Abstract
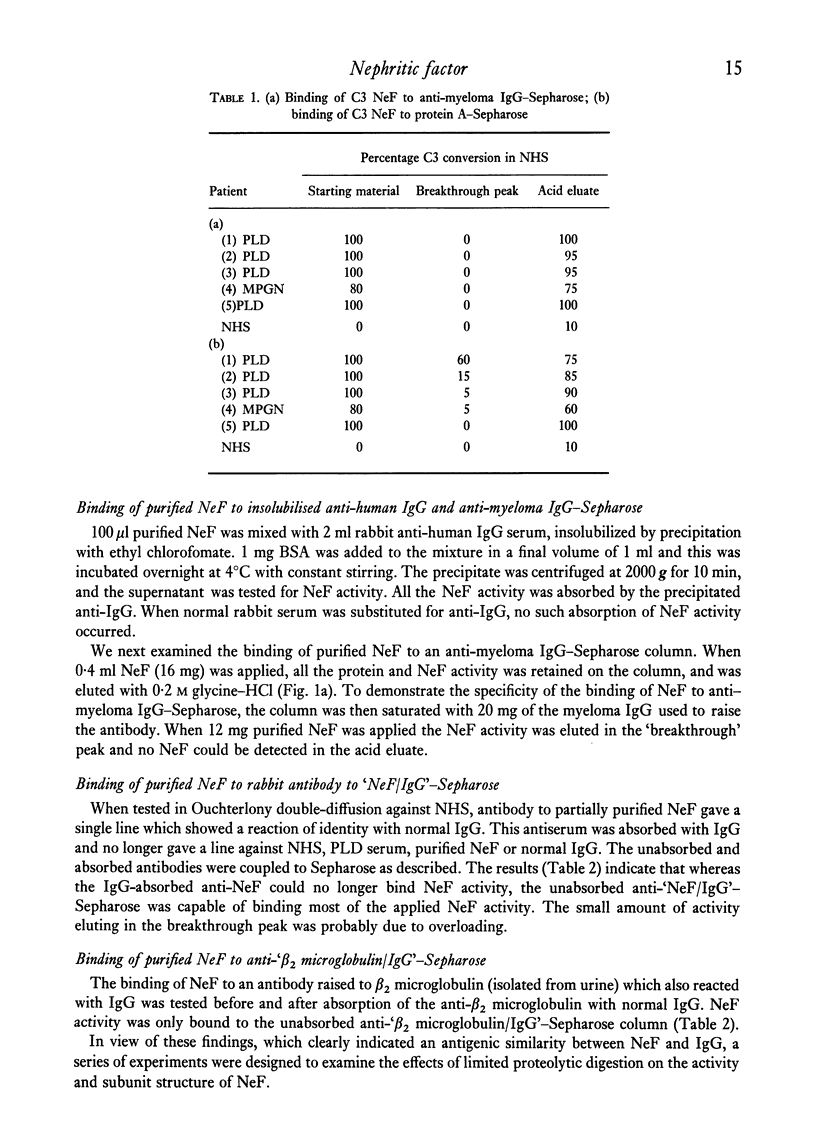
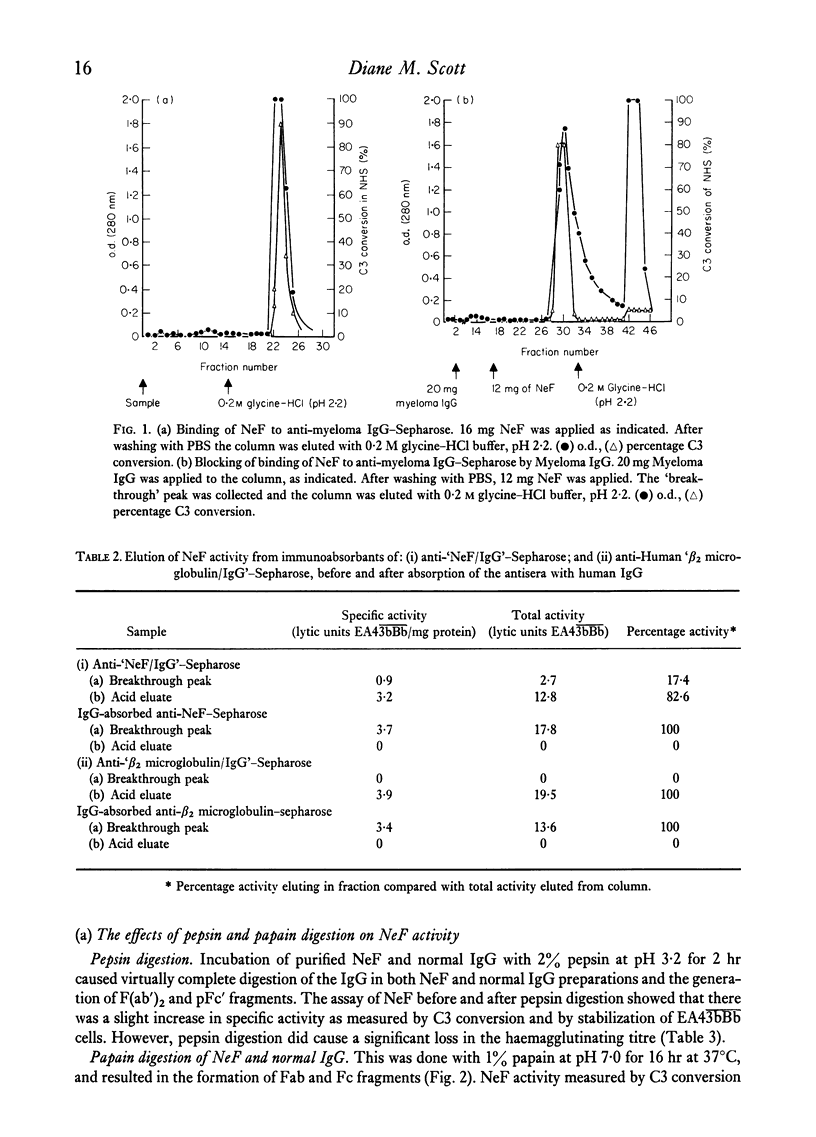
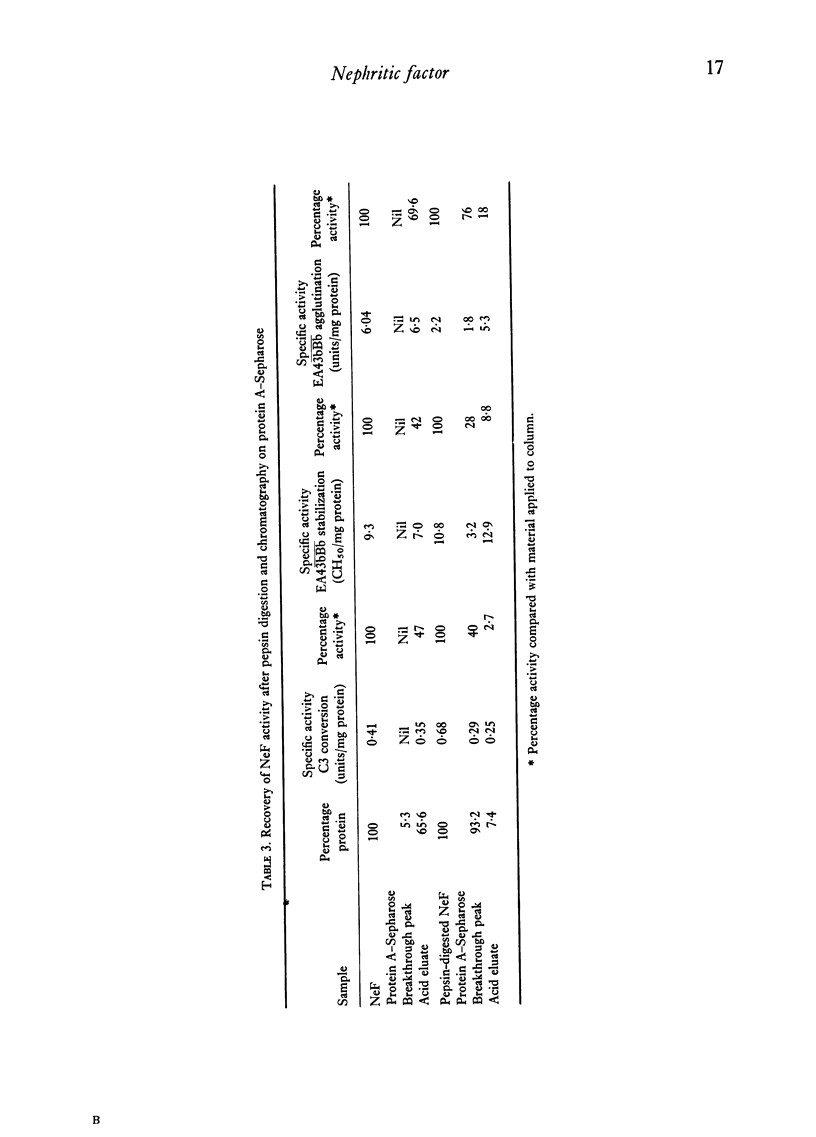
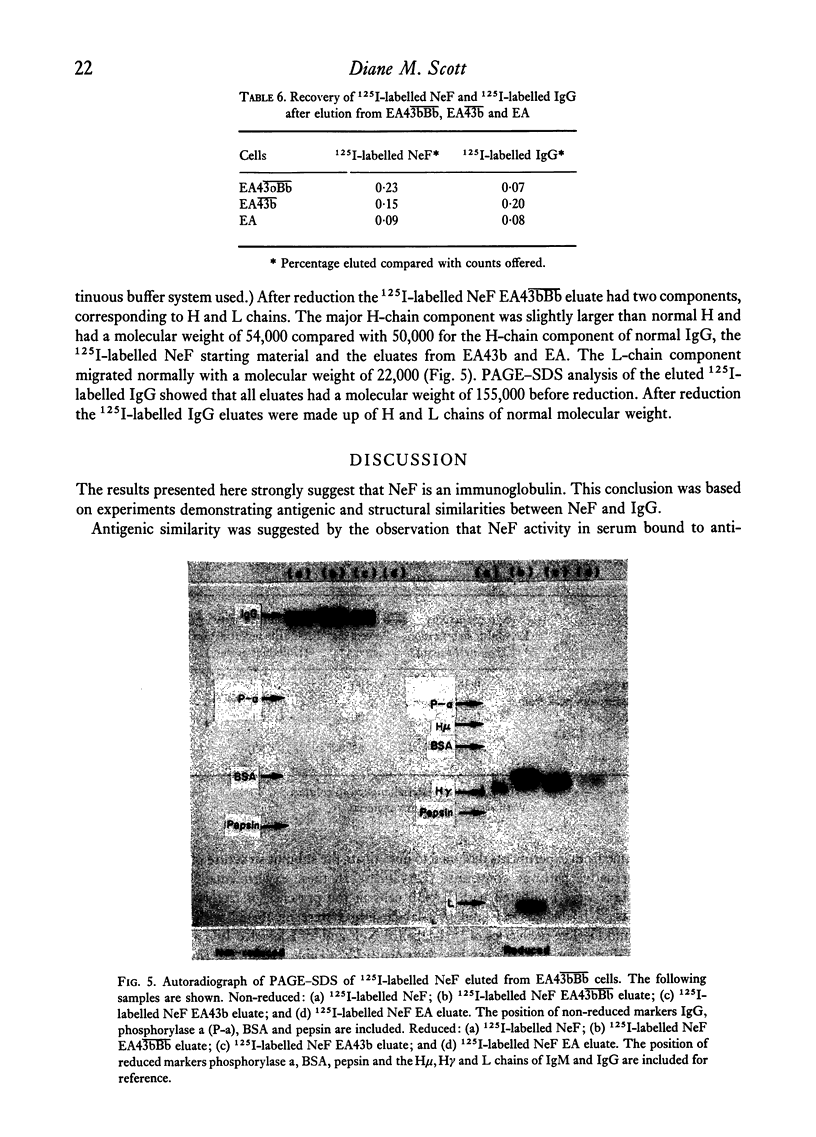
NeF was shown to be antigenically and structurally similar to IgG by the following experiments: (1) NeF activity in serum was absorbed by and, under acid conditions, could be eluted from (a) anti-myeloma IgG antibody coupled to Sepharose and (b) protein A-Sepharose. (2) Purified NeF could bind to anit-myeloma IgG-Sepharose and could be eluted with acid, and this binding was blocked by myeloma IgG. (3) An antibody to beta2, microglobulin, showing strong cross-reactivity with normal IgG, bound NeF activity before, but not after, absorption of the antiserum with IgG. (4) Sepharose-coupled antibodies to NeF could bind activity which was recovered in the acid eluate. This binding capacity was lost after absorption of the antibody with normal and myeloma IgG. (5) Structural similarity was demonstrated by pepsin and papain digestion, which resulted in NeF activity eluting with F(ab')2 and Fab fragments from protein A-Sepharose and Sephadex G-150. (6) Autoradiography of PAGE-SDS of 125I-labelled NeF eluted from EA43bBb cells showed that NeF had a larger H chain than normal IgG, suggesting that NeF might be an abnormal IgG molecule.
Full text
PDF


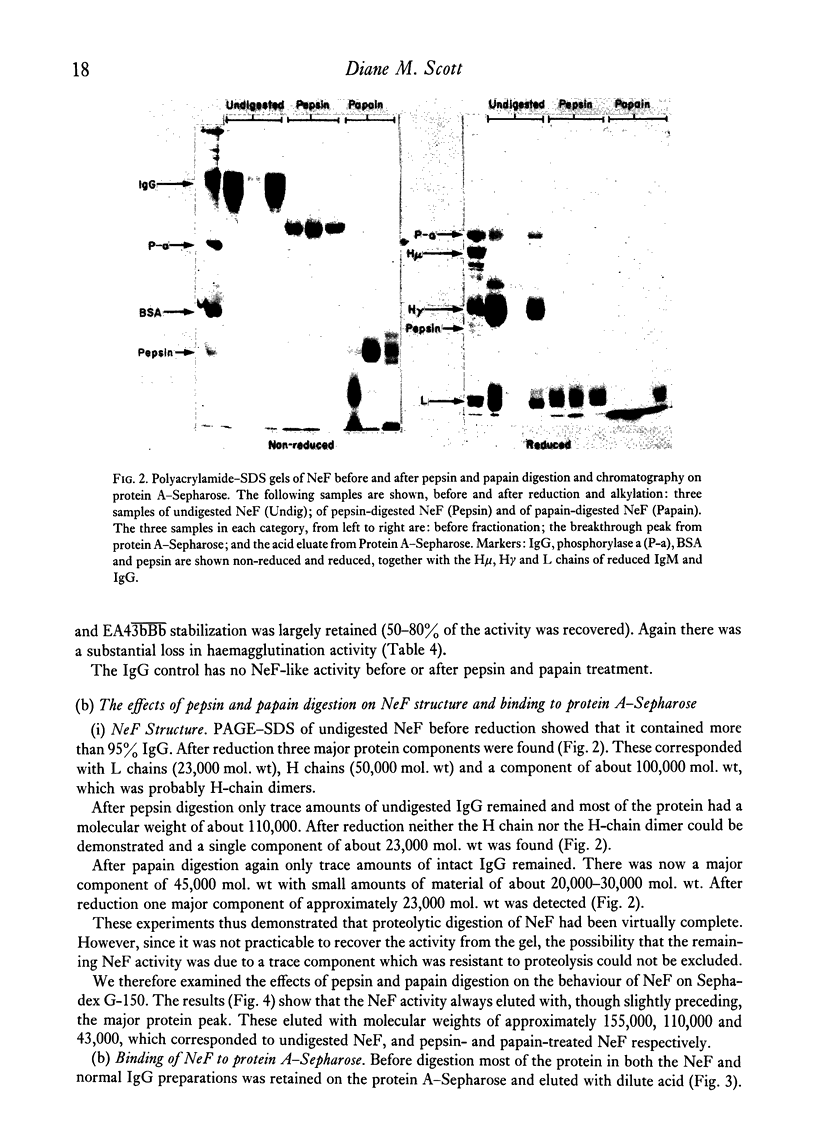
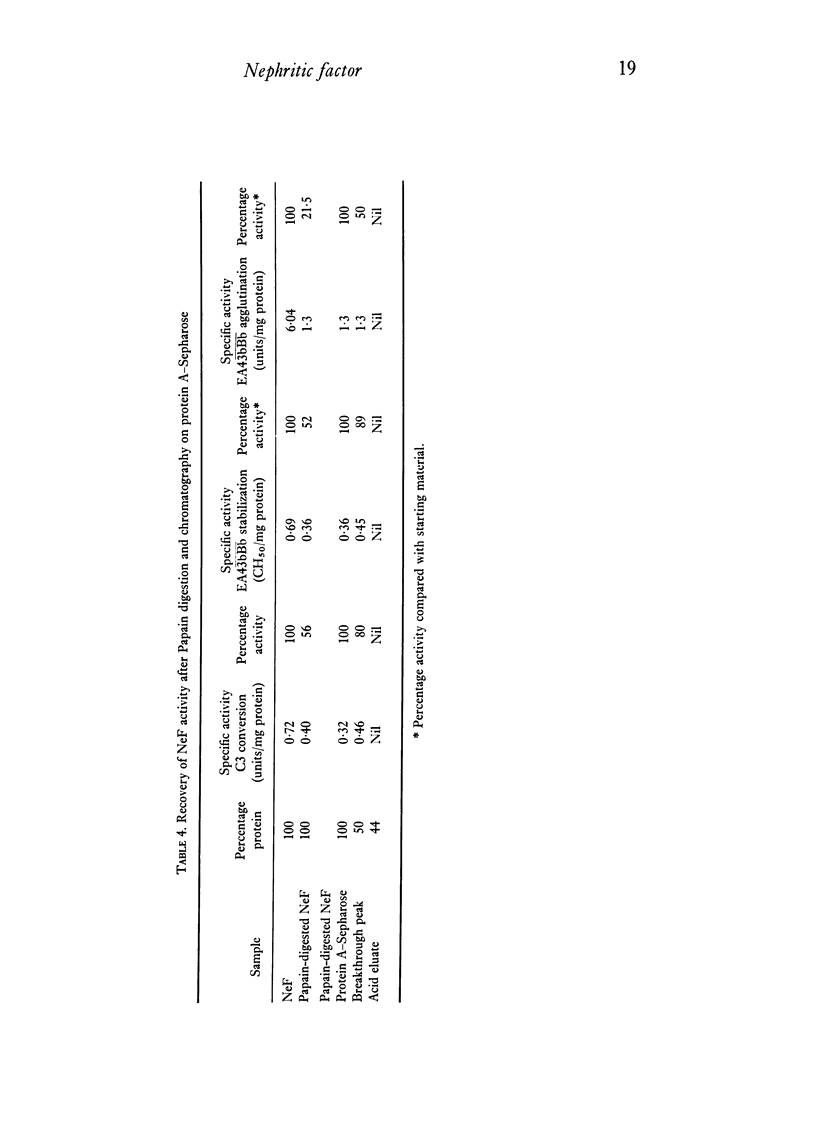
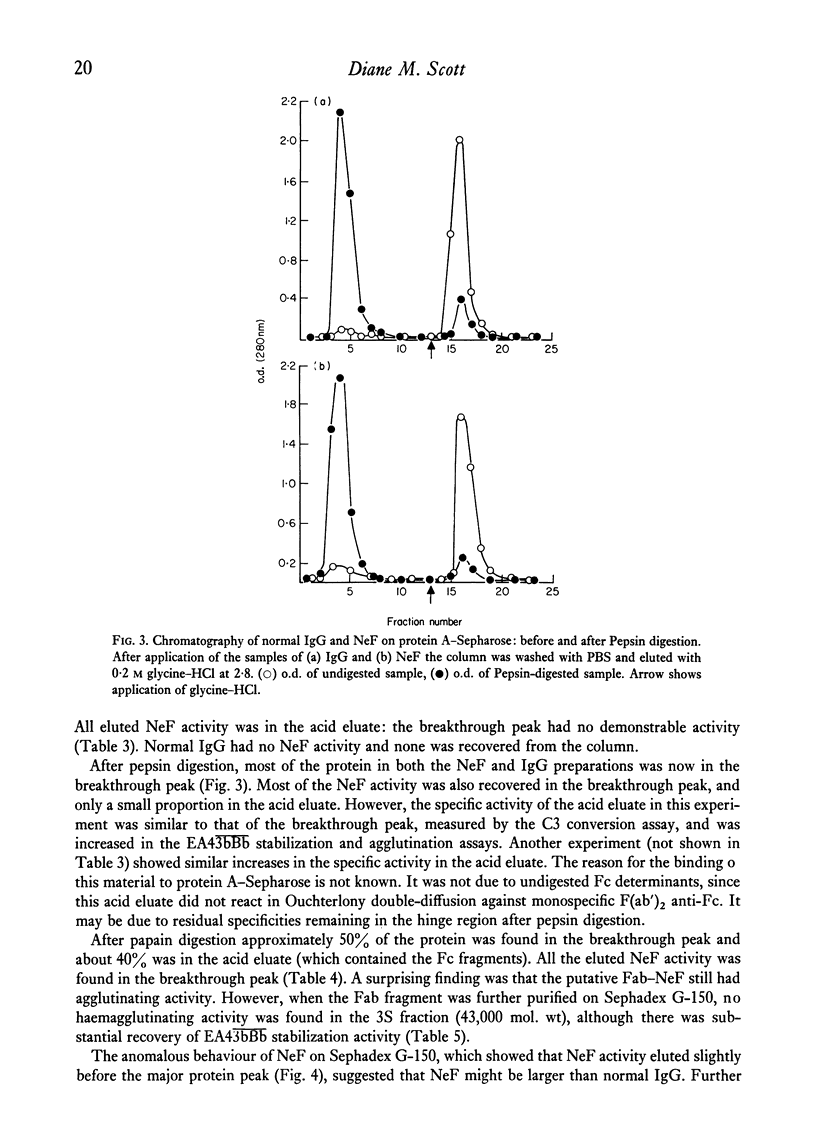
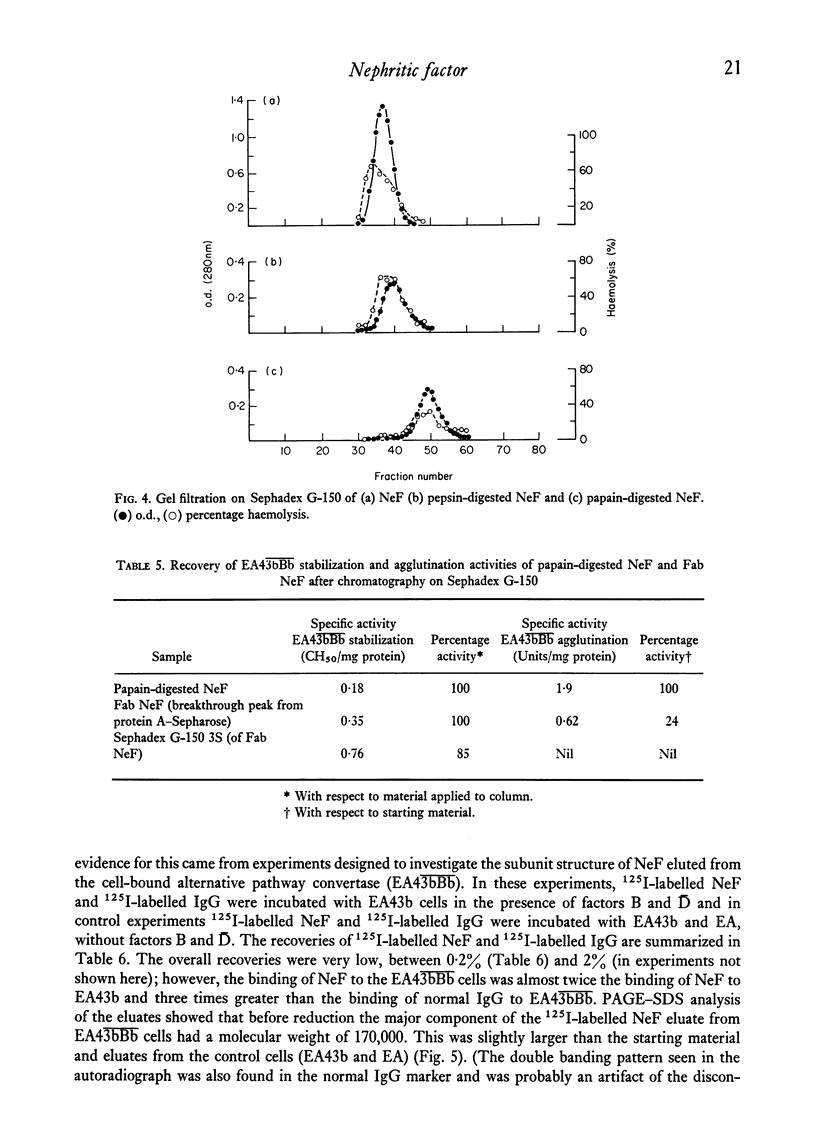


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amos N., Sissons J. G., Girard J. F., Lachmann P. J., Peters D. K. The cofactors required by C3 nephritic factor to generate a C3 convertase in vitro. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Jun;24(3):474–482. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avrameas S., Ternynck T. Biologically active water-insoluble protein polymers. I. Their use for isolation of antigens and antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 10;242(7):1651–1659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P., Wilchek M., Anfinsen C. B. Selective enzyme purification by affinity chromatography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):636–643. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daha M. R., Fearon D. T., Austen K. F. C3 nephritic factor (C3NeF): stabilization of fluid phase and cell-bound alternative pathway convertase. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis A. E., 3rd, Arnaout M. A., Alper C. A., Rosen F. S. Transfer of C3 nephritic factor from mother to fetus. Is C3 nephritic factor IgG? N Engl J Med. 1977 Jul 21;297(3):144–145. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197707212970306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heusser C., Boesman M., Nordin J. H., Isliker H. Effect of chemical and enzymatic radioiodination on in vitro human Clq activities. J Immunol. 1973 Mar;110(3):820–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURELL C. B. ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY CROSSED ELECTROPHORESIS. Anal Biochem. 1965 Feb;10:358–361. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J. The purification of specific antibody as F(ab')2 by the pepsin digestion of antigen-antibody precipitates, and its application to immunoglobulin and complement antigens. Immunochemistry. 1971 Jan;8(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90423-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison M., Bayse G. S., Webster R. G. Use of lactoperoxidase catalyzed iodination in immunochemical studies. Immunochemistry. 1971 Mar;8(3):289–297. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90484-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER R. R. The hydrolysis of rabbit y-globulin and antibodies with crystalline papain. Biochem J. 1959 Sep;73:119–126. doi: 10.1042/bj0730119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters D. K., Williams D. G. Complement and the kidney. Proc R Soc Med. 1972 Dec;65(12):1095–1098. doi: 10.1177/003591577206501221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B., Lowe D. M., Porter R. R. Isolation and characterization of C1q, a subcomponent of the first component of complement, from human and rabbit sera. Biochem J. 1972 Dec;130(3):749–763. doi: 10.1042/bj1300749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber R. D., Götze O., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Alternative pathway of complement: demonstration and characterization of initiating factor and its properdin-independent function. J Exp Med. 1976 Oct 1;144(4):1062–1075. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.4.1062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber R. D., Götze O., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Nephritic factor: its structure and function and its relationship to initiating factor of the alternative pathway. Scand J Immunol. 1976;5(6-7):705–713. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1976.tb03020.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sissons J. G., West R. J., Fallows J., Williams D. G., Boucher B. J., Amos N., Peters D. K. The complement abnormalities of lipodystrophy. N Engl J Med. 1976 Feb 26;294(9):461–465. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197602262940902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitzer R. E., Vallota E. H., Forristal J., Sudora E., Stitzel A., Davis N. C., West C. D. Serum C'3 lytic system in patients with glomerulonephritis. Science. 1969 Apr 25;164(3878):436–437. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3878.436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. A. C3 inactivating factor in the serum of a patient with chronic hypocomplementaemic proliferative glomerulo-nephritis. Immunology. 1972 Jan;22(1):147–158. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallota E. H., Forristal J., Spitzer R. E., Davis N. C., West C. D. Characteristics of a non-complement-dependent C3-reactive complex formed form factors in nephritic and normal serum. J Exp Med. 1970 Jun 1;131(6):1306–1324. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.6.1306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallota E. H., Götze O., Spiegelberg H. L., Forristal J., West C. D., Müller-Eberhard H. J. A serum factor in chronic hypocomplementemic hephritis distinct from immunoglobulins and activating the alternate pathway of complement. J Exp Med. 1974 May 1;139(5):1249–1261. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.5.1249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiler J. M., Daha M. R., Austen K. F., Fearon D. T. Control of the amplification convertase of complement by the plasma protein beta1H. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3268–3272. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whaley K., Ruddy S. Modulation of the alternative complement pathways by beta 1 H globulin. J Exp Med. 1976 Nov 2;144(5):1147–1163. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.5.1147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. G., Lachmann P. J., Charlesworth J. A., Peters D. K. Role of C3b in the breakdown of C3 in hypocomplementaemic mesangiocapillary glomerulonephritis. Lancet. 1973 Mar 3;1(7801):447–449. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91877-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]