Abstract
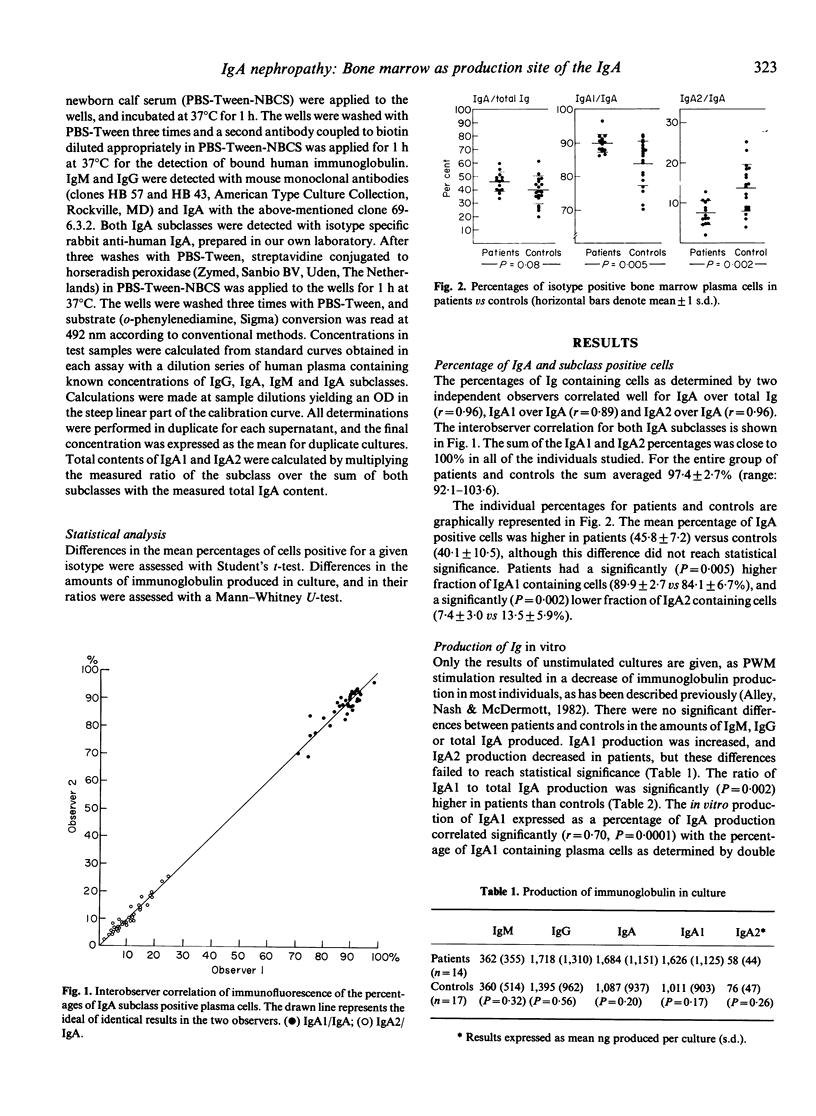
Patients with primary IgA nephropathy have increased plasma levels of polymeric IgA1 and deposits of IgA1 in their kidneys. The origin of this material is unknown. The production of IgA and its subclasses was investigated in the bone marrow of 14 patients and 19 controls using two colour immunofluorescence and tissue culture. Patients had an increase in the percentage of plasma cells containing IgA (45.8 +/- 7.2 mean +/- s.d.) compared to controls (40.1 +/- 10.5) (P = 0.08). IgA plasma cells containing subclass IgA1 were significantly (P less than 0.01) increased in patients (89.9 +/- 2.7%) compared to controls (84.1 +/- 6.7%). Correspondingly IgA plasma cells containing subclass IgA2 were significantly decreased (P less than 0.01) in patients (7.4 +/- 3.0%) compared to controls (13.5 +/- 5.9%). Production of IgA in bone marrow culture in patients was increased (1,684 +/- 1,151 ng/culture) compared to controls (1,087 +/- 937), but this difference was not significant (P = 0.2). However, in patients the IgA1 subclass contributed significantly (P less than 0.01) more to the IgA synthesis in culture (ratio of IgA1 over IgA: 0.96 +/- 0.02) than in controls (ratio 0.90 +/- 0.06). These findings suggest that the bone marrow may well be the site of long-term overproduction of the IgA1 found in the circulation and mesangial deposits in IgA nephropathy.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alley C. D., Kiyono H., McGhee J. R. Murine bone marrow IgA responses to orally administered sheep erythrocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4414–4419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alley C. D., Nash G. S., MacDermott R. P. Marked in vitro spontaneous secretion of IgA by human rib bone marrow mononuclear cells. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2604–2608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannister K. M., Drew P. A., Clarkson A. R., Woodroffe A. J. Immunoregulation in glomerulonephritis, Henoch--Schonlein purpura and lupus nephritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Aug;53(2):384–390. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bene M. C., Faure G., Duheille J. IgA nephropathy: characterization of the polymeric nature of mesangial deposits by in vitro binding of free secretory component. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Mar;47(3):527–534. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bene M. C., Faure G., Hurault de Ligny B., Kessler M., Duheille J. Immunoglobulin A nephropathy. Quantitative immunohistomorphometry of the tonsillar plasma cells evidences an inversion of the immunoglobulin A versus immunoglobulin G secreting cell balance. J Clin Invest. 1983 May;71(5):1342–1347. doi: 10.1172/JCI110886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benner R., Hijmans W., Haaijman J. J. The bone marrow: the major source of serum immunoglobulins, but still a neglected site of antibody formation. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Oct;46(1):1–8. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger J., Yaneva H., Nabarra B., Barbanel C. Recurrence of mesangial deposition of IgA after renal transplantation. Kidney Int. 1975 Apr;7(4):232–241. doi: 10.1038/ki.1975.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. R., Smith P. D., Lee E., McCalmon R. T., Nagura H. A search for an enriched source of polymeric IgA in human thoracic duct lymph, portal vein blood and aortic blood. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Apr;48(1):85–90. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnett D., Crocker J., Stockley R. A. Cells containing IgA subclasses in bronchi of subjects with and without chronic obstructive lung disease. J Clin Pathol. 1987 Oct;40(10):1217–1220. doi: 10.1136/jcp.40.10.1217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley M. E., Cooper M. D., Michael A. F. Selective deposition of immunoglobulin A1 in immunoglobulin A nephropathy, anaphylactoid purpura nephritis, and systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1980 Dec;66(6):1432–1436. doi: 10.1172/JCI109998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crago S. S., Kutteh W. H., Moro I., Allansmith M. R., Radl J., Haaijman J. J., Mestecky J. Distribution of IgA1-, IgA2-, and J chain-containing cells in human tissues. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):16–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czerkinsky C., Koopman W. J., Jackson S., Collins J. E., Crago S. S., Schrohenloher R. E., Julian B. A., Galla J. H., Mestecky J. Circulating immune complexes and immunoglobulin A rheumatoid factor in patients with mesangial immunoglobulin A nephropathies. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):1931–1938. doi: 10.1172/JCI112522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egido J., Blasco R., Lozano L., Sancho J., Garcia-Hoyo R. Immunological abnormalities in the tonsils of patients with IgA nephropathy: inversion in the ratio of IgA: IgG bearing lymphocytes and increased polymeric IgA synthesis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Jul;57(1):101–106. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egido J., Blasco R., Sancho J., Lozano L., Sanchez-Crespo M., Hernando L. Increased rates of polymeric IgA synthesis by circulating lymphoid cells in IgA mesangial glomerulonephritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Feb;47(2):309–316. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egido J., Blasco R., Sancho J., Lozano L. T-cell dysfunctions in IgA nephropathy: specific abnormalities in the regulation of IgA synthesis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1983 Feb;26(2):201–212. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(83)90138-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson C. O., Ealding W. Generalized systemic and mucosal immunity in mice after mucosal stimulation with cholera toxin. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):2736–2741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feehally J., Beattie T. J., Brenchley P. E., Coupes B. M., Mallick N. P., Postlethwaite R. J. Sequential study of the IgA system in relapsing IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 1986 Dec;30(6):924–931. doi: 10.1038/ki.1986.274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hijmans W., Schuit H. R., Hulsing-Hesselink E. An immunofluorescence study on intracellular immunoglobulins in human bone marrow cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Jun 21;177:290–305. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb35059.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kett K., Brandtzaeg P., Radl J., Haaijman J. J. Different subclass distribution of IgA-producing cells in human lymphoid organs and various secretory tissues. J Immunol. 1986 May 15;136(10):3631–3635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutteh W. H., Prince S. J., Mestecky J. Tissue origins of human polymeric and monomeric IgA. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):990–995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenormand P., Crocker J. Distribution of IgA1 and IgA2 subclasses in normal bone marrow trephines and in trephines infiltrated by IgA producing multiple myeloma. J Clin Pathol. 1987 Feb;40(2):200–205. doi: 10.1136/jcp.40.2.200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomino Y., Sakai H., Miura M., Endoh M., Nomoto Y. Detection of polymeric IgA in glomeruli from patients with IgA nephropathy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Aug;49(2):419–425. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trascasa M. L., Egido J., Sancho J., Hernando L. IgA glomerulonephritis (Berger's disease): evidence of high serum levels of polymeric IgA. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Nov;42(2):247–254. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turesson I. Distribution of immunoglobulin-containing cells in human bone marrow and lymphoid tissues. Acta Med Scand. 1976;199(4):293–304. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1976.tb06735.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentijn R. M., Kauffmann R. H., de la Rivière G. B., Daha M. R., Van ES L. A. Presence of circulating macromolecular IgA in patients with hematuria due to primary IgA nephropathy. Am J Med. 1983 Mar;74(3):375–381. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)90954-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentijn R. M., Radl J., Haaijman J. J., Vermeer B. J., Weening J. J., Kauffmann R. H., Daha M. R., van Es L. A. Circulating and mesangial secretory component-binding IgA-1 in primary IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 1984 Nov;26(5):760–766. doi: 10.1038/ki.1984.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J. L. The production of anti-IgG2a autoantibody in the 129/Sv mouse: onset in the lymph nodes draining the intestinal tract and prevention by neonatal thymectomy. J Immunol. 1981 Mar;126(3):815–818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldo F. B., Beischel L., West C. D. IgA synthesis by lymphocytes from patients with IgA nephropathy and their relatives. Kidney Int. 1986 Jun;29(6):1229–1233. doi: 10.1038/ki.1986.132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westberg N. G., Baklien K., Schmekel B., Gillberg R., Brandtzaeg P. Quantitation of immunoglobulin-producing cells in small intestinal mucosa of patients with IgA nephropathy. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1983 Mar;26(3):442–445. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(83)90130-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


