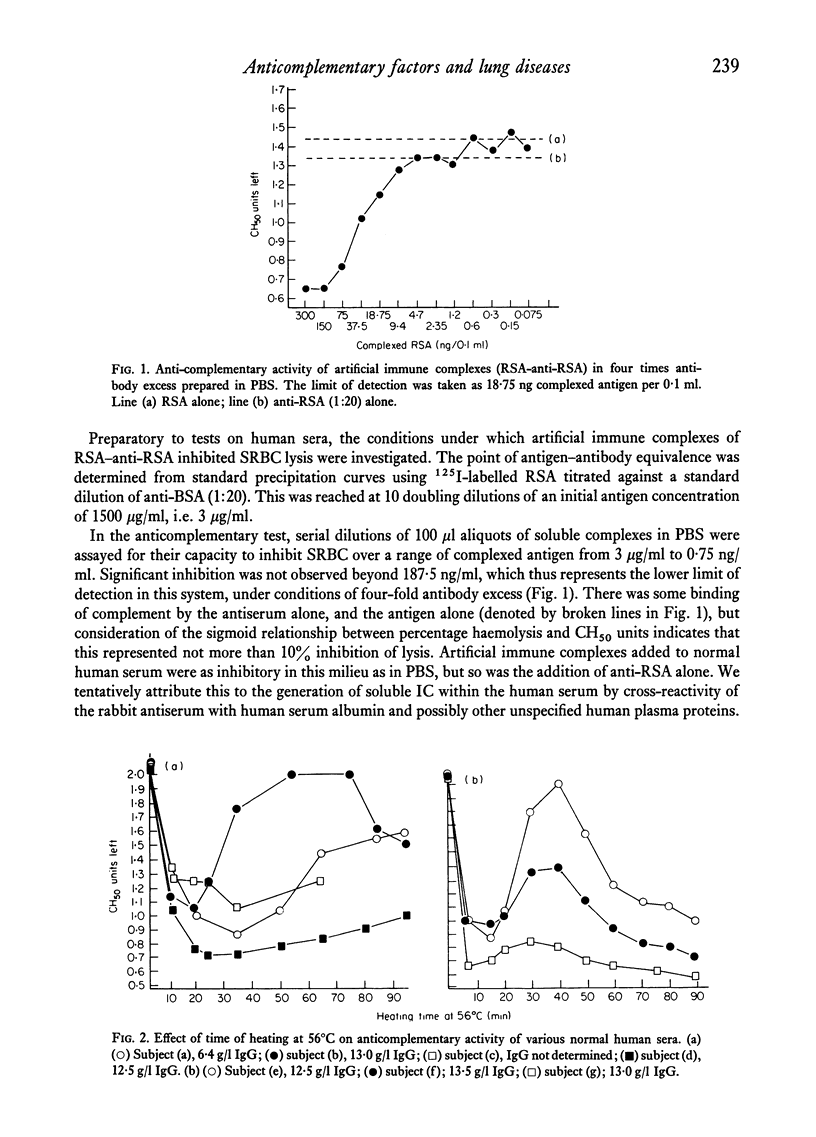
An anticomplementary technique, based upon the ability of circulating immune complexes to bind added exogenous C1 after inactivation of bound endogenous C1 by heating, was used to detect anticomplementary factors in the sera of patients with bronchiectasis (chronic bronchial suppuration), chronic bronchitis and bronchial asthma. The validity of the method was determined using artificial immune complexes (rat serum albumin–anti-rat serum albumin) and the limit of detection estimated to be of the order of 200 ng complexed antigen per ml. Because heat inactivation of endogenous C1 is an essential part of the procedure, the anticomplementary activity of normal sera as a function of time of heating at 56°C was examined. Wide variations in anticomplementary activity were demonstrated in these sera, which did not entirely correlate with the IgG levels. Comparison of the anticomplementary activity of control (n = 11) and pathological sera (n = 19) at two arbitrarily chosen time intervals (30 and 60 min) nevertheless disclosed significant differences, which were greatest after the longer heating time. These differences were consolidated when the series was extended to include larger numbers of sera (107 pathological; forty-three normal) and indicate that the frequency and/or level of anticomplementary factors in pathological sera is greater than those in controls.
It is postulated that qualitative changes in IgG as a result of heat aggregation or the presence of immune complexes could account for part of the anticomplementary activity of both normal and pathological sera. The quantitative differences between the two groups, however, are interpreted to indicate the presence, in addition, of anticomplementary factors associated with the various disease states.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agnello V., Winchester R. J., Kunkel H. G. Precipitin reactions of the C1q component of complement with aggregated gamma-globulin and immune complexes in gel diffusion. Immunology. 1970 Dec;19(6):909–919. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augener W., Grey H. M., Cooper N. R., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The reaction of monomeric and aggregated immunoglobulins with C1. Immunochemistry. 1971 Nov;8(11):1011–1020. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90489-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calder E. A., Penhale W. J., Barnes E. W., Irvine W. J. Evidence for circulating immune complexes in thyroid disease. Br Med J. 1974 Apr 6;2(5909):30–31. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5909.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Götze O., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The alternative pathway of complement activation. Adv Immunol. 1976;24:1–35. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60328-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. H., Mowbray J. F., Porter K. A. Detection of circulating immune complexes in pathological human sera. Lancet. 1975 Apr 5;1(7910):762–765. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92433-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lurhuma A. Z., Cambiaso C. L., Masson P. L., Heremans J. F. Detection of circulating antigen-antibody complexes by their inhibitory effect on the agglutination of IgG-coated particles by rheumatioid factor of Clq. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Aug;25(2):212–226. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan I. C. Competition for receptors for immunoglobulin on cytotoxic lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Feb;10(2):275–283. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarlane H., Holzel A., Brenchley P., Allan J. D., Wallwork J. C., Singer B. E., Worsley B. Immune complexes in cystic fibrosis. Br Med J. 1975 Feb 22;1(5955):423–428. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5955.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowbray J. F., Hoffbrand A. V., Holborow E. J., Seah P. P., Fry L. Circulating immune complexes in dermatitis herpetiformis. Lancet. 1973 Feb 24;1(7800):400–402. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90253-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel J., Rent R., Gewurz H. Interactions of C-reactive protein with the complement system. I. Protamine-induced consumption of complement in acute phase sera. J Exp Med. 1974 Sep 1;140(3):631–647. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.3.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubler R. H., Lange G., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. Detection of immune complexes in unheated sera by modified 125I-Clq binding test. Effect of heating on the binding of Clq by immune complexes and application of the test to systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):232–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


