Abstract
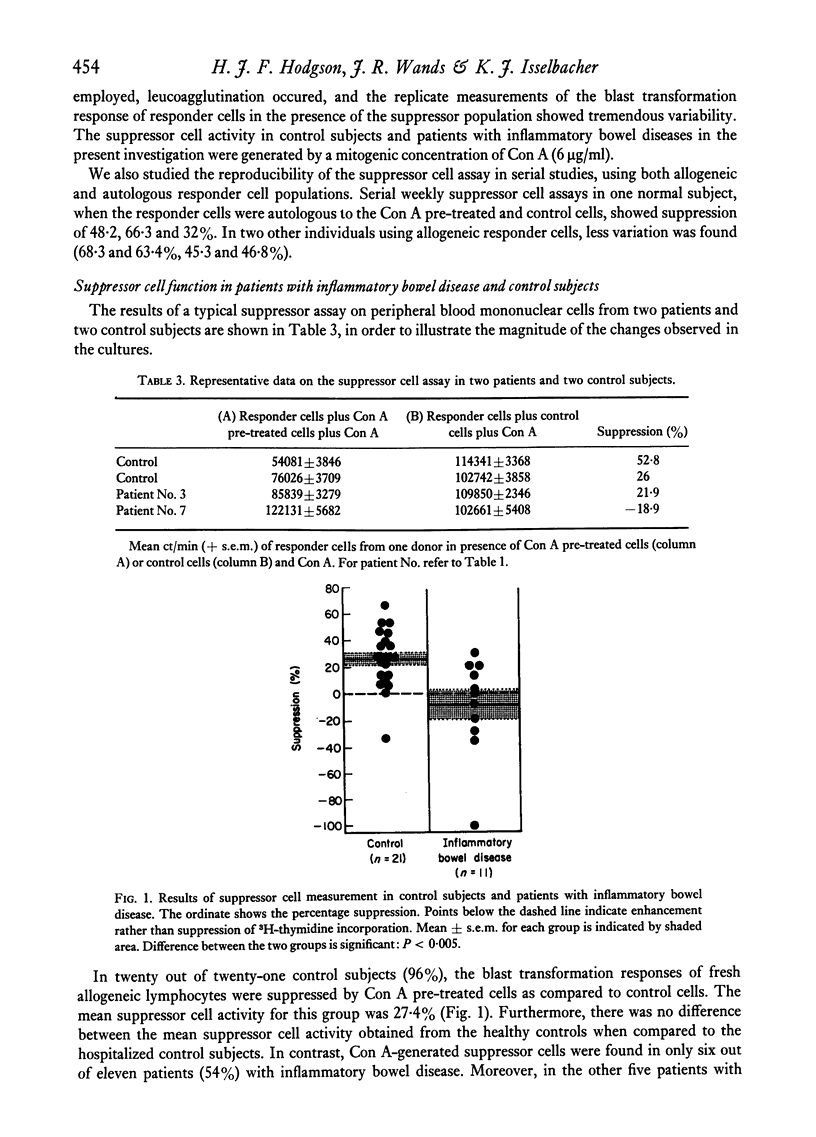
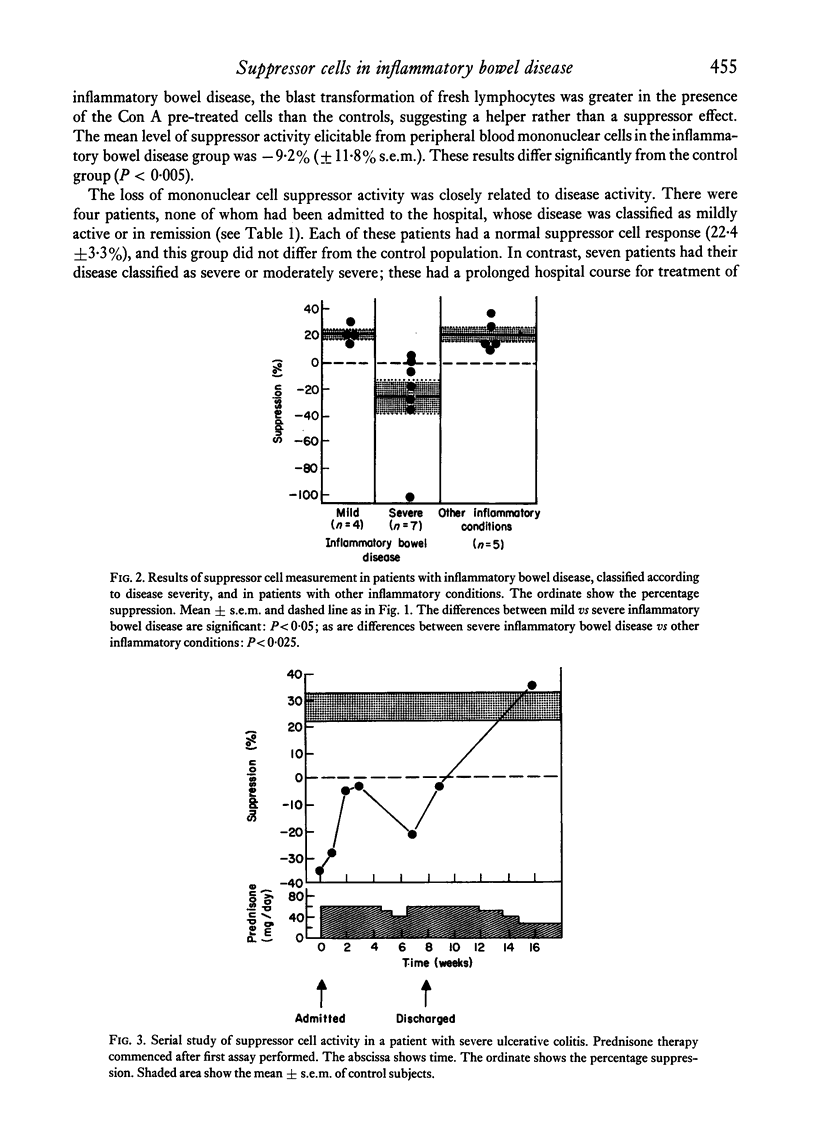
Studies were performed on eleven patients with inflammatory bowel disease to determine if there was an alteration in concanavalin A (Con A) induced suppressor cell activity. Similar investigations were also performed on twenty-one control subjects and five patients with other inflammatory conditions. Supressor cells were generated by pre-incubation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells with a mitogenic concentration of Con A, followed by treatment with mitomycin C and alpha-methyl mannoside. Under these conditions, cells obtained from normal individuals are then capable of suppressing the Con A-stimulated blast transformation responses of fresh allogeneic lymphocytes in new cultures. We found that in twenty out of twenty-one control subjects, and all five patients with other inflammatory disorders, Con A-stimulated suppressor cell activity was demonstrable. Four patients with inflammatory bowel disease, whose disease was mildly active or was in clinical remission, had elicitable suppressor cell activity which fell within the normal range. In contrast, suppressor cell activity was markedly diminished or absent in seven patients with severe and active inflammatory bowel disease. These studies suggest that an alternation in Con A-stimulated suppressor cells exists in patients with active inflammatory bowel disease, which may contribute, in part, to the persistent inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aas J., Huizenga A., Newcomer A. D., Shorter R. G. Inflammatory bowel disease: lymphocytic responses to nonspecific stimulation in vitro. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1972;7(4):299–303. doi: 10.3109/00365527209180746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abdou N. I., Sagawa A., Pascual E., Hebert J., Sadeghee S. Suppressor T-cell abnormality in idiopathic systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1976 Sep;6(2):192–199. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(76)90110-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asquith P., Kraft S. C., Rothberg R. M. Lymphocyte responses to nonspecific mitogens in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1973 Jul;65(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartnik W., Swarbrick E. T., Williams C. A study of peripheral leucocyte migration in agarose medium in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 1974 Apr;15(4):294–300. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.4.294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. G., Britton S. No evidence for decreased lymphocyte reactivity in Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1974 Nov;67(5):926–932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnihan B., Jasin H. E. Suppressor function of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in normal individuals and in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jan;59(1):106–116. doi: 10.1172/JCI108607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broder S., Humphrey R., Durm M., Blackman M., Meade B., Goldman C., Strober W., Waldmann T. Impaired synthesis of polyclonal (non-paraprotein) immunoglobulins by circulating lymphocytes from patients with multiple myeloma Role of suppressor cells. N Engl J Med. 1975 Oct 30;293(18):887–892. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197510302931801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. M., Taub R. N., Present D. H., Janowitz H. D. Short-term lymphocyte cultures in regional enteritis. Lancet. 1970 May 23;1(7656):1112–1112. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)92776-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull D. M., Ignaczak T. F. Enterobacterial common antigen-induced lymphocyte reactivity in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1973 Jan;64(1):43–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cave D. R., Mitchell D. N., Kane S. P., Brooke B. N. Further animal evidence of a transmissible agent in Crohn's disease. Lancet. 1973 Nov 17;2(7838):1120–1122. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90936-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Dombal F. T., Burton I. L., Clamp S. E., Goligher J. C. Short-term course and prognosis of Crohn's disease. Gut. 1974 Jun;15(6):435–443. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.6.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton R. W. Suppressor T cells. Transplant Rev. 1975;26:39–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1975.tb00174.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Dale D. C. The effect of in vivo hydrocortisone on subpopulations of human lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jan;53(1):240–246. doi: 10.1172/JCI107544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink S., Mais R. F. Cell-mediated immune reaction to colon altered by bacteria. Gut. 1968 Dec;9(6):629–632. doi: 10.1136/gut.9.6.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinz C. F., Jr, Perlmann P., Hammarström S. Reactivity in vitro of lymphocytes from patients with ulcerative colitis. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Nov;70(5):752–759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubert C., Delespesse G., Govaerts A. Concanavalin A-activated suppressor cells in normal human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Oct;26(1):95–98. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt P. S., Trotter S. Lymphoblastic response to autologous colon epithelial cells in ulcerative colitis in vitro. Gut. 1973 Nov;14(11):875–879. doi: 10.1136/gut.14.11.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERLMANN P., BROBERGER O. In vitro studies of ulcerative colitis. II. Cytotoxic action of white blood cells from patients on human fetal colon cells. J Exp Med. 1963 May 1;117:717–733. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.5.717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane T., Green I. Human suppressor T cells induced by concanavalin A: suppressor T cells belong to distinctive T cell subclasses. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):1169–1178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shorter R. G., Cardoza M., Spencer R. J., Huizenga K. A. Further studies on in vitro cytotoxicity of lymphocytes from patients with ulcerative and granulomatous colitis for allogeneic colonic epithelial cells, including the effects of colectomy. Gastroenterology. 1969 Feb;56(2):304–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shorter R. G., Huizenga K. A., Spencer R. J. A working hypothesis for the etiology and pathogenesis of nonspecific inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Dig Dis. 1972 Nov;17(11):1024–1032. doi: 10.1007/BF02239143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shou L., Schwartz S. A., Good R. A. Suppressor cell activity after concanavalin A treatment of lymphocytes from normal donors. J Exp Med. 1976 May 1;143(5):1100–1110. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.5.1100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegal F. P., Siegal M., Good R. A. Suppression of B-cell differentiation by leukocytes from hypogammaglobulinemic patients. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jul;58(1):109–122. doi: 10.1172/JCI108439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefani S., Fink S. Effect of E. coli antigens, tuberculin, and phytohaemagglutinin upon ulcerative colitis lymphocytes. Gut. 1967 Jun;8(3):249–252. doi: 10.1136/gut.8.3.249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stobo J. D., Paul S., Van Scoy R. E., Hermans P. E. Suppressor thymus-derived lymphocytes in fungal infection. J Clin Invest. 1976 Feb;57(2):319–328. doi: 10.1172/JCI108283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stobo J. D., Tomasi T. B., Huizenga K. A., Spencer R. J., Shorter R. G. In vitro studies of inflammatory bowel disease. Surface receptors of the mononuclear cell required to lyse allogeneic colonic epithelial cells. Gastroenterology. 1976 Feb;70(2):171–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland R. G., Husby G., Black W. C., Williams R. C., Jr Peripheral blood and intestinal lymphocyte sub-populations in Crohn's disease. Gut. 1975 Nov;16(11):847–853. doi: 10.1136/gut.16.11.847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRUELOVE S. C., WITTS L. J. Cortisone in ulcerative colitis; final report on a therapeutic trial. Br Med J. 1955 Oct 29;2(4947):1041–1048. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4947.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer W. R., Jr, Charland C., Field C. E. The subpopulations of circulating white blood cells in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1976 Sep;71(3):379–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twomey J. J., Laughter A. H., Farrow S., Douglass C. C. Hodgkin's disease. An immunodepleting and immunosuppressive disorder. J Clin Invest. 1975 Aug;56(2):467–475. doi: 10.1172/JCI108113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A., Durm M., Broder S., Blackman M., Blaese R. M., Strober W. Role of suppressor T cells in pathogenesis of common variable hypogammaglobulinaemia. Lancet. 1974 Sep 14;2(7881):609–613. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91940-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. G., Greaves M. F. Delayed hypersensitivity and lymphocyte transformation in Crohn's disease and proctocolitis. Gut. 1969 May;10(5):414–414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. W., Quigley A., Bolt R. J. Effect of lymphocytes from patients with ulcerative colitis on human adult colon epithelial cells. Gastroenterology. 1966 Dec;51(6):985–993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


