Abstract
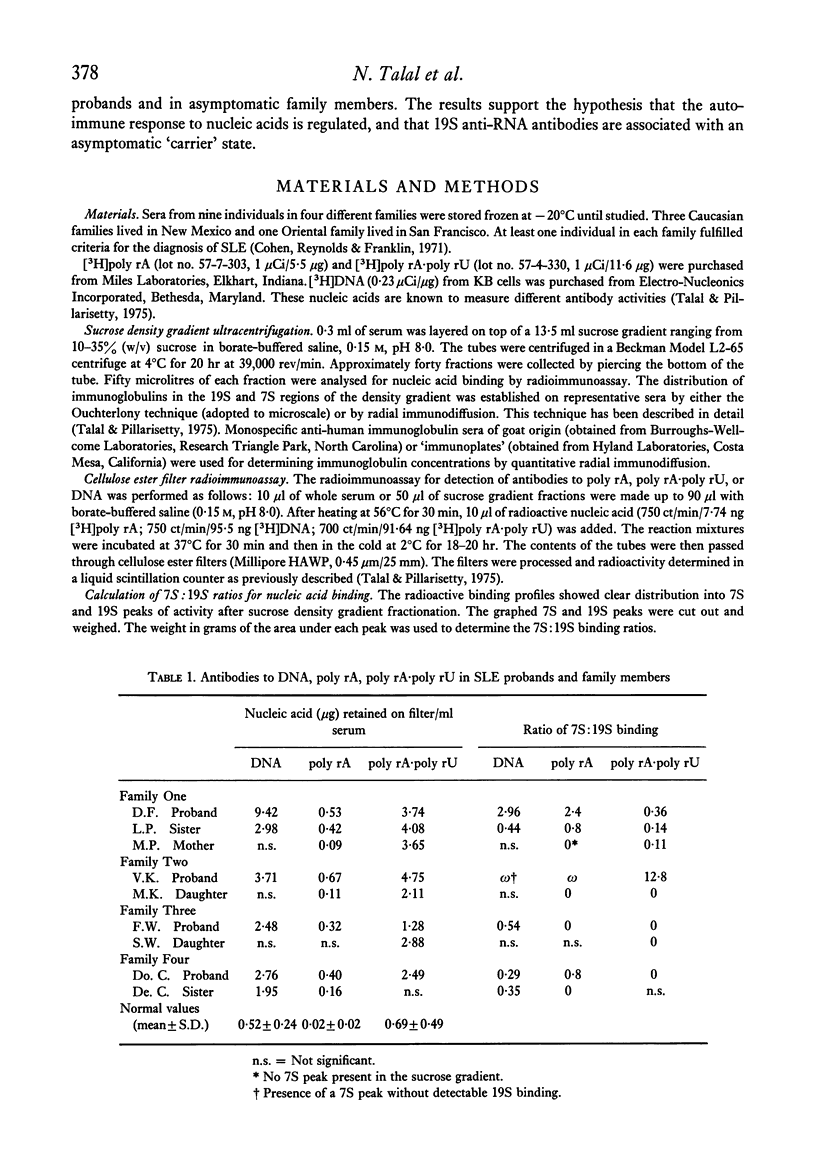
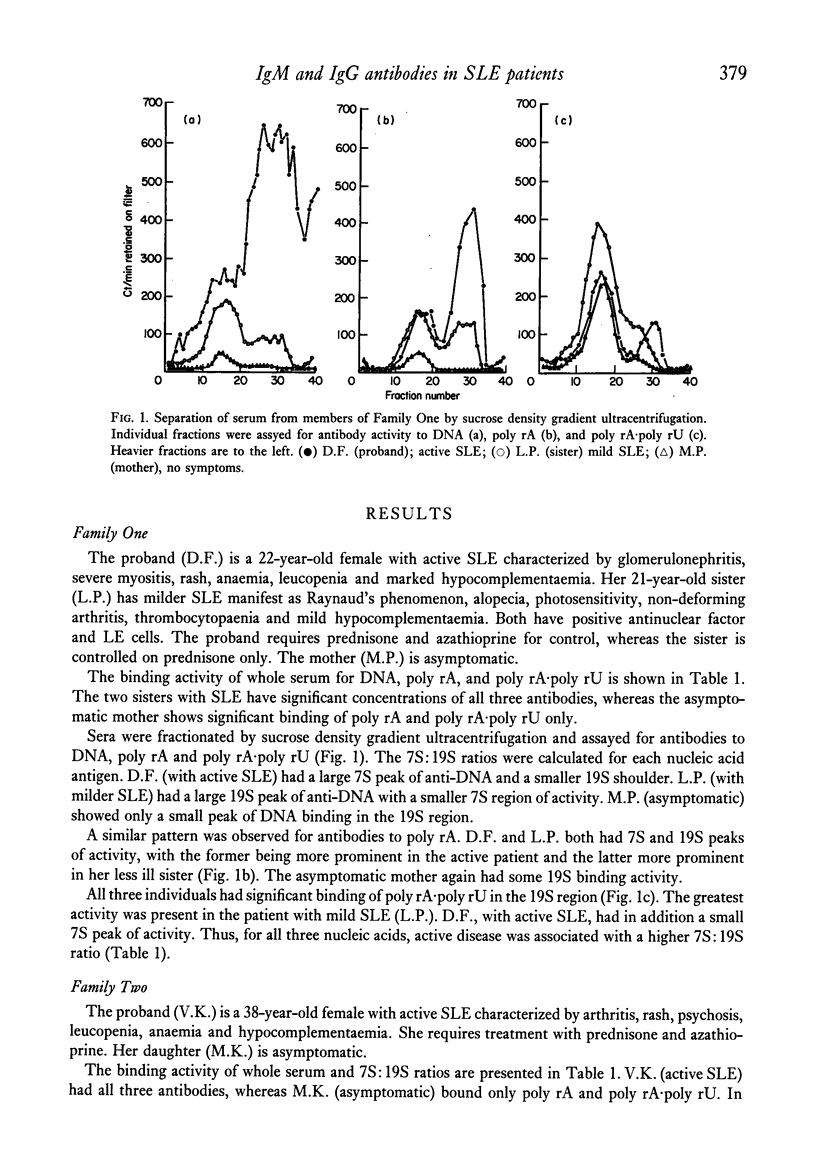
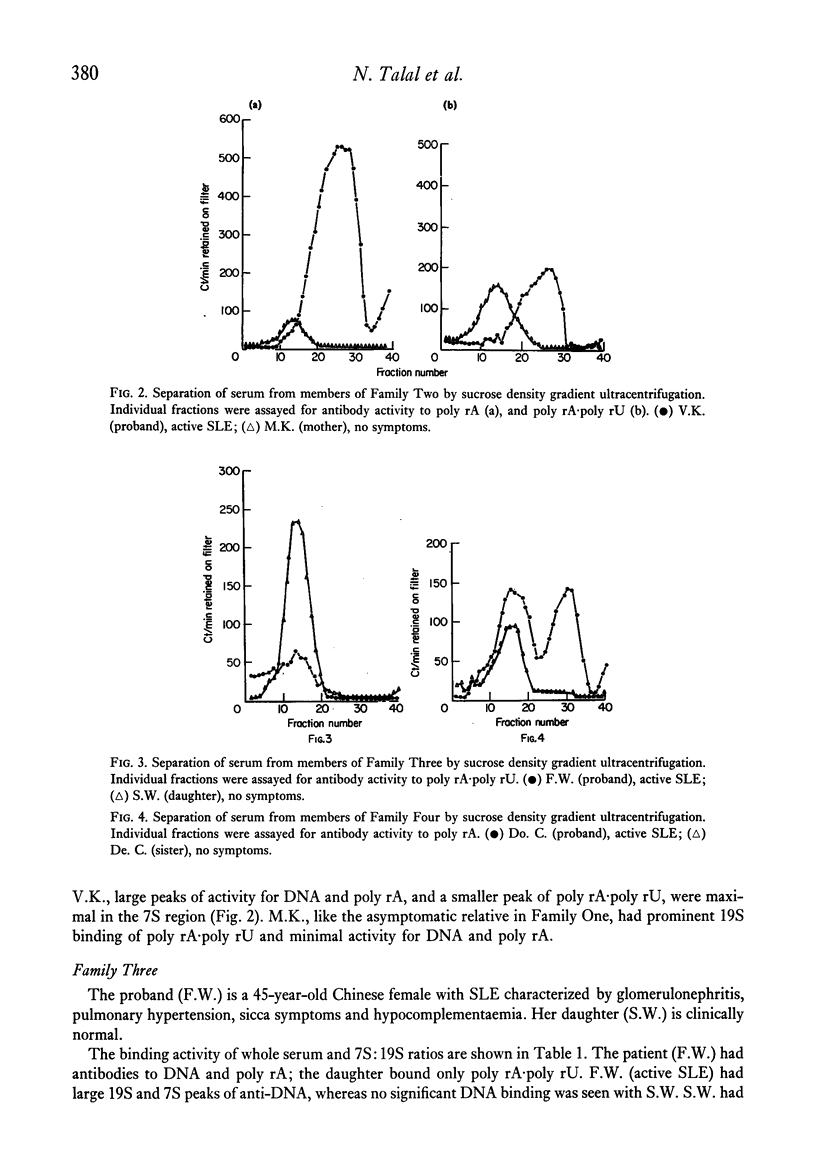
Nine individuals from four families of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) were studied by sucrose density gradient fractionation and filter radioimmunoassay for the presence of 19S IgM and 7S IgG antibodies to DNA, poly rA, and poly rA-poly rU. One individual in each family was totally asymptomatic, and at least one had actively systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The results indicate: (1) a correlation between 7S antibody to DNA and RNA and active SLE, and (2) the presence of 19S antibody to RNA in the asymptomatic relatives. These findings suggest that SLE may be a disorder of immunological regulation. The distribution of antibodies between IgM and IgG is closely related to disease severity. the asymptomatic relatives may have a partial regulatory abnormality resulting in the limited production of IgM antibodies to RNA. SLE patients may have a more complex failure of regulation permitting the additional synthesis of IgG antibodies to DNA and RNA.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson B., Blomgren H. Evidence for thymus-independent humoral antibody production in mice against polyvinylpyrrolidone and E. coli lipopolysaccharide. Cell Immunol. 1971 Oct;2(5):411–424. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(71)90052-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arana R., Seligmann M. Antibodies to native and denatured deoxyribonucleic acid in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1967 Nov;46(11):1867–1882. doi: 10.1172/JCI105677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. J., Stashak P. W., Amsbaugh D. F., Prescott B. Regulation of the antibody response to type 3 pneumococcal polysaccharide. II. Mode of action of thymic-derived suppressor cells. J Immunol. 1974 Jan;112(1):404–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bankhurst A. D., Torrigiani G., Allison A. C. Lymphocytes binding human thyroglobulin in healthy people and its relevance to tolerance for autoantigens. Lancet. 1973 Feb 3;1(7797):226–230. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90066-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bankhurst A. D., Williams R. C., Jr Identification of DNA-binding lymphocytes in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1975 Dec;56(6):1378–1385. doi: 10.1172/JCI108218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold D. R., Kysela S., Steinberg A. D. Decline in suppressor T cell function with age in female NZB mice. J Immunol. 1974 Jan;112(1):9–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnet F. M., Holmes M. C. The natural history of the NZB/NZW F1 hybrid mouse: a laboratory model of systemic lupus erythematosus. Australas Ann Med. 1965 Aug;14(3):185–191. doi: 10.1111/imj.1965.14.3.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chused T. M., Steinberg A. D., Parker L. M. Enhanced antibody response of mice to polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid by antithymocyte serum and its age-dependent loss in NZB-W mice. J Immunol. 1973 Jul;111(1):52–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeHoratius R. J., Pillarisetty R., Messner R. P., Talal N. Anti-nucleic acid antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus patients and their families. Incidence and correlation with lymphocytotoxic antibodies. J Clin Invest. 1975 Nov;56(5):1149–1154. doi: 10.1172/JCI108190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grumet F. C. Genetic control of the immune response. A selective defect in immunologic (IgG) memory in nonresponder mice. J Exp Med. 1972 Jan;135(1):110–125. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.1.110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koffler D., Agnello V., Kimkel H. G. Polynucleotide immune complexes in serum and glomeruli of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Pathol. 1974 Jan;74(1):109–124. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koffler D., Schur P. H., Kunkel H. G. Immunological studies concerning the nephritis of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Exp Med. 1967 Oct 1;126(4):607–624. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.4.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothfield N. F., Stollar B. D. The relation of immunoglobulin class, pattern of anti-nuclear antibody, and complement-fixing antibodies to DNA in sera from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1967 Nov;46(11):1785–1794. doi: 10.1172/JCI105669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOLLAR D., LEVINE L., LEHRER H. I., VAN VUNAKIS H. The antigenic determinants of denatured DNA reactive with lupus erythematosus serum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 May 15;48:874–880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.5.874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schur P. H., Monroe M. Antibodies to ribonucleic acid in systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Aug;63(4):1108–1112. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.4.1108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talal N. Autoimmunity and lymphoid malignancy in New Zealand black mice. Prog Clin Immunol. 1974;2:101–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talal N. Disordered immunologic regulation and autoimmunity. Transplant Rev. 1976;31:240–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1976.tb01456.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talal N. Immunologic and viral factors in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1970 Nov-Dec;13(6):887–894. doi: 10.1002/art.1780130620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talal N., Pillarisetty R. IgM and IgG antibodies to DNA, RNA, and DNA:RNA in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1975 May;4(1):24–31. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(75)90035-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


