Abstract
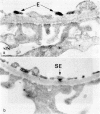
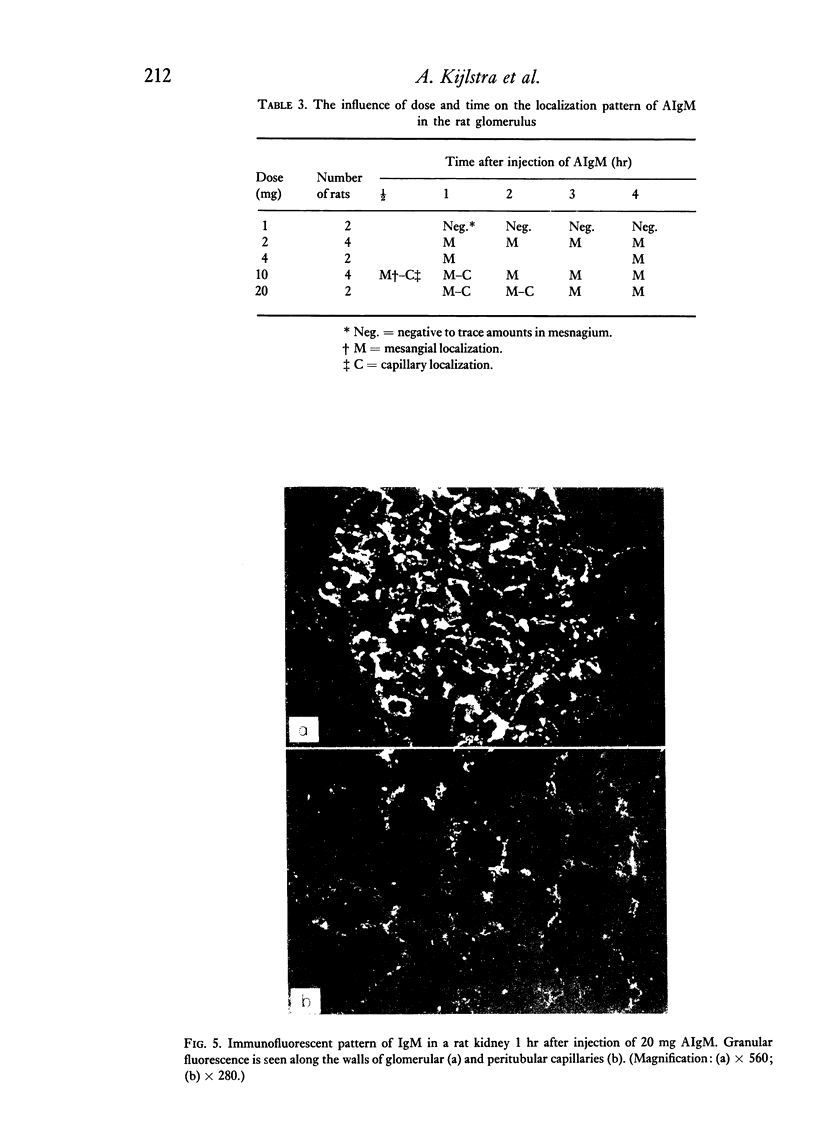
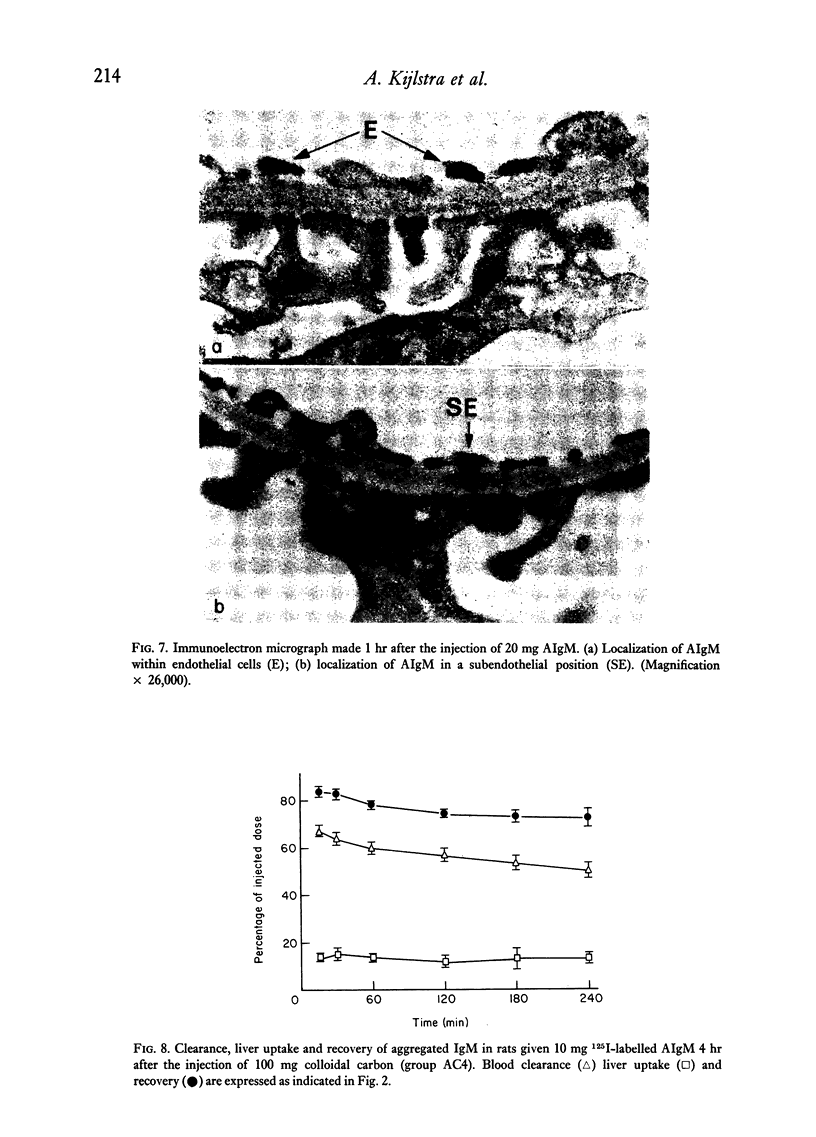
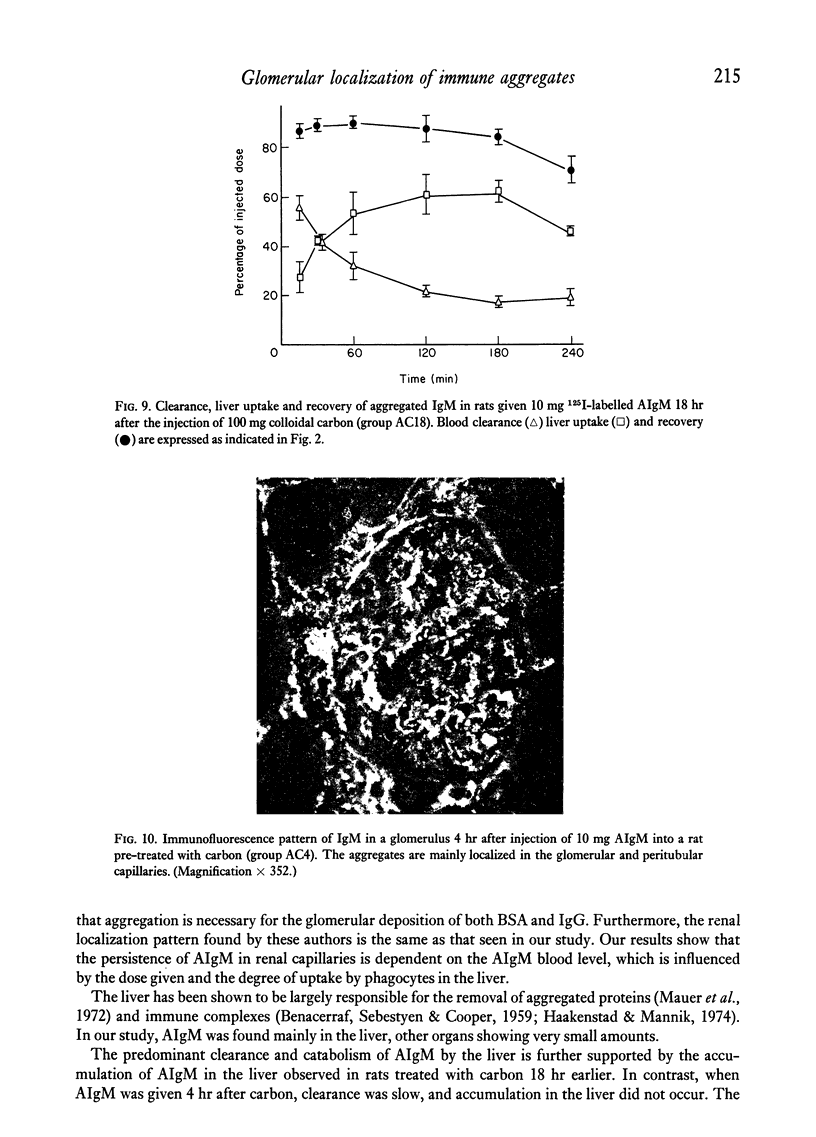
The blood clearance and hepatic localization of aggregated human IgM (AIgM) were studied in relation to the glomerular localization patterns in rats. AIgM was cleared rapidly from the circulation by sinusoidal cells in the liver, monomeric IgM (MIgM) was cleared less rapidly. Localization of AIgM within the glomerulus was dependent on the level in the blood. Low doses led only to a mesangial localization, whereas high doeses resulted in a localization along the capillary walls. Immunoelectron microscopy showed that in the glomerular capillaries the AIgM was localized within endothelial cells or subendothelially, and did not occur within the glomerular basement membrane. Inhibition of the hepatic uptake of AIgM by colloidal carbon resulted in increased levels of circulating AIgM and prolonged the deposition of AIgM in the glomerular capillaries.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDRES G. A., SEEGAL B. C., HSU K. C., ROTHENBERG M. S., CHAPEAU M. L. Electron microscopic studies of experimental nephritis with ferritin-conjugated antibody. Localization of antigen-antibody complexes in rabbit glomeruli following repeated injections of bovine serum albumin. J Exp Med. 1963 Apr 1;117:691–704. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.4.691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENACERRAF B., SEBESTYEN M., COOPER N. S. The clearance of antigen antibody complexes from the blood by the reticuloendothelial system. J Immunol. 1959 Feb;82(2):131–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIOZZI G., BENACERRAF B., HALPERN B. N. Quantitative study of the granulopectic activity of the reticulo-endothelial system. II. A study of the kinetics of the R. E. S. in relation to the dose of carbon injected; relationship between the weight of the organs and their activity. Br J Exp Pathol. 1953 Aug;34(4):441–457. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer A. S., Theofilopoulos A. N., Eisenberg R., Dixon F. J., Guze L. B. Circulating immune complexes in infective endocarditis. N Engl J Med. 1976 Dec 30;295(27):1500–1505. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197612302952703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste J., Henson P. M., Cochrane C. G. Leukocyte-dependent histamine release from rabbit platelets. The role of IgE, basophils, and a platelet-activating factor. J Exp Med. 1972 Dec 1;136(6):1356–1377. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.6.1356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G., Hawkins D. Studies on circulating immune complexes. 3. Factors governing the ability of circulating complexes to localize in blood vessels. J Exp Med. 1968 Jan 1;127(1):137–154. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.1.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G., Koffler D. Immune complex disease in experimental animals and man. Adv Immunol. 1973;16(0):185–264. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60298-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elema J. D., Hoyer J. R., Vernier R. L. The glomerular mesangium: uptake and transport of intravenously injected colloidal carbon in rats. Kidney Int. 1976 May;9(5):395–406. doi: 10.1038/ki.1976.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford P. M. The effect of manipulation of reticuloendothelial system activity on glomerular deposition of aggregated protein and immune complexes in two different strains of mice. Br J Exp Pathol. 1975 Dec;56(6):523–529. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haakenstad A. O., Mannik M. Saturation of the reticuloendothelial system with soluble immune complexes. J Immunol. 1974 May;112(5):1939–1948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haakenstad A. O., Mannik M. The disappearance kinetics of soluble immune complexes prepared with reduced and alkylated antibodies and with intact antibodies in mice. Lab Invest. 1976 Sep;35(3):283–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haakenstad A. O., Striker G. E., Mannik M. The glomerular deposition of soluble immune complexes prepared with reduced and alkylated antibodies and with intact antibodies in mice. Lab Invest. 1976 Sep;35(3):293–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kniker W. T., Cochrane C. G. The localization of circulating immune complexes in experimental serum sickness. The role of vasoactive amines and hydrodynamic forces. J Exp Med. 1968 Jan 1;127(1):119–136. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightfoot R. W., Jr, Drusin R. E., Christian C. L. Properties of soluble immune complexes. J Immunol. 1970 Dec;105(6):1493–1500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCLUSKEY R. T., BENACERRAF B., POTTER J. L., MILLER F. The pathologic effects of intravenously administered soluble antigen-antibody complexes. I. Passive serum sickness in mice. J Exp Med. 1960 Feb 1;111:181–194. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.2.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauer S. M., Fish A. J., Blau E. B., Michael A. F. The glomerular mesangium. I. Kinetic studies of macromolecular uptake in normal and nephrotic rats. J Clin Invest. 1972 May;51(5):1092–1101. doi: 10.1172/JCI106901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael A. F., Fish A. J., Good R. A. Glomerular localization and transport of aggregated proteins in mice. Lab Invest. 1967 Jul;17(1):14–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A. G., Steward M. W. Macrophage clearance function and immune complex disease in New Zealand Black/White F1 hybrid mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Oct;26(1):133–136. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normann S. J. Function of the Reticuloendothelial System IV. Evidence for Two Types of Particle-Induced Reticuloendothelial Paralysis. Infect Immun. 1970 Apr;1(4):327–333. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.4.327-333.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normann S. J. Kinetics of phagocytosis. II. Analysis of in vivo clearance with demonstration of competitive inhibition between similar and dissimilar foreign particles. Lab Invest. 1974 Aug;31(2):161–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okumura K., Kondo Y., Tada T. Studies on passive serum sickness. I. The glomerular fine structure of serum sickness nephritis induced by preformed antigen-antibody complexes in the mouse. Lab Invest. 1971 May;24(5):383–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHARPE L. M., CULBRETH G. G., KLEIN J. R. Blood and packed cell volume of the adult rat as measured by tagged cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1950 Aug;74(4):681–685. doi: 10.3181/00379727-74-18014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinomiya T., Koyama J. In vitro uptake and digestion of immune complexes containing guinea-pig IgG1 and IgG2 antibodies by macrophages. Immunology. 1976 Feb;30(2):267–275. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vriesman P. J., Feldman J. D. Rat M immunoglobulin: isolation and some biological characteristics. Immunochemistry. 1972 May;9(5):525–534. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90062-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardle E. N. Reticuloendothelial clearance studies in the course of horse serum induced nephritis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1974 Apr;55(2):149–152. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]