Abstract
The isotype profile, particularly emphasizing IgG subclass distribution, of dsDNA antibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus was evaluated using an especially adapted ELISA technique. Anti-dsDNA antibodies were quantified with class-specific antisera and subclass-specific monoclonal antibodies. IgG subclass specificity was proven with 20 myeloma proteins differing in light chains and allotypes. The standardization with myeloma proteins proved to be useful and reliable. Results from more than 100 anti-dsDNA positive sera from SLE patients showed specific antibodies within the three subclasses (IgG1: 52-100%, IgG2: 0-39%, IgG3: 0-48%). IgG4 was not detected in significant amounts. No correlation to the subclass distribution of total IgG was found. Each patients' serum displayed an individual isotype pattern that remained constant in longitudinal studies, independent of anti-dsDNA titre fluctuations. These results suggest a stable population of autoreactive clones in the progress of the disease.
Full text
PDF

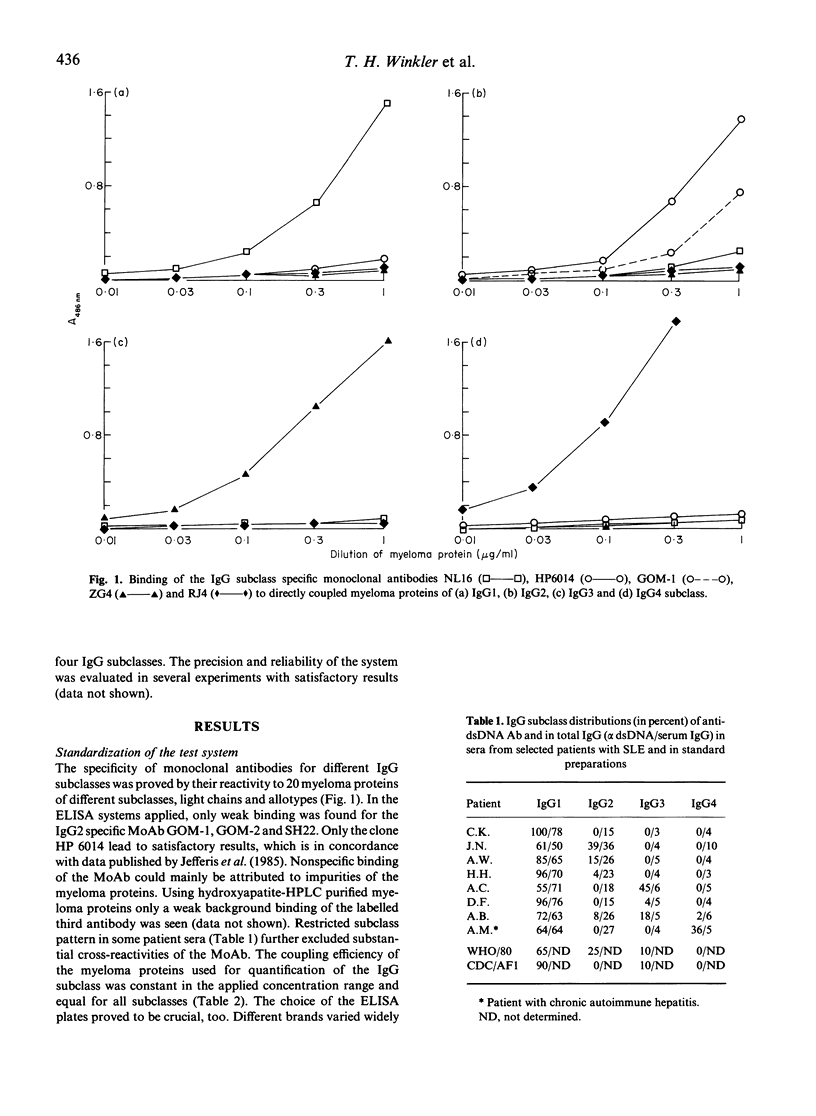
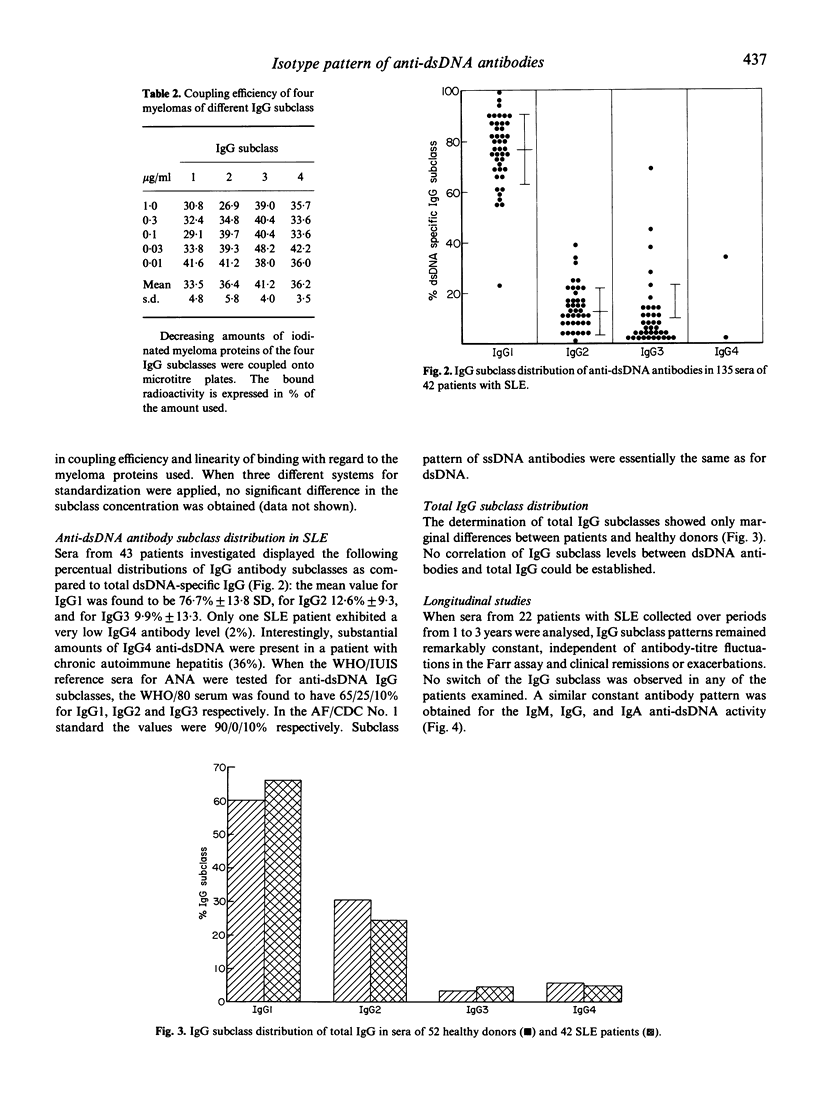


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson P. M., Lampman G. W., Furie B. C., Naparstek Y., Schwartz R. S., Stollar B. D., Furie B. Homology of the NH2-terminal amino acid sequences of the heavy and light chains of human monoclonal lupus autoantibodies containing the dominant 16/6 idiotype. J Clin Invest. 1985 Apr;75(4):1138–1143. doi: 10.1172/JCI111808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton D. R. Immunoglobulin G: functional sites. Mol Immunol. 1985 Mar;22(3):161–206. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(85)90151-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll P., Stafford D., Schwartz R. S., Stollar B. D. Murine monoclonal anti-DNA autoantibodies bind to endogenous bacteria. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2):1086–1090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David G. S. Solid state lactoperoxidase: a highly stable enzyme for simple, gentle iodination of proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jul 25;48(2):464–471. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80074-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. A., Dyer K., Craven S. Y., Fuller C. R., Yount W. J. Subclass restriction and polyclonality of the systemic lupus erythematosus marker antibody anti-Sm. J Clin Invest. 1985 Apr;75(4):1270–1277. doi: 10.1172/JCI111826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagan D. L., Slaughter C. A., Capra J. D., Sullivan T. J. Monoclonal antibodies to immunoglobulin G4 induce histamine release from human basophils in vitro. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1982 Nov;70(5):399–404. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(82)90031-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarström L., Heigl Z., Smith C. I. IgG subclass distribution of autoantibodies against ribonucleoproteins. Scand J Rheumatol. 1986;15(1):75–79. doi: 10.3109/03009748609092672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferis R., Reimer C. B., Skvaril F., de Lange G., Ling N. R., Lowe J., Walker M. R., Phillips D. J., Aloisio C. H., Wells T. W. Evaluation of monoclonal antibodies having specificity for human IgG sub-classes: results of an IUIS/WHO collaborative study. Immunol Lett. 1985;10(3-4):223–252. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(85)90082-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiger J. A., Jr, Sinsheimer R. L. Vegetative lambda DNA. IV. Fractionation of replicating lambda DNA on benzoylated-naphthoylated DEAE cellulose. J Mol Biol. 1969 Mar 28;40(3):467–490. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90166-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein F., Skvaril F., Vermeeren R., Vlug A., Duimel W. J. The quantification of human IgG subclasses in reference preparations. Clin Chim Acta. 1985 Aug 15;150(2):119–127. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(85)90262-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohleisen B., Kalies I., Kölble K., Kalden J. R. Patient-specific heterogeneity of antinuclear antibodies as revealed by an isoelectric focusing immunoblot system. Scand J Immunol. 1987 Jul;26(1):71–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1987.tb02236.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. L., Tang F. L., Chan E. K., Pollard K. M., Tsay G., Tan E. M. IgG subclasses of autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjogren's syndrome, and drug-induced autoimmunity. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 15;137(8):2528–2534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sela O., el-Roeiy A., Isenberg D. A., Kennedy R. C., Colaco C. B., Pinkhas J., Shoenfeld Y. A common anti-DNA idiotype in sera of patients with active pulmonary tuberculosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Jan;30(1):50–56. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seppälä I. J., Routonen N., Sarnesto A., Mattila P. A., Mäkelä O. The percentages of six immunoglobulin isotypes in human antibodies to tetanus toxoid: standardization of isotype-specific second antibodies in solid-phase assay. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Sep;14(9):868–875. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zouali M., Jefferis R., Eyquem A. IgG subclass distribution of autoantibodies to DNA and to nuclear ribonucleoproteins in autoimmune diseases. Immunology. 1984 Mar;51(3):595–600. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Roiey A., Sela O., Isenberg D. A., Feldman R., Colaco B. C., Kennedy R. C., Shoenfeld Y. The sera of patients with Klebsiella infections contain a common anti-DNA idiotype (16/6) Id and anti-polynucleotide activity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Mar;67(3):507–515. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


