Abstract
Anti-complementary (AC) activity and C1q-binding are increased in acute type A and B hepatitis, alcohol-induced hepatitis, HB surface antigen-positive and -negative chronic active hepatitis and primary biliary cirrhosis.
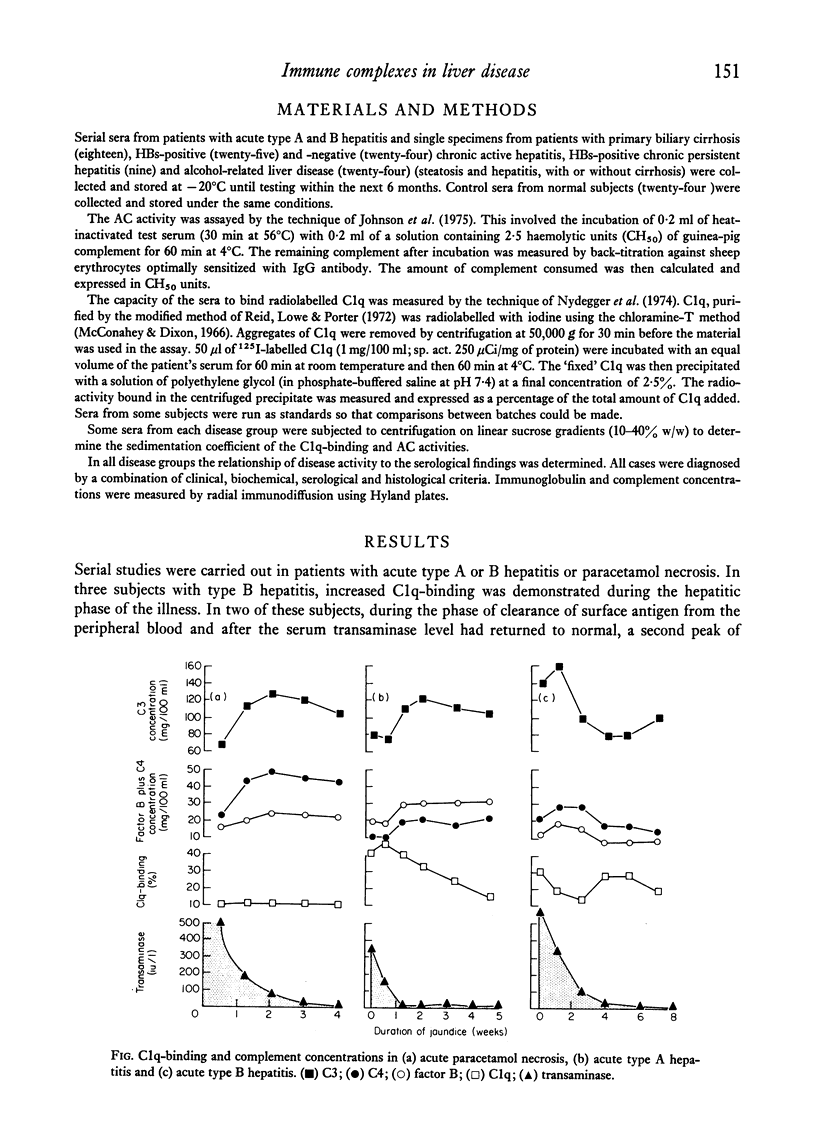
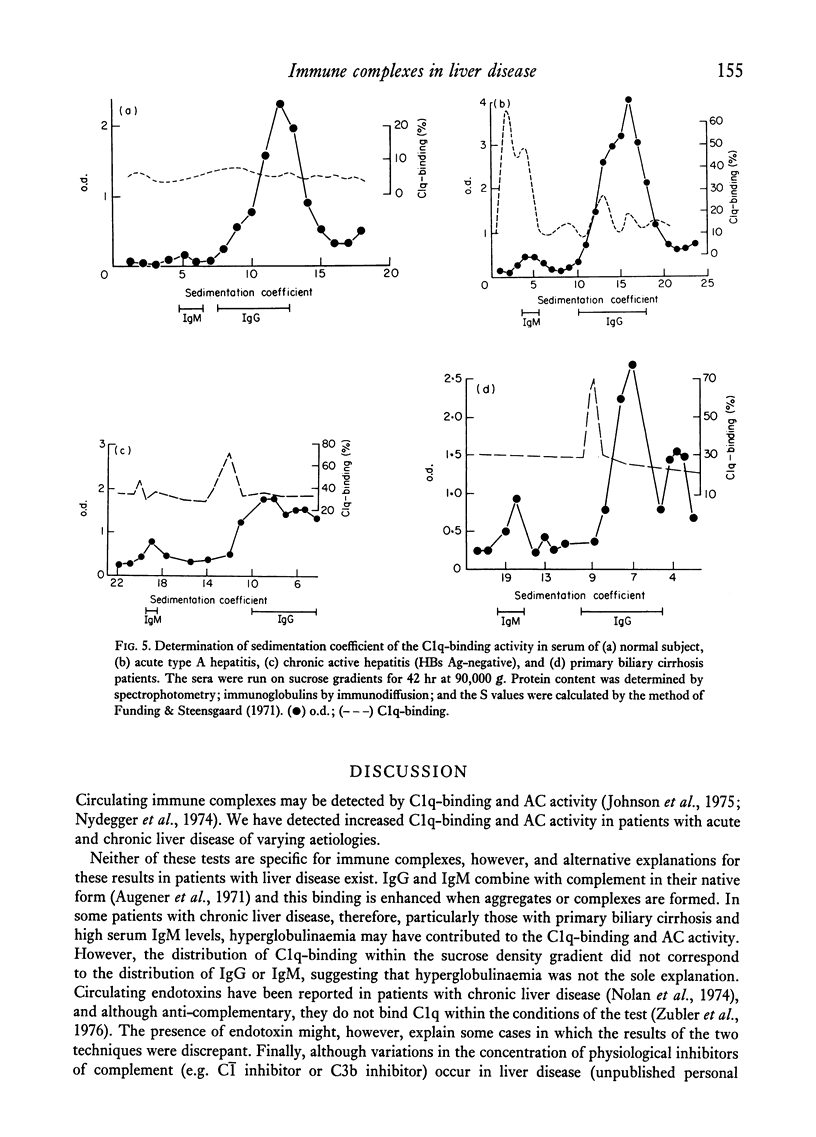
In acute type A hepatitis, a large increase in C1q-binding was demonstrated during the period of elevated transaminases. In type B hepatitis, the initial peak was small, but was followed by a further peak during the period of falling serum HB surface (HBs) antigen titre. In both diseases the C1q-binding was associated with >20S particles. In paracetamol-induced necrosis, C1q-binding remained normal. In type A and B hepatitis and in paracetamol-induced necrosis, C4, C3 and factor B concentrations were depressed in the early phase of the disease. This change may reflect either diminished synthesis or increased catabolism.
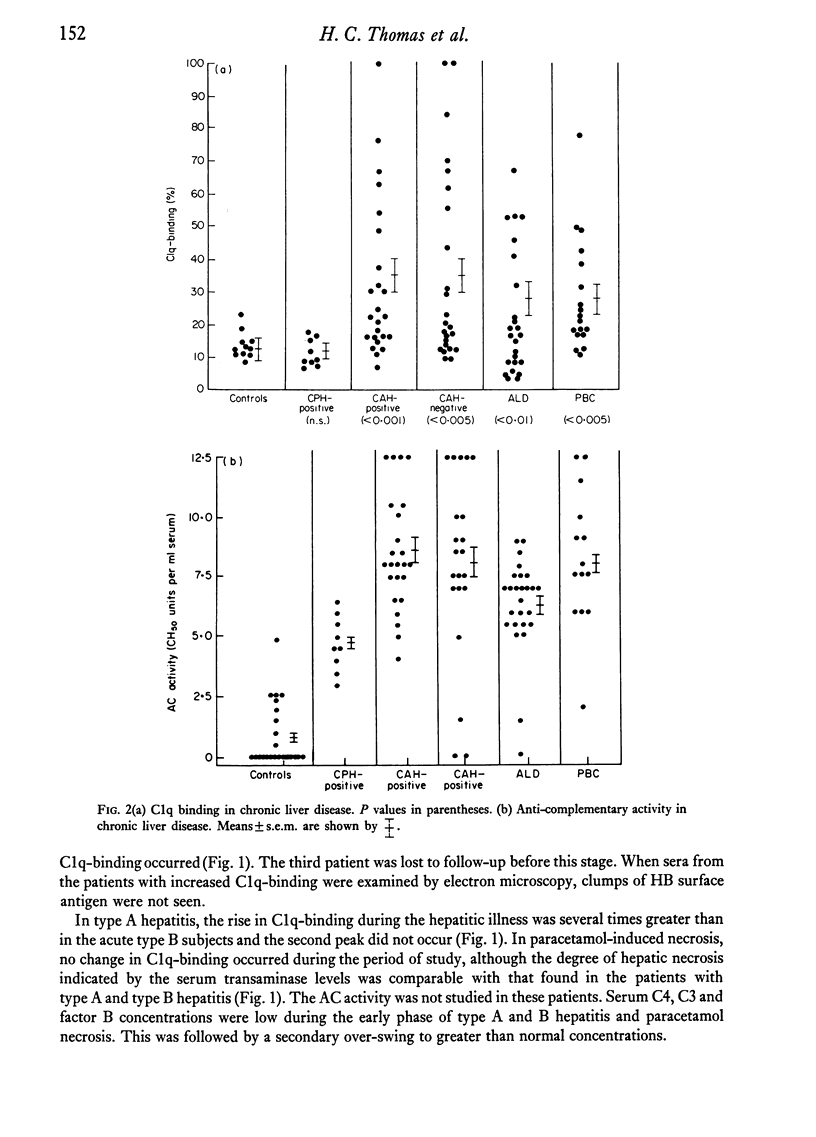
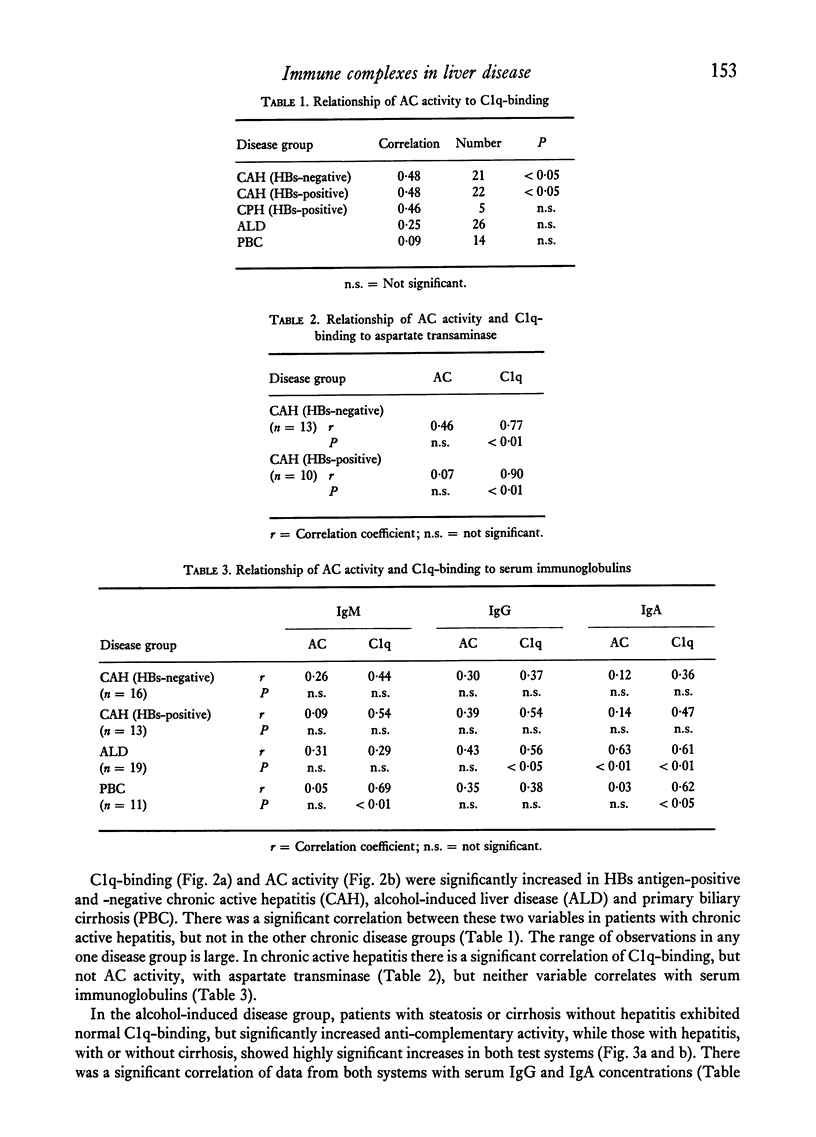
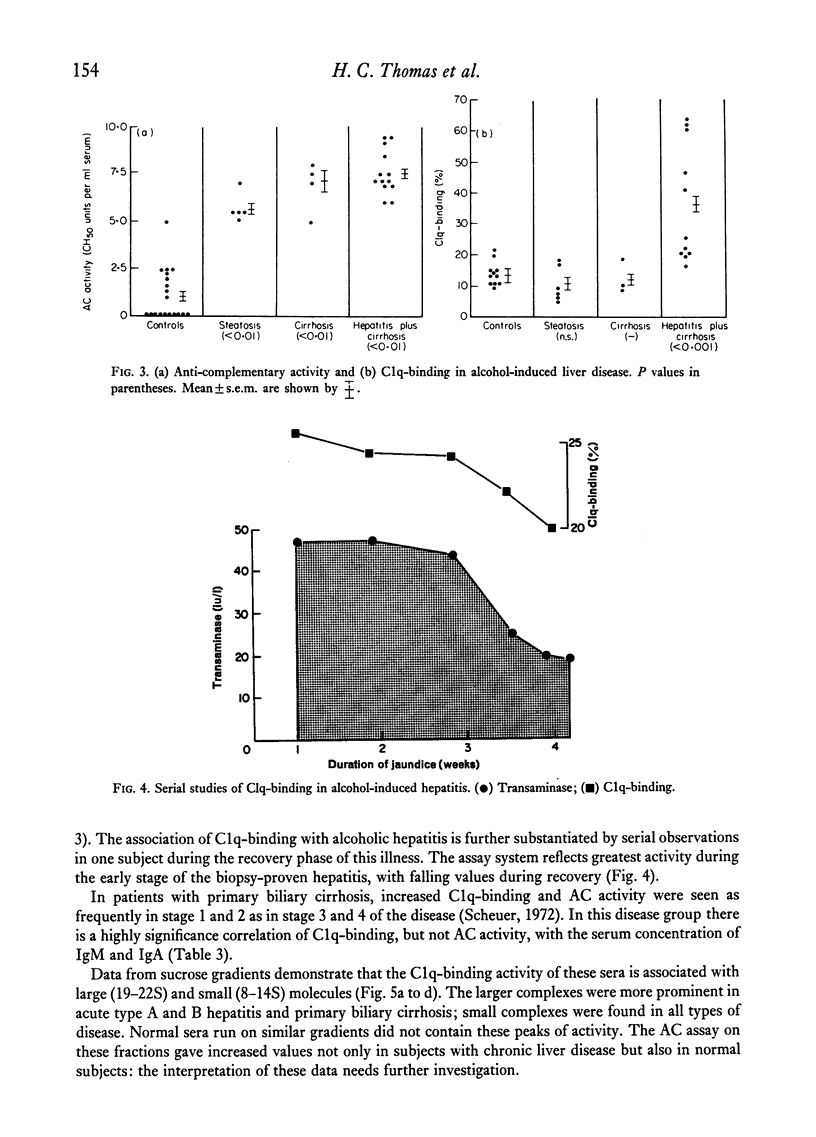
In chronic active hepatitis (HBs-positive and -negative) and in alcohol-induced disease there is a significant correlation between C1q-binding and the severity of hepatitis. C1q-binding and AC activity were also increased in primary biliary cirrhosis. Density gradient studies indicate that the C1q-binding activity in these subjects lies in the 8–14S and >19S particle-containing fractions.
These findings suggest the presence of immune complexes in patients with acute and chronic liver disease. In some cases the complexes may contained hepatitis viral antigens, but in alcohol-induced and autoimmune disease other types of complex formation must exist. The accumulation of large and small complexes in subjects with liver disease may be a reflection of an impaired function of the mononuclear phagocytes in these diseases. The potential of these complexes to activate complement will determine their pathological importance, and in this respect those found in primary biliary cirrhosis may have special significance.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alper C. A., Rosen F. S., Lachmann P. J. Inactivator of the third component of complement as an inhibitor in the properdin pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2910–2913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augener W., Grey H. M., Cooper N. R., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The reaction of monomeric and aggregated immunoglobulins with C1. Immunochemistry. 1971 Nov;8(11):1011–1020. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90489-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eleftheriou N., Thomas H. C., Heathcote J., Sherlock S. Incidence and clinical significance of e antigen and antibody in acute and chronic liver disease. Lancet. 1975 Dec 13;2(7946):1171–1173. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92657-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funding L., Steensgaard J. Determination of the sedimentation coefficients of D-glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase from normal and deficient human erythrocytes by s-zonal ultracentrifugation. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1971 Dec;28(4):445–452. doi: 10.3109/00365517109095722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigli I., Ruddy S., Austen K. F. The stoichiometric measurement of the serum inhibition of the first component of complement by the inhibition of immune hemolysis. J Immunol. 1968 Jun;100(6):1154–1164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. H., Mowbray J. F., Porter K. A. Detection of circulating immune complexes in pathological human sera. Lancet. 1975 Apr 5;1(7910):762–765. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92433-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosmidis J. C., Leader-Williams L. K. Complement levels in acute infectious hepatitis and serum hepatitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 May;11(1):31–35. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannik M., Arend M. P., Hall A. P., Gilliland B. C. Studies on antigen-antibody complexes. I. Elimination of soluble complexes from rabbit circulation. J Exp Med. 1971 Apr 1;133(4):713–739. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.4.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nydegger U. E., Lambert P. H., Gerber H., Miescher P. A. Circulating immune complexes in the serum in systemic lupus erythematosus and in carriers of hepatitis B antigen. Quantitation by binding to radiolabeled C1q. J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;54(2):297–309. doi: 10.1172/JCI107765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paronetto F., Schaffner F., Popper H. Antibodies to cytoplasmic antigens in primary biliary cirrhosis and chronic active hepatitis. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Jun;69(6):979–988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter B. J., Elias E., Jones E. A. Hypercatabolism of the third component of complement in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Sep;88(3):427–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince A. M., Trepo C. Role of immune complexes involving SH antigen in pathogenesis of chronic active hepatitis and polyarteritis nodosa. Lancet. 1971 Jun 26;1(7713):1309–1312. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91883-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B., Lowe D. M., Porter R. R. Isolation and characterization of C1q, a subcomponent of the first component of complement, from human and rabbit sera. Biochem J. 1972 Dec;130(3):749–763. doi: 10.1042/bj1300749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheuer P. Primary biliary cirrhosis. Proc R Soc Med. 1967 Dec;60(12):1257–1260. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector W. G., Heesom N. The production of granulomata by antigen-antibody complexes. J Pathol. 1969 May;98(1):31–39. doi: 10.1002/path.1710980105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas H. C., McSween R. N., White R. G. Role of the liver in controlling the immunogenicity of commensal bacteria in the gut. Lancet. 1973 Jun 9;1(7815):1288–1291. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91300-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas H. C., Vaez-Zadeh F. A homeostatic mechanism for the removal of antigen from the portal circulation. Immunology. 1974 Feb;26(2):375–382. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. A., Carter R., Stokes R. P., Geddes A. M., Goodall J. A. Serum immunoglobulins, complement component levels and autoantibodies in liver disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Jul;14(3):335–346. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wands J. R., Alpert E., Isselbacher K. J. Arthritis associated with chronic active hepatitis: complement activation and characterization of circulating immune complexes. Gastroenterology. 1975 Dec;69(6):1286–1291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wands J. R., Mann E., Alpert E., Isselbacher K. J. The pathogenesis of arthritis associated with acute hepatitis-B surface antigen-positive hepatitis. Complement activation and characterization of circulating immune complexes. J Clin Invest. 1975 May;55(5):930–936. doi: 10.1172/JCI108022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubler R. H., Lange G., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. Detection of immune complexes in unheated sera by modified 125I-Clq binding test. Effect of heating on the binding of Clq by immune complexes and application of the test to systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):232–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


