Abstract
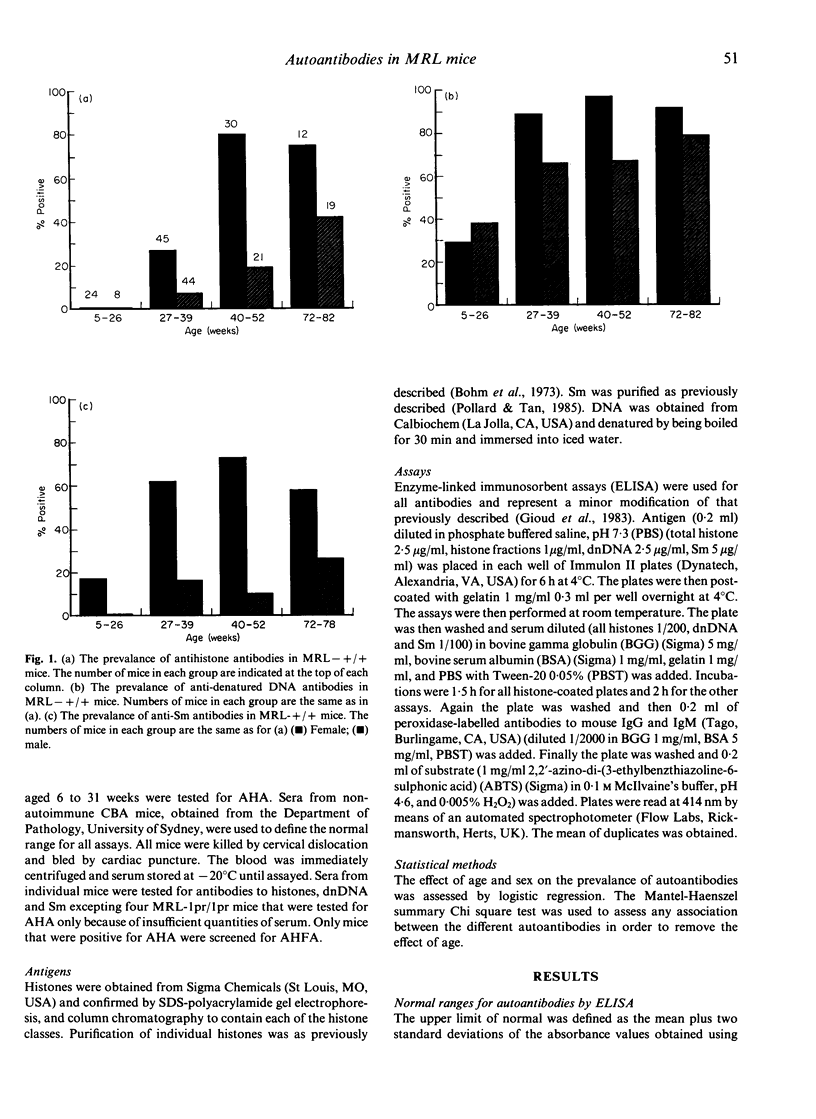
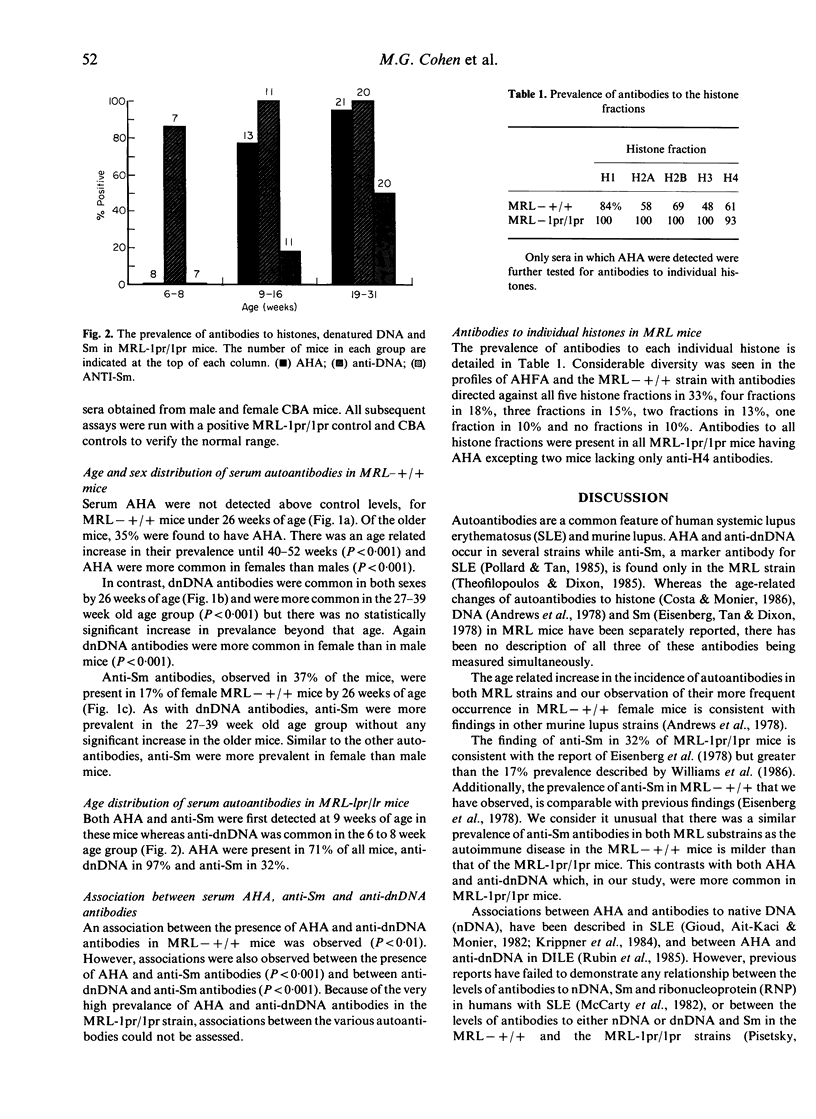
Despite the protean nature of the clinical characteristics of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), autoantibodies represent an almost constant feature. Furthermore they are common to both human SLE and murine lupus. Nonetheless, the mechanism by which they arise has not been established. Amongst the several processes that have been proposed, evidence has emerged supporting specific antigen drive as a significant mechanism. We have documented the age- and sex-related differences in the prevalence of antibodies to both chromatin-related (histone and DNA) and non-chromatin-related (Sm) antigens in MRL mice. Our finding of an association between antihistone antibodies and anti-denatured DNA antibodies is consistent with chromatin being the putative antigen. Additionally, antibodies to the individual histones H1 and H2B, the most exposed histones in chromatin, were more prevalent than antibodies to the remaining histones (H2A, H3, H4). This, again, supports specific antigen drive as a mechanism for autoantibody production. However, associations were also found between antibodies to histone and DNA and antibodies to Sm. As Sm is a non-chromatin protein antigen, the associations between antibodies to Sm and those to histone and DNA suggest that mechanisms in addition to specific antigen drive are important in autoantibody production.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews B. S., Eisenberg R. A., Theofilopoulos A. N., Izui S., Wilson C. B., McConahey P. J., Murphy E. D., Roths J. B., Dixon F. J. Spontaneous murine lupus-like syndromes. Clinical and immunopathological manifestations in several strains. J Exp Med. 1978 Nov 1;148(5):1198–1215. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.5.1198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein R. M., Hobbs R. N., Lea D. J., Ward D. J., Hughes G. R. Patterns of antihistone antibody specificity in systemic rheumatic disease. I Systemic lupus erythematosus, mixed connective tissue disease, primary sicca syndrome, and rheumatoid arthritis with vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Mar;28(3):285–293. doi: 10.1002/art.1780280308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhm E. L., Strickland W. N., Strickland M., Thwaits B. H., van der Westhuizen D. R., von Holt C. Purification of the five main calf thymus histone fractions by gel exclusion chromatography. FEBS Lett. 1973 Aug 15;34(2):217–221. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80797-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa O., Monier J. C. Antihistone antibodies detected by micro-ELISA and immunoblotting in mice with lupus-like syndrome (MRL/1, MRL/n, PN, and NZB strains). Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 Aug;40(2):276–282. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(86)90031-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson A., Shefner R., Livneh A., Diamond B. The role of somatic mutation of immunoglobulin genes in autoimmunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:85–108. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.000505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. A., Tan E. M., Dixon F. J. Presence of anti-Sm reactivity in autoimmune mouse strains. J Exp Med. 1978 Feb 1;147(2):582–587. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.2.582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gioud M., Kaci M. A., Monier J. C. Histone antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. A possible diagnostic tool. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Apr;25(4):407–413. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gioud M., Kotzin B. L., Rubin R. L., Joslin F. G., Tan E. M. In vivo and in vitro production of anti-histone antibodies in NZB/NZW mice. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):269–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gohill J., Cary P. D., Couppez M., Fritzler M. J. Antibodies from patients with drug-induced and idiopathic lupus erythematosus react with epitopes restricted to the amino and carboxyl termini of histone. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3116–3121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldblatt D., Bustin M. Exposure of histone antigenic determinants in chromatin. Biochemistry. 1975 Apr 22;14(8):1689–1695. doi: 10.1021/bi00679a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardin J. A., Thomas J. O. Antibodies to histones in systemic lupus erythematosus: localization of prominent autoantigens on histones H1 and H2B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7410–7414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krippner H., Springer B., Merle S., Pirlet K. Antibodies to histones of the IgG and IgM class in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Oct;58(1):49–56. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarty G. A., Rice J. R., Bembe M. L., Pisetsky D. S. Independent expression of autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 1982 Sep-Oct;9(5):691–695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migliorini P., Ardman B., Kaburaki J., Schwartz R. S. Parallel sets of autoantibodies in MRL-lpr/lpr mice. An anti-DNA, anti-SmRNP, anti-gp70 network. J Exp Med. 1987 Feb 1;165(2):483–499. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.2.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisetsky D. S., McCarty G. A., Peters D. V. Mechanisms of autoantibody production in autoimmune MRL mice. J Exp Med. 1980 Nov 1;152(5):1302–1310. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.5.1302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard K. M., Tan E. M. Purification of the Sm nuclear autoantigen. Detection and clinical significance of IgM antibody. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Jun;60(3):586–596. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portanova J. P., Arndt R. E., Tan E. M., Kotzin B. L. Anti-histone antibodies in idiopathic and drug-induced lupus recognize distinct intrahistone regions. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 15;138(2):446–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portanova J. P., Claman H. N., Kotzin B. L. Autoimmunization in murine graft-vs-host disease. I. Selective production of antibodies to histones and DNA. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):3850–3856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. L., McNally E. M., Nusinow S. R., Robinson C. A., Tan E. M. IgG antibodies to the histone complex H2A-H2B characterize procainamide-induced lupus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1985 Jul;36(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(85)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Dixon F. J. Murine models of systemic lupus erythematosus. Adv Immunol. 1985;37:269–390. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60342-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. G., Brennan F. M., Stocks M. R., Maini R. N. Individual variation of anti-Sm autoantibodies in the MRL/MP-lpr/lpr mouse: age-related increase in diversity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Sep;65(3):506–512. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


