Abstract
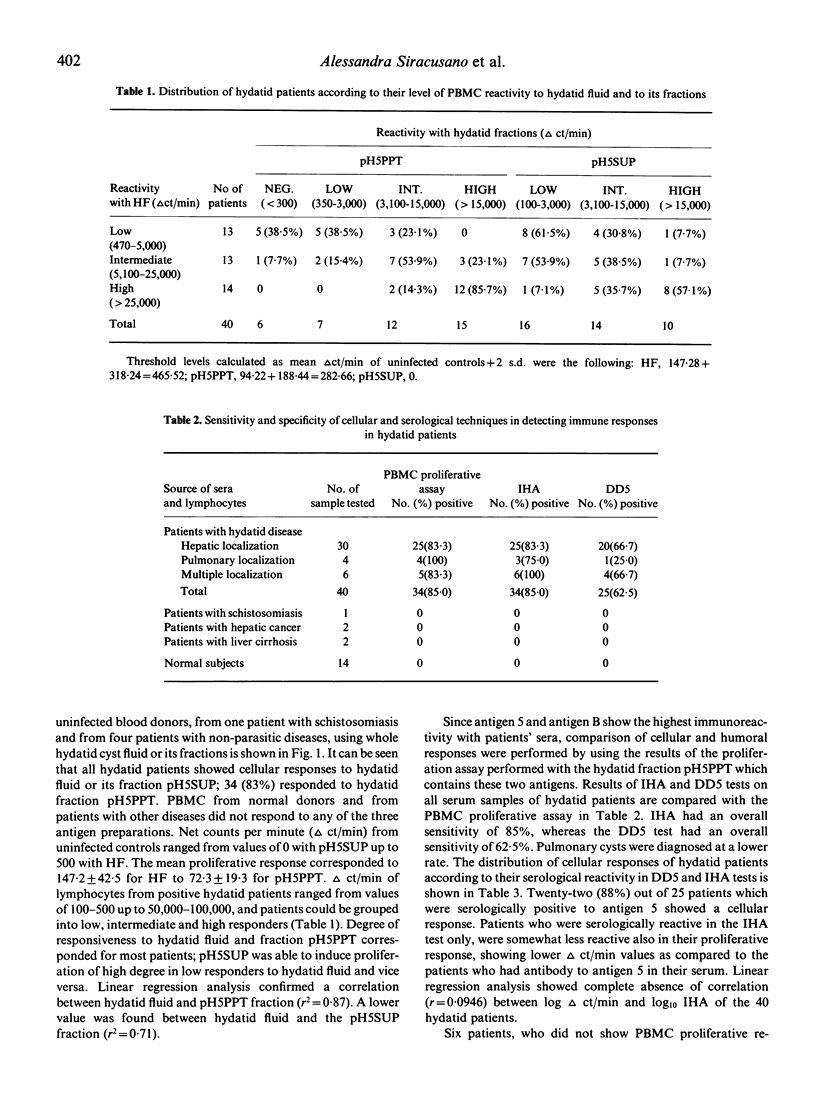
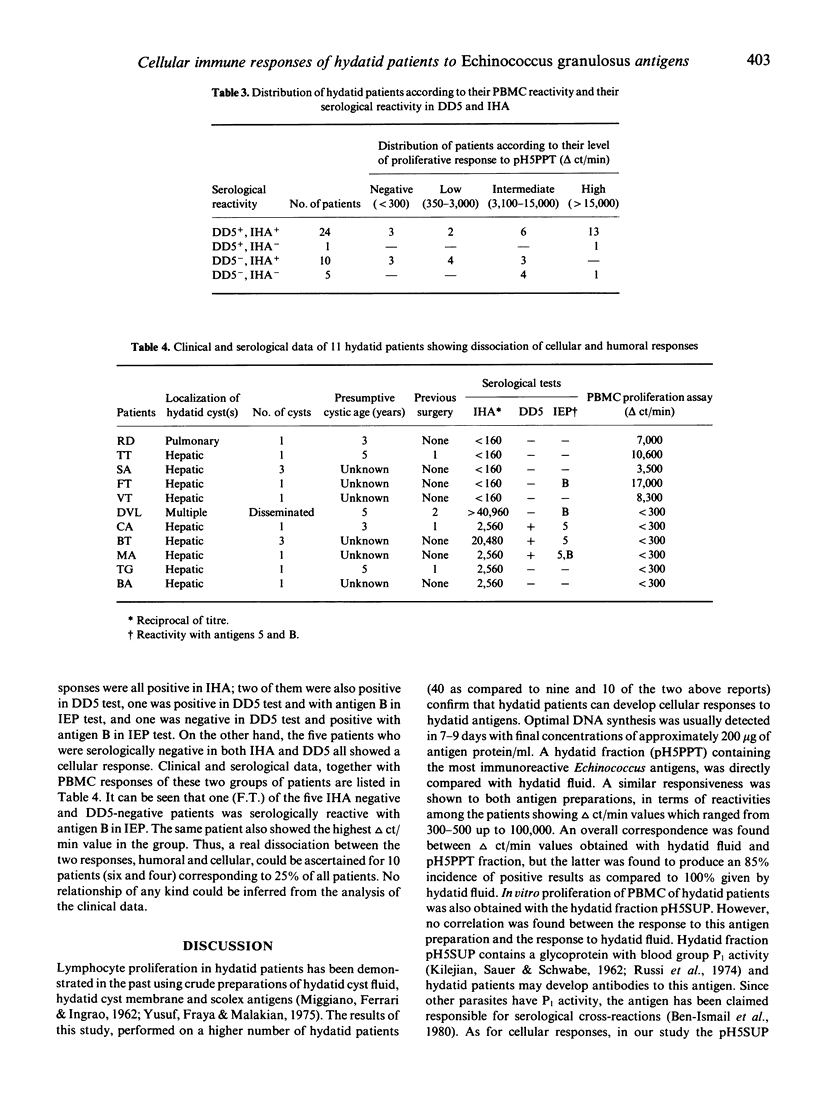
The reactivity of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from 40 hydatid patients to hydatid fluid (HF) and to two hydatid fractions (pH5PPT and pH5SUP) was evaluated by the incorporation of 3H-methylthymidine into DNA. Maximal responses were detected using 200 micrograms/ml protein after 7-9 days incubation. The three antigen preparations were inducers of PBMC proliferation, with a good correlation (r2 = 0.87) of the responses induced by HF and by the fraction pH5PPT, which contains the two major hydatid antigens (5 and B). Lymphocytes from healthy donors and non-hydatid patients showed no response to these antigens. Neither direct nor inverse correlation was found between the results of the serological tests and of the PBMC proliferation assays. The majority of the patients (75%) responded in serological and in cellular tests. Of the remaining patients, six showed high antibody response associated with a negative PBMC proliferation assay and conversely four seronegative patients were found to respond positively in the PBMC proliferation assay. No relationship of the pattern of immune responsiveness to the patient's clinical forms could be established. Use of the PBMC proliferation assay with hydatid antigens appears rational in those patients which are low antibody producers, but the test is still not to be considered applicable for routine diagnosis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apt W., Knierim F. An evaluation of diagnostic tests for hydatid disease. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1970 Nov;19(6):943–946. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1970.19.943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ismail R., Carme B., Niel G., Gentilini M. Non-specific serological reactions with Echinococcus granulosus antigens: role of anti-P1 antibodies. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1980 Mar;29(2):239–245. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1980.29.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bombardieri S., Giordano F., Ingrao F., Ioppolo S., Siracusano A., Vicari G. An evaluation of an agar gel diffusion test with crude and purified antigens in the diagnosis of hydatid disease. Bull World Health Organ. 1974;51(5):525–530. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capron A., Yarzabal L., Vernes A., Fruit J. Le diagnostic immunologique de l'échinococcose humaine. (Bilan personnel a propos de 400 observations) Pathol Biol (Paris) 1970 Apr;18(7):357–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coltorti E. A., Varela-Díaz V. M. Detection of antibodies against Echinococcus granulosus arc 5 antigens by double diffusion test. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(3):226–229. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90198-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Felice G., Pini C., Afferni C., Vicari G. Purification and partial characterization of the major antigen of Echinococcus granulosus (antigen 5) with monoclonal antibodies. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1986 Aug;20(2):133–142. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(86)90025-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iacona A., Pini C., Vicari G. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in the serodiagnosis of hydatid disease. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1980 Jan;29(1):95–102. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1980.29.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Judson D. G., Dixon J. B., Clarkson M. J., Pritchard J. Ovine hydatidosis: some immunological characteristics of the seronegative host. Parasitology. 1985 Oct;91(Pt 2):349–357. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000057413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAGAN I. G., NORMAN L. Antigenic analysis of Echinococcus antigens by agar diffusion techniques. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1961 Sep;10:727–734. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1961.10.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KILEJIAN A., SAUER K., SCHWABE C. W. Host-parasite relationships in echnoccosis. VIII. Infrared spectra and chemical composition of the hydatid cyst. Exp Parasitol. 1962 Oct;12:377–392. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(62)90049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilejian A., Schwabe C. W. Studies on the polysaccharides of the Echinococcus granulosus cyst, with observations on a possible mechanism for laminated membrane formation. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1971 Sep 15;40(1):25–36. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(71)90058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oriol C., Oriol R. Physiocochemical properties of a lipoprotein antigen of Echinococcus granulosus. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1975 Jan;24(1):96–100. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1975.24.96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oriol R., Williams J. F., Pérez Esandi M. V., Oriol C. Purification of lipoprotein antigens of Echinococcus granulosus from sheep hydatid fluid. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1971 Jul;20(4):569–574. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1971.20.569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley E. M., Dixon J. B., Kelly D. F., Cox D. A. The immune response to Echinococcus granulosus: sequential histological observations of lymphoreticular and connective tissues during early murine infection. J Comp Pathol. 1985 Jan;95(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(85)90081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russi S., Siracusano A., Vicari G. Isolation and characterization of a blood P1 active carbohydrate antigen of Echinococcus granulosus cyst membrane. J Immunol. 1974 Mar;112(3):1061–1069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHIFFMAN G., KABAT E. A., THOMPSON W. IMMUNOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON BLOOD GROUPS. XXX. CLEAVAGE OF A, B, AND H BLOOD-GROUP SUBSTANCES BY ALKALI. Biochemistry. 1964 Jan;3:113–120. doi: 10.1021/bi00889a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd J. C., McManus D. P. Specific and cross-reactive antigens of Echinococcus granulosus hydatid cyst fluid. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Sep;25(2):143–154. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todorov T., Dakov I., Kosturkova M., Tenev S., Dimitrov A. Immunoreactivity in pulmonary echinococcosis. A comparative study of immunodiagnostic tests. Bull World Health Organ. 1979;57(5):735–740. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varela-Díaz V. M., Coltorti E. A., D'Alessandro A. Immunoelectrophoresis tests showing Echinococcus granulosus arc 5 in human cases of Echinococcus vogeli and cysticercosis-multiple myeloma. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1978 May;27(3):554–557. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1978.27.554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varela-Díaz V. M., Coltorti E. A., Prezioso U., López-Lemes M. H., Guisantes J. A., Yarzábal L. A. Evaluation of three immunodiagnostic tests for human hydatid disease. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1975 Mar;24(2):312–319. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1975.24.312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varela-Díaz V. M., Eckert J., Rausch R. L., Coltorti E. A., Hess U. Detection of the Echinococcus granulosus diagnostic arc 5 in sera from patients with surgically-confirmed E. multilocularis infection. Z Parasitenkd. 1977 Sep 21;53(2):183–188. doi: 10.1007/BF00380463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarzábal L. A., Leiton J., López-Lemes M. H. The diagnosis of human pulmonary hydatidosis by the immunoelectrophoresis test. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1974 Jul;23(4):662–666. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1974.23.662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarzábal L. A., Schantz P. M., López-Lemes M. H. Comparative sensitivity and specificity of the Casoni intradermal and the immunoelectrophoresis tests for the diagnosis of hydatid disease. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1975 Sep;24(5):843–848. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1975.24.843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


