Abstract
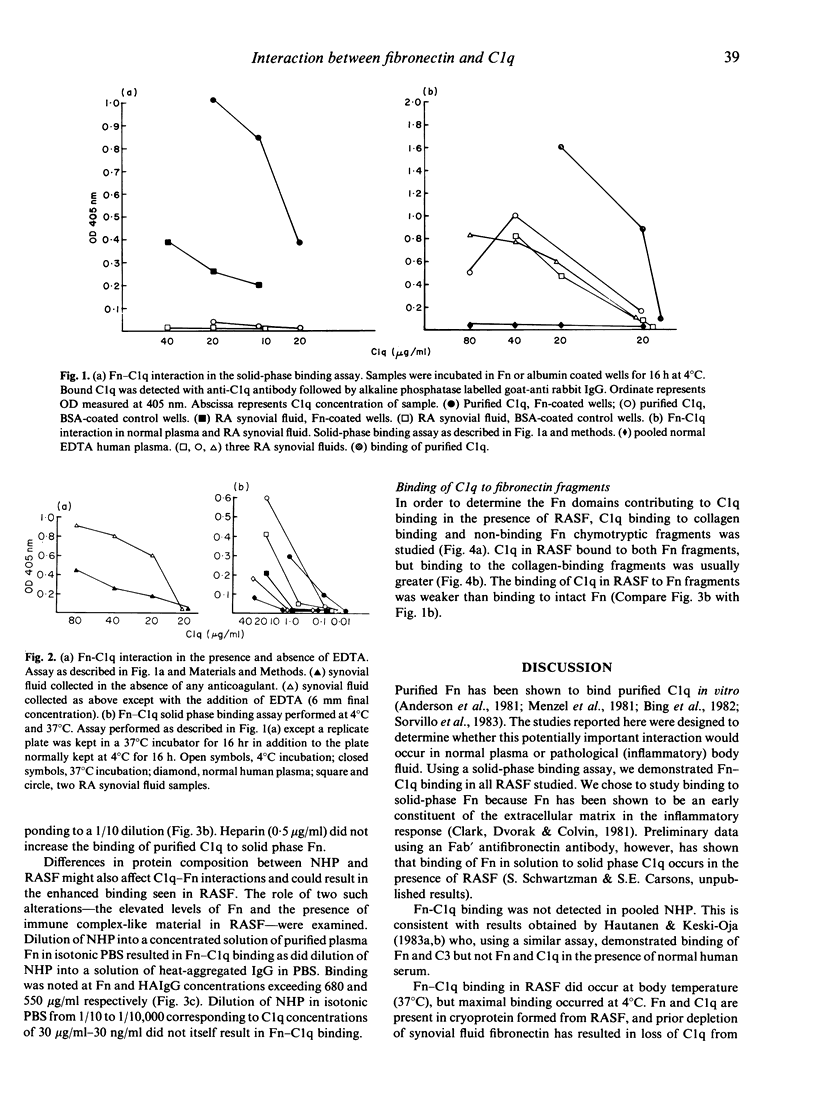
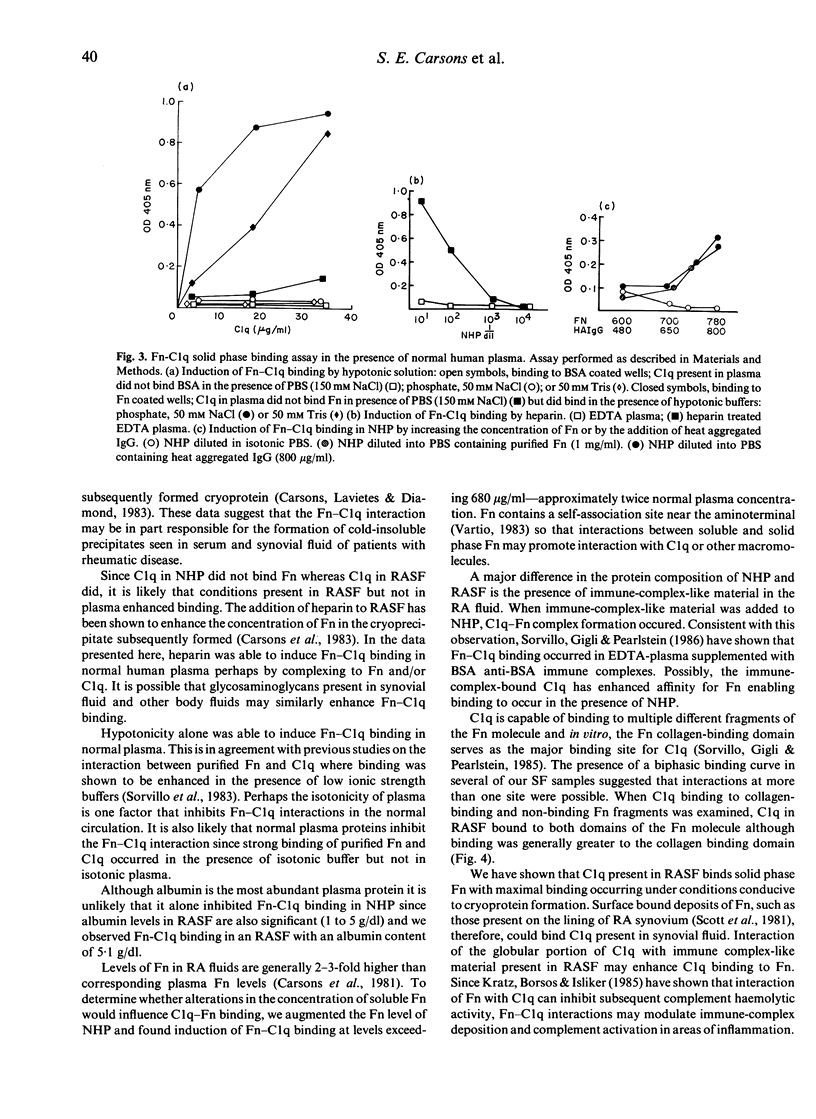
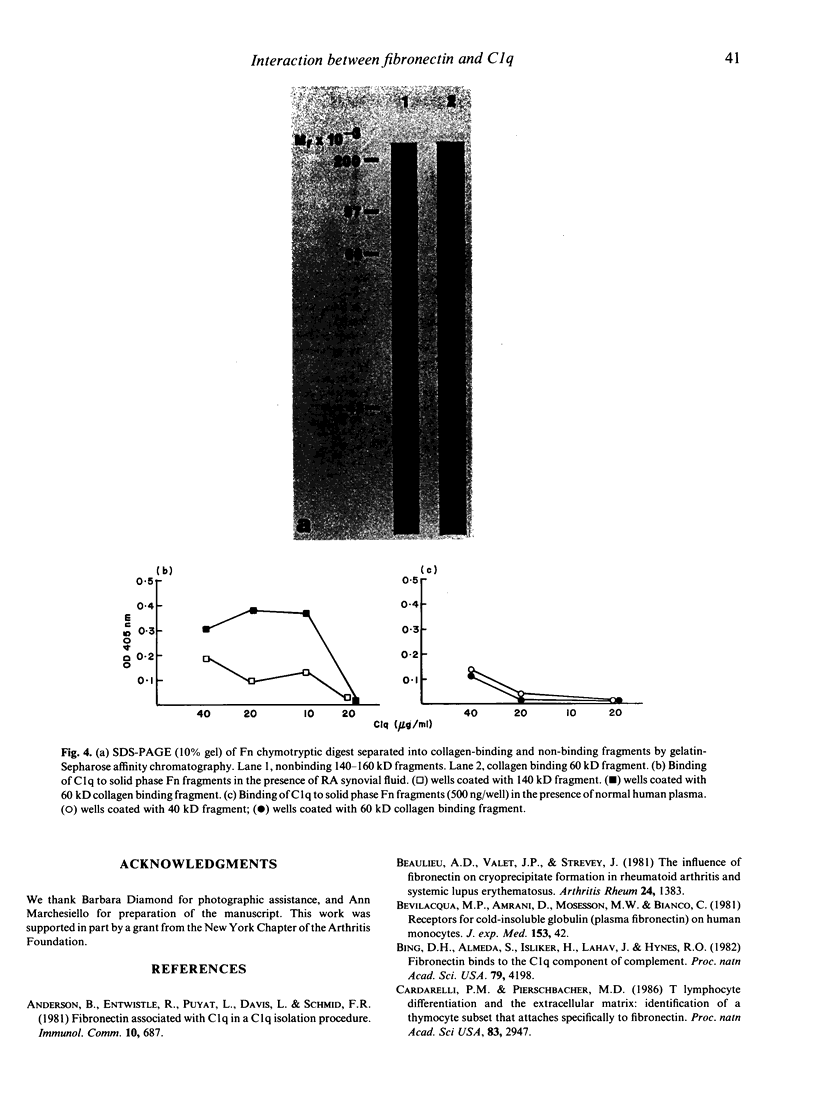
The interaction between fibronectin and C1q was studied in the presence of normal human plasma and rheumatoid synovial fluid by solid phase binding assay. Fibronectin-C1q binding occurred in the presence of rheumatoid synovial fluid but not in the presence of normal plasma. Binding was strongest at 4 degrees C and in the presence of EDTA. Fibronectin-C1q binding could be induced in the presence of normal plasma by hypotonicity, augmentation of the concentration of solution-phase fibronectin or by the addition of heat-aggregated IgG. The C1q present in rheumatoid synovial fluid bound to both aminoterminal collagen-binding and carboxyterminal noncollagen binding fibronectin fragments although binding to the aminoterminal fragment was stronger. The interaction between fibronectin and C1q in rheumatoid synovial fluid may modulate immune-complex deposition and complement activation in the inflamed joint.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson B., Entwistle R., Puyat L., Davis L., Schmid F. R. Fibronectin associated with Clq in a Clq isolation procedure. Immunol Commun. 1981;10(8):687–696. doi: 10.3109/08820138109051955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaulieu A. D., Valet J. P., Strevey J. The influence of fibronectin on cryoprecipitate formation in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Nov;24(11):1383–1388. doi: 10.1002/art.1780241108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Amrani D., Mosesson M. W., Bianco C. Receptors for cold-insoluble globulin (plasma fibronectin) on human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1981 Jan 1;153(1):42–60. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.1.42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bing D. H., Almeda S., Isliker H., Lahav J., Hynes R. O. Fibronectin binds to the C1q component of complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4198–4201. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carsons S., Lavietes B. B., Diamond H. S. Factors influencing the incorporation of fibronectin into synovial fluid cryoprotein. J Lab Clin Med. 1983 Nov;102(5):722–731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carsons S., Mosesson M. W., Diamond H. S. Detection and quantitation of fibronectin in synovial fluid from patients with rheumatic disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Oct;24(10):1261–1267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Dvorak H. F., Colvin R. B. Fibronectin in delayed-type hypersensitivity skin reactions: associations with vessel permeability and endothelial cell activation. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):787–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hautanen A., Keski-Oja J. Affinity of myeloma IgG proteins for fibronectin. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Jul;53(1):233–238. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hautanen A., Keski-Oja J. Interaction of fibronectin with complement component C3. Scand J Immunol. 1983 Mar;17(3):225–230. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1983.tb00785.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menzel E. J., Smolen J. S., Liotta L., Reid K. B. Interaction of fibronectin with C1q and its collagen-like fragment (CLF). FEBS Lett. 1981 Jun 29;129(1):188–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80787-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. L., Delamere J. P., Walton K. W. The distribution of fibronectin in the pannus in rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1981 Aug;62(4):362–368. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorvillo J., Gigli I., Pearlstein E. Fibronectin binding to C1q associated with antigen-antibody complexes in EDTA-treated plasma. Scand J Immunol. 1986 Feb;23(2):153–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1986.tb01953.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorvillo J., Gigli I., Pearlstein E. Fibronectin binding to complement subcomponent C1q. Localization of their respective binding sites. Biochem J. 1985 Feb 15;226(1):207–215. doi: 10.1042/bj2260207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorvillo J., Gigli I., Pearlstein E. Requirements for the binding of human plasma fibronectin to the C1q subunit of the first component of complement. J Immunol. 1983 Sep;131(3):1400–1404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vartio T. Fibronectin: multiple interactions assigned to structural domains. Med Biol. 1983;61(6):283–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonemasu K., Stroud R. M. Clq: rapid purification method for preparation of monospecific antisera and for biochemical studies. J Immunol. 1971 Feb;106(2):304–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]