Abstract
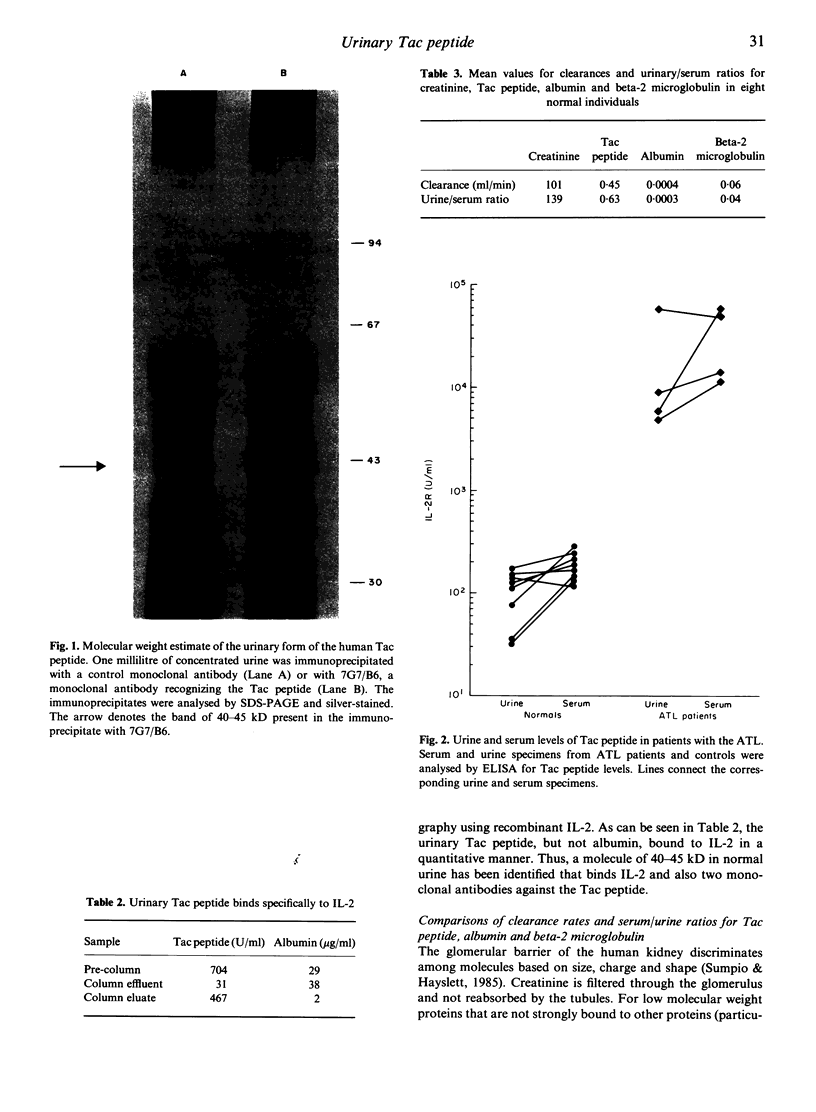
The T lymphocyte-derived lymphokine interleukin 2 and the cell-associated receptor for this molecule play major roles in the activation and regulation of the human immune response. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay has been developed to measure quantitatively a soluble form of one component of the human interleukin 2 receptor, namely the Tac peptide. In the present studies, soluble Tac peptide was measured in the urine of normal individuals (mean = 92 U/ml), a level not significantly different (0.01 less than P less than 0.05) from the corresponding serum concentrations (mean = 175). The urinary Tac peptide had a molecular weight of 40-45 kD by sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis and specifically bound interleukin 2. Elevated levels of urinary Tac peptide were found in four patients with adult T cell leukaemia who also had elevated serum levels of Tac peptide. Thus, urine may represent a valuable source of lymphokine-binding proteins that may serve as important markers of immunological activation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benveniste E. N., Merrill J. E. Stimulation of oligodendroglial proliferation and maturation by interleukin-2. Nature. 1986 Jun 5;321(6070):610–613. doi: 10.1038/321610a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann F., Cannistra S. A., Levine H., Griffin J. D. Expression of interleukin 2 receptors and binding of interleukin 2 by gamma interferon-induced human leukemic and normal monocytic cells. J Exp Med. 1985 Sep 1;162(3):1111–1116. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.3.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hession C., Decker J. M., Sherblom A. P., Kumar S., Yue C. C., Mattaliano R. J., Tizard R., Kawashima E., Schmeissner U., Heletky S. Uromodulin (Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein): a renal ligand for lymphokines. Science. 1987 Sep 18;237(4821):1479–1484. doi: 10.1126/science.3498215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holter W., Goldman C. K., Casabo L., Nelson D. L., Greene W. C., Waldmann T. A. Expression of functional IL 2 receptors by lipopolysaccharide and interferon-gamma stimulated human monocytes. J Immunol. 1987 May 1;138(9):2917–2922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett D. H., Ryan J. L., Sterzel R. B. A thymocyte-activating factor derived from glomerular mesangial cells. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1796–1801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muchmore A. V., Decker J. M. Uromodulin. An immunosuppressive 85-kilodalton glycoprotein isolated from human pregnancy urine is a high affinity ligand for recombinant interleukin 1 alpha. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13404–13407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muchmore A. V., Decker J. M. Uromodulin: a unique 85-kilodalton immunosuppressive glycoprotein isolated from urine of pregnant women. Science. 1985 Aug 2;229(4712):479–481. doi: 10.1126/science.2409603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. L., Rubin L. A., Kurman C. C., Fritz M. E., Boutin B. An analysis of the cellular requirements for the production of soluble interleukin-2 receptors in vitro. J Clin Immunol. 1986 Mar;6(2):114–120. doi: 10.1007/BF00918743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Munck A., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor receptors. Quantitation, specificity, and biological relevance. J Exp Med. 1981 Nov 1;154(5):1455–1474. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.5.1455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Lotze M. T., Muul L. M., Leitman S., Chang A. E., Ettinghausen S. E., Matory Y. L., Skibber J. M., Shiloni E., Vetto J. T. Observations on the systemic administration of autologous lymphokine-activated killer cells and recombinant interleukin-2 to patients with metastatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 5;313(23):1485–1492. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512053132327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy S. K., McGregor W. C., Orichowskyj S. T. Automated high-performance immunosorbent assay for recombinant leukocyte A interferon. J Chromatogr. 1985 Jun 26;327:189–192. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)81648-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin L. A., Jay G., Nelson D. L. The released interleukin 2 receptor binds interleukin 2 efficiently. J Immunol. 1986 Dec 15;137(12):3841–3844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin L. A., Kurman C. C., Biddison W. E., Goldman N. D., Nelson D. L. A monoclonal antibody 7G7/B6, binds to an epitope on the human interleukin-2 (IL-2) receptor that is distinct from that recognized by IL-2 or anti-Tac. Hybridoma. 1985 Summer;4(2):91–102. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1985.4.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin L. A., Kurman C. C., Fritz M. E., Biddison W. E., Boutin B., Yarchoan R., Nelson D. L. Soluble interleukin 2 receptors are released from activated human lymphoid cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3172–3177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon M., Klausner R. D., Cullen B. R., Chizzonite R., Leonard W. J. Novel interleukin-2 receptor subunit detected by cross-linking under high-affinity conditions. Science. 1986 Nov 14;234(4778):859–863. doi: 10.1126/science.3095922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner G., Tschachler E., Tani M., Malek T. R., Shevach E. M., Holter W., Knapp W., Wolff K., Stingl G. Interleukin 2 receptors on cultured murine epidermal Langerhans cells. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 1;137(1):155–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumpio B. E., Maack T. Kinetics, competition, and selectivity of tubular absorption of proteins. Am J Physiol. 1982 Oct;243(4):F379–F392. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.243.4.F379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teshigawara K., Wang H. M., Kato K., Smith K. A. Interleukin 2 high-affinity receptor expression requires two distinct binding proteins. J Exp Med. 1987 Jan 1;165(1):223–238. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.1.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsudo M., Kozak R. W., Goldman C. K., Waldmann T. A. Demonstration of a non-Tac peptide that binds interleukin 2: a potential participant in a multichain interleukin 2 receptor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9694–9698. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchiyama T., Broder S., Waldmann T. A. A monoclonal antibody (anti-Tac) reactive with activated and functionally mature human T cells. I. Production of anti-Tac monoclonal antibody and distribution of Tac (+) cells. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1393–1397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchiyama T., Yodoi J., Sagawa K., Takatsuki K., Uchino H. Adult T-cell leukemia: clinical and hematologic features of 16 cases. Blood. 1977 Sep;50(3):481–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A., Goldman C. K., Robb R. J., Depper J. M., Leonard W. J., Sharrow S. O., Bongiovanni K. F., Korsmeyer S. J., Greene W. C. Expression of interleukin 2 receptors on activated human B cells. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1450–1466. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]