Abstract
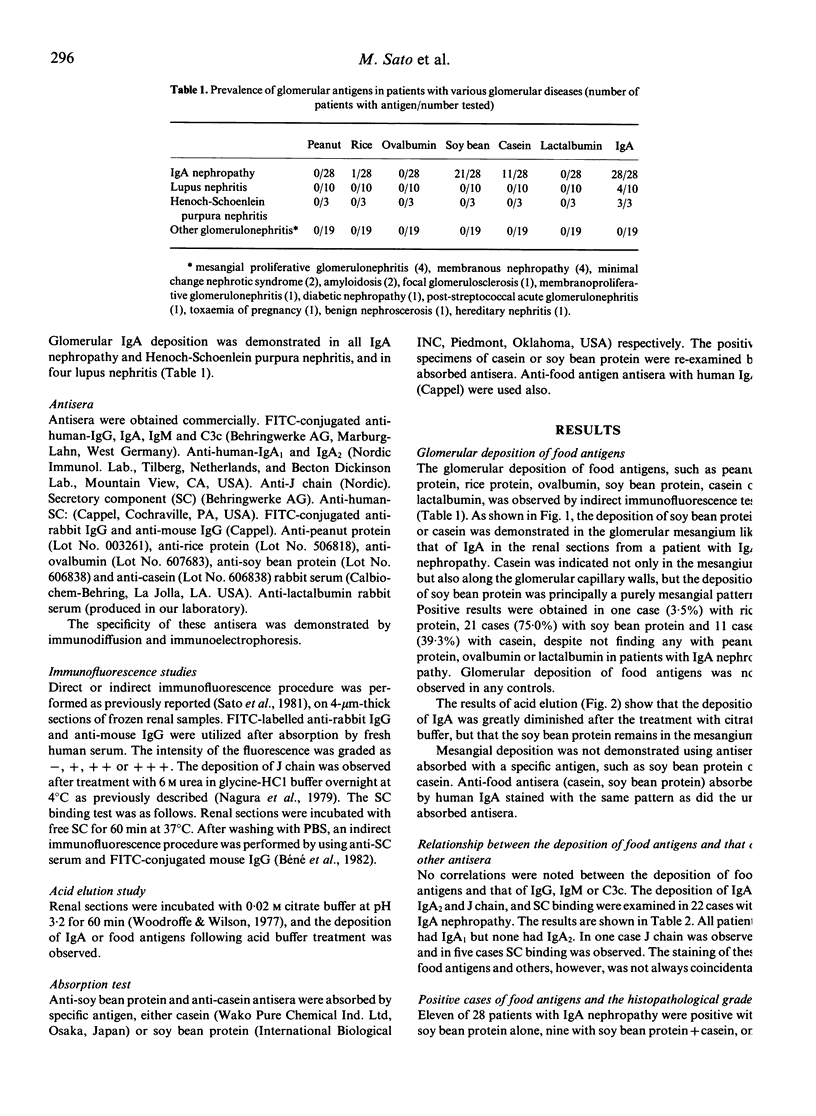
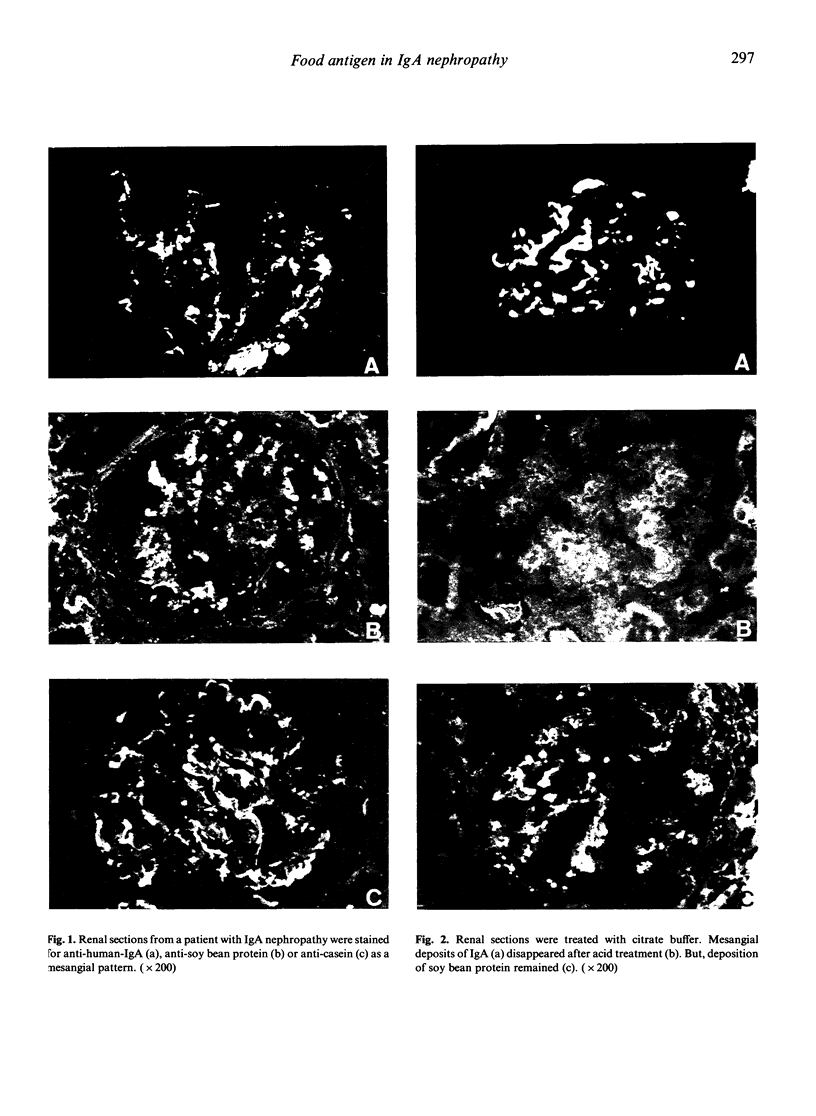
Recently, we reported on the importance of food antigens on the pathogenesis of an experimentally-induced model of, and some patients with, IgA nephropathy. In this paper, the glomerular deposition of food antigens (casein, lactalbumin, peanut protein, soy bean protein, rice protein, ovalbumin) was investigated by an immunofluorescence technique in 28 patients with IgA nephropathy and 32 controls (ten with lupus nephritis, three with Henoch-Schoenlein purpura nephritis and 19 with other glomerulonephritis). Glomerular IgA deposition was demonstrated in all IgA nephropathy and Henoch-Schoenlein purpura nephritis, and in four lupus nephritis. Positive findings of food antigens, observed as mesangial pattern, were obtained in eleven cases (39.3%) with casein, 21 (75.0%) with soy bean protein and one (3.6%) with rice protein in IgA nephropathy, even though no such findings were seen in the control group. Eleven of 28 patients with IgA nephropathy were positive with soy bean protein alone, nine were positive with soy bean protein + casein, one was positive with soy bean protein + casein + rice protein, and one was positive with casein alone. The deposition of food antigens was not observed in six cases only. Furthermore, no correlation was noted between the deposition of food antigens and the deposition of IgA1, IgA2 or J chain, in vitro binding of the secretory component, or histopathological grades. These results suggest that the exact meanings of glomerular deposition are unclear. Food antigens are postulated, however, as possibly participating strongly in the pathogenesis and as being localized in the glomerular mesangium as an antigen in some patients with IgA nephropathy.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clarkson A. R., Woodroffe A. J., Bannister K. M., Lomax-Smith J. D., Aarons I. The syndrome of IgA nephropathy. Clin Nephrol. 1984 Jan;21(1):7–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppo R., Basolo B., Rollino C., Roccatello D., Martina G., Amore A., Bongiorno G., Piccoli G. Mediterranean diet and primary IgA nephropathy. Clin Nephrol. 1986 Aug;26(2):72–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emancipator S. N., Gallo G. R., Lamm M. E. Experimental IgA nephropathy induced by oral immunization. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):572–582. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornasieri A., Sinico R. A., Maldifassi P., Bernasconi P., Vegni M., D'Amico G. IgA-antigliadin antibodies in IgA mesangial nephropathy (Berger's disease). Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1987 Jul 11;295(6590):78–80. doi: 10.1136/bmj.295.6590.78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent J., Branellec A., Heslan J. M., Rostoker G., Bruneau C., André C., Intrator L., Lagrue G. An increase in circulating IgA antibodies to gliadin in IgA mesangial glomerulonephritis. Am J Nephrol. 1987;7(3):178–183. doi: 10.1159/000167460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagura H., Brandtzaeg P., Nakane P. K., Brown W. R. Ultrastructural localization of J chain in human intestinal mucosa. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1044–1050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy J., Uj M., Szücs G., Trinn C., Burger T. Herpes virus antigens and antibodies in kidney biopsies and sera of IgA glomerulonephritic patients. Clin Nephrol. 1984 May;21(5):259–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell M. W., Mestecky J., Julian B. A., Galla J. H. IgA-associated renal diseases: antibodies to environmental antigens in sera and deposition of immunoglobulins and antigens in glomeruli. J Clin Immunol. 1986 Jan;6(1):74–86. doi: 10.1007/BF00915367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancho J., Egido J., Rivera F., Hernando L. Immune complexes in IgA nephropathy: presence of antibodies against diet antigens and delayed clearance of specific polymeric IgA immune complexes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Oct;54(1):194–202. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato M., Ideura T., Koshikawa S. Experimental IgA nephropathy in mice. Lab Invest. 1986 Apr;54(4):377–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato M., Koshikawa S., Arakawa M. Glomerular deposition of antihemophilic factor antigen in various renal diseases. Clin Nephrol. 1981 Feb;15(2):80–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato M., Nakajima Y., Koshikawa S. Effect of sodium cromoglycate on an experimental model of IgA nephropathy. Clin Nephrol. 1987 Mar;27(3):141–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato M., Takayama K., Wakasa M., Koshikawa S. Estimation of circulating immune complexes following oral challenge with cow's milk in patients with IgA nephropathy. Nephron. 1987;47(1):43–48. doi: 10.1159/000184455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodroffe A. J., Wilson C. B. An evaluation of elution techniques in the study of immune complex glomerulonephritis. J Immunol. 1977 May;118(5):1788–1794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



