Abstract
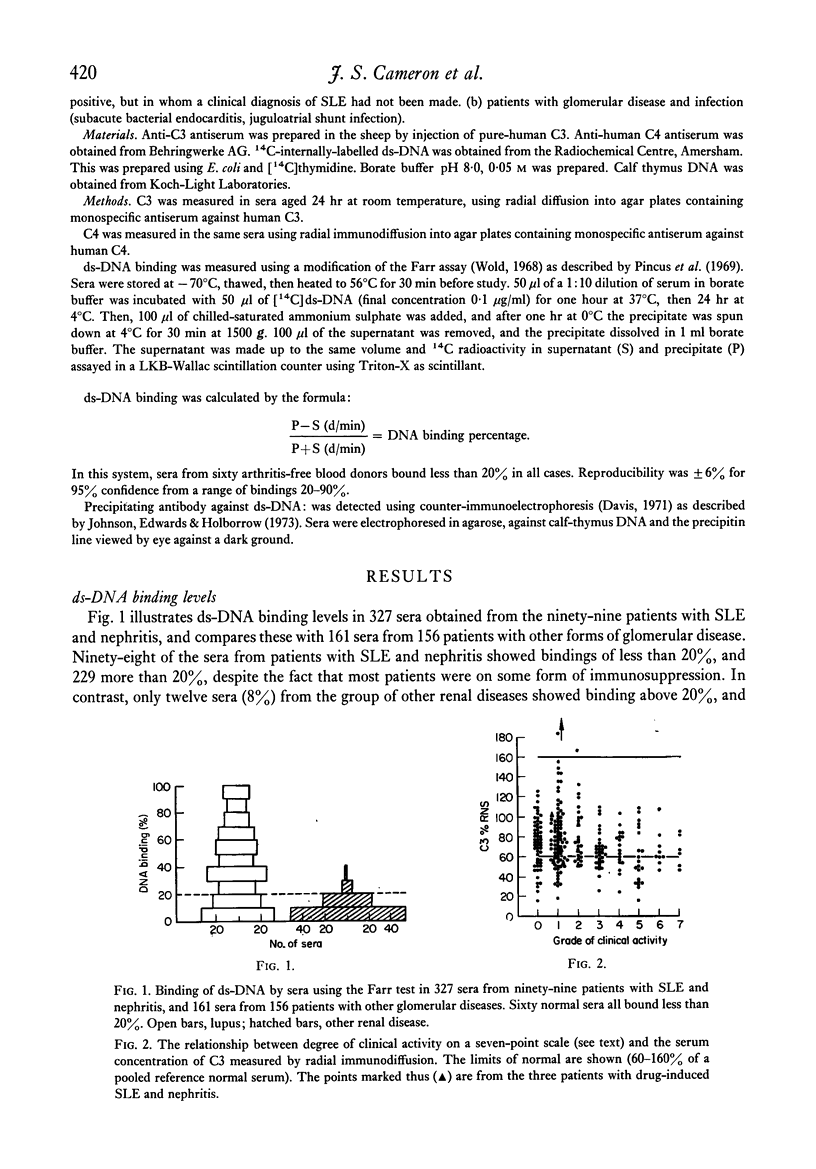
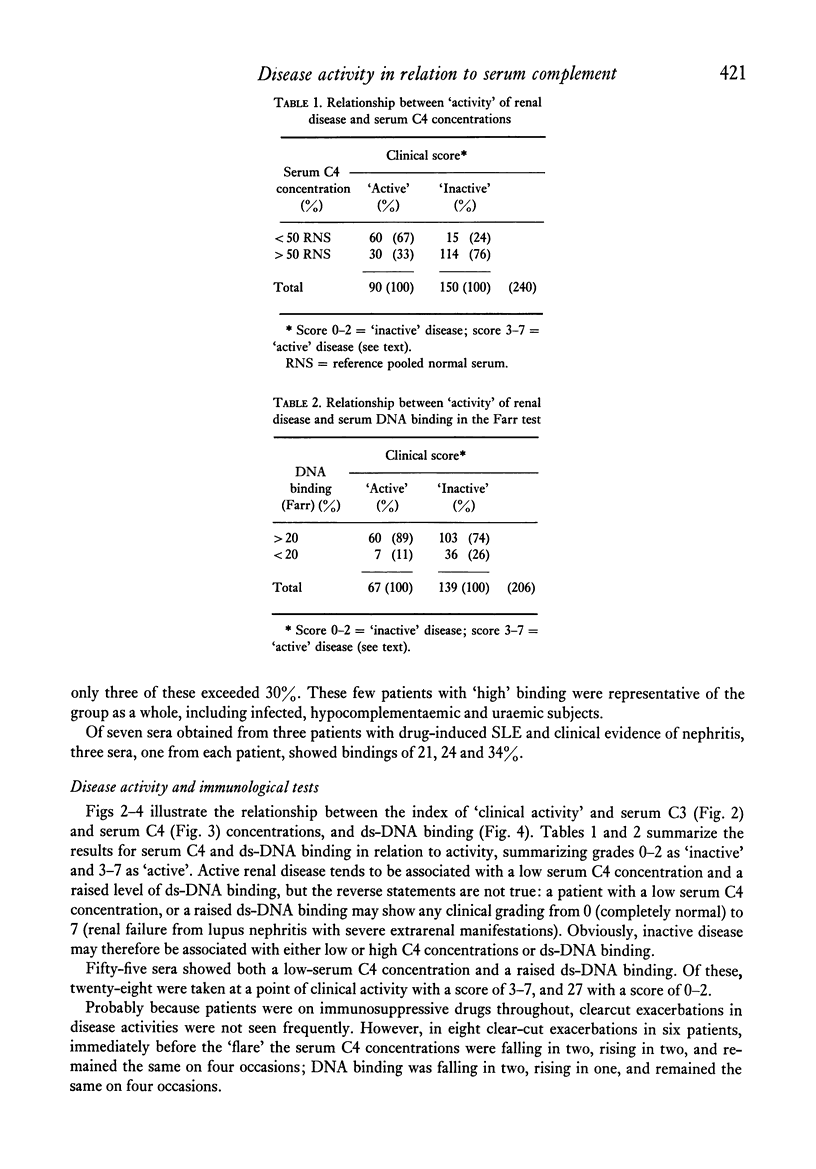
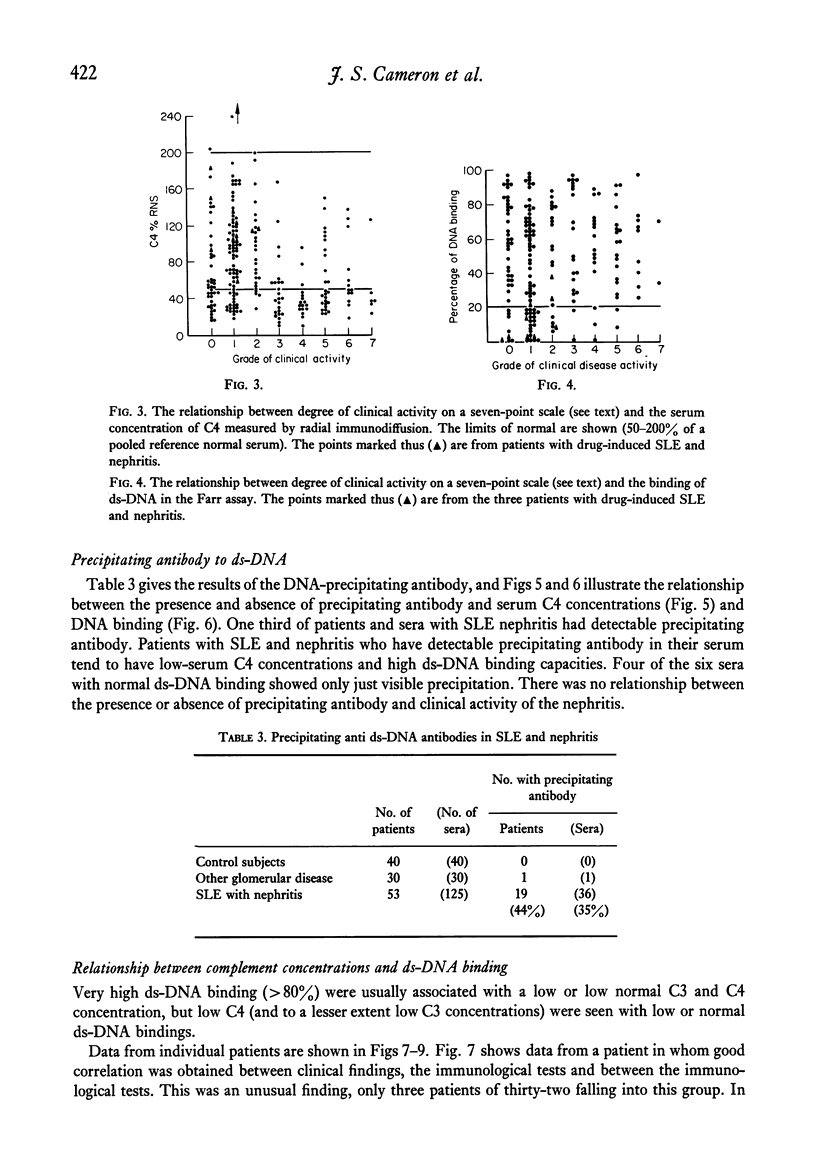
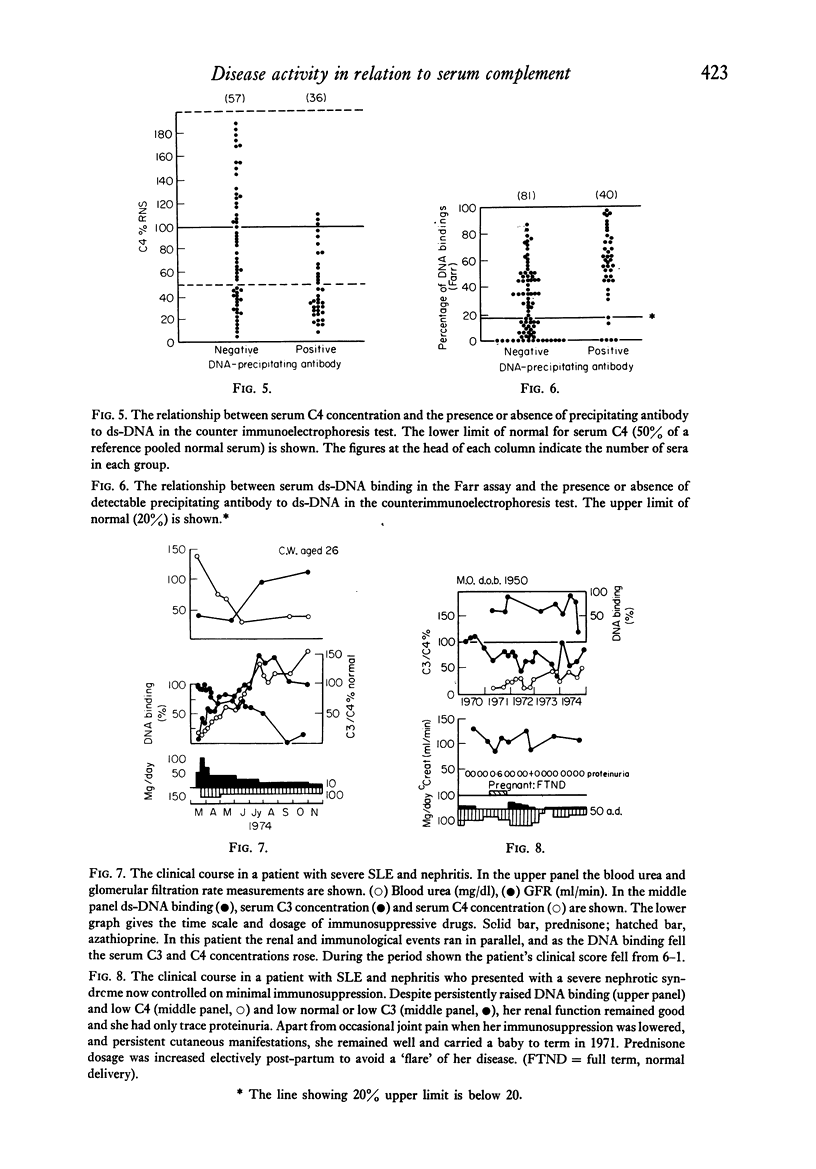
Serum C4 and C3 concentration and binding of double-stranded-DNA (ds-DNA) were measured in sera from ninety-nine patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and clinical evidence of nephritis. C3 and C4 concentrations correlated poorly with ds-DNA binding. In sera from fifty-three patients, precipitating antibody was sought using the counterimmunoelectrophoretic technique. Precipitating antibody was detected on at least one occasion in 44% of the patients, and these sera with precipitating antibody showed higher binding of ds-DNA and lower C4 concentrations than those without precipitating antibody. In thirty-two patients, serial assessments of the activity of the renal disease were made using decline or improvement in glomerular filtration rate, degree of proteinuria, oedema and hypertension as indices of "activity". All patients were receiving immunosuppressive drugs. Active nephritis was rarely found in patients showing, at that time, a normal serum C4 or normal ds-DNA binding; but a raised ds-DNA binding or lowered serum C4 were found in both active and inactive nephritis. There was no correlation of activity with serum concentrations of C3, or the presence or absence of precipitating antibody. We conclude that measurements of serum-complement concentrations and binding of ds-DNA are of most use in the diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus, and that in patients with nephritis and taking immunosuppressive drugs, these tests are of limited use in guiding treatment.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aarden L. A., de Groot E. R., Feltkamp T. E. Immunology of DNA. III. Crithidia luciliae, a simple substrate for the determination of anti-dsDNA with the immunofluorescence technique. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 30;254:505–515. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb29197.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alarcon-Segovia D., Fishbein E., Estrada-Parra S. The heterogeneity of anti-DNA antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus and other diseases. J Rheumatol. 1975 Jun;2(2):172–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alarcón-Segovia D., Fishbein E., Alcalá H., Olguín-Palacios E., Estrada-Parra S. The range and specificity of antinuclear antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Apr;6(4):557–571. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin D. S., Lowenstein J., Rothfield N. F., Gallo G., McCluskey R. T. The clinical course of the proliferative and membranous forms of lupus nephritis. Ann Intern Med. 1970 Dec;73(6):929–942. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-73-6-929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. A., Hughes G. R., Noel G. L., Christian C. L. Character of anti-DNA antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Apr;8(4):551–561. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruchaud A., Chenais F., Fournié G. J., Humair L., Lambert P. H., Mulli J. C., Chatelanat F. Immune complex deposits in systemic lupus erythematosus kidney without histological or functional alterations. Eur J Clin Invest. 1975 Jun 12;5(3):297–309. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1975.tb00458.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker J. L., Klippel J. H., Plotz P. H., Steinberg A. D. Cyclophosphamide or azathioprine in lupus glomerulonephritis. A controlled trial: results at 28 months. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Nov;83(5):606–615. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-83-5-606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsch C., Barnett E. V. The occurrence and nature of precipitating antibodies in anti-DNA sera. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1974 Apr;2(3):310–321. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(74)90049-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds J. P., Johnson G. D., Ansell B. M., Holborow E. J. The value of tests for antibodies to DNA in monitoring the clinical course of SLE. A long-term study using the Farr test and the DNA counterimmunoelectrophoretic method. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Oct;22(1):9–15. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng P. H., Cheah P. S., Lee Y. K. Mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus: a 10-year review. Br Med J. 1973 Dec 29;4(5895):772–774. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5895.772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershwin M. E., Steinberg A. D. Qualitative characteristics of anti-DNA antibodies in lupus nephritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1974 Nov-Dec;17(6):947–954. doi: 10.1002/art.1780170605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn B. H., Kantor O. S., Osterland C. K. Azathioprine plus prednisone compared with prednisone alone in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus. Report of a prospective controlled trial in 24 patients. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Nov;83(5):597–605. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-83-5-597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbeck R. J., Bardana E. J., Kohler P. F., Carr R. I. DNA:anti-DNA complexes: their detection in systemic lupus erythematosus sera. J Clin Invest. 1973 Apr;52(4):789–795. doi: 10.1172/JCI107242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes G. R., Cohen S. A., Christian C. L. Anti-DNA activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. A diagnostic and therapeutic guide. Ann Rheum Dis. 1971 May;30(3):259–264. doi: 10.1136/ard.30.3.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. D., Edmonds J. P., Holborow E. J. Precipitating antibody to D.N.A. detected by two-stage electroimmunodiffusion. Study in S.L.E. and in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1973 Oct 20;2(7834):883–885. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koffler D., Carr R. I., Agnello V., Fiezi T., Kunkel H. G. Antibodies to polynucleotides: distribution in human serums. Science. 1969 Dec 26;166(3913):1648–1649. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3913.1648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty R. E., Steward M. W., Soothill J. F. The heterogeneity of antibody affinity in inbred mice and its possible immunopathologic significance. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Oct;12(2):231–241. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus T., Haberkern R., Christian C. L. Experimental chronic glomerulitis. J Exp Med. 1968 Apr 1;127(4):819–832. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.4.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus T., Schur P. H., Rose J. A., Decker J. L., Talal N. Measurement of serum DNA-binding activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 1969 Sep 25;281(13):701–705. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196909252811304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schur P. H., Sandson J. Immunologic factors and clinical activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 1968 Mar 7;278(10):533–538. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196803072781004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staples P. J., Gerding D. N., Decker J. L., Gordon R. S., Jr Incidence of infection in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1974 Jan-Feb;17(1):1–10. doi: 10.1002/art.1780170102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg A. D., Kaltreider H. B., Staples P. J., Goetzl E. J., Talal N., Decker J. L. Cyclophosphamide in lupus nephritis: a controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 1971 Aug;75(2):165–171. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-75-2-165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward M. W., Katz F. E., West N. J. The role of low affinity antibody in immune complex disease. The quantity of anti-DNA antibodies in NZB/W F1 hybrid mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Jul;21(1):121–130. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sztejnbok M., Stewart A., Diamond H., Kaplan D. Azathioprine in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus. A controlled study. Arthritis Rheum. 1971 Sep-Oct;14(5):639–645. doi: 10.1002/art.1780140511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tojo T., Friou G. J. Lupus nephritis: varying complement-fixing properties of immunoglobulin G antibodies to antigens of cell nuclei. Science. 1968 Aug 30;161(3844):904–906. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3844.904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. G., Peters D. K., Fallows J., Petrie A., Kourilsky O., Morel-Maroger L., Cameron J. S. Studies of serum complement in the hypocomplementaemic nephritides. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Nov;18(3):391–405. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold R. T., Young F. E., Tan E. M., Farr R. S. Deoxyribonucleic acid antibody: a method to detect its primary interaction with deoxyribonucleic acid. Science. 1968 Aug 23;161(3843):806–807. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3843.806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


