Abstract
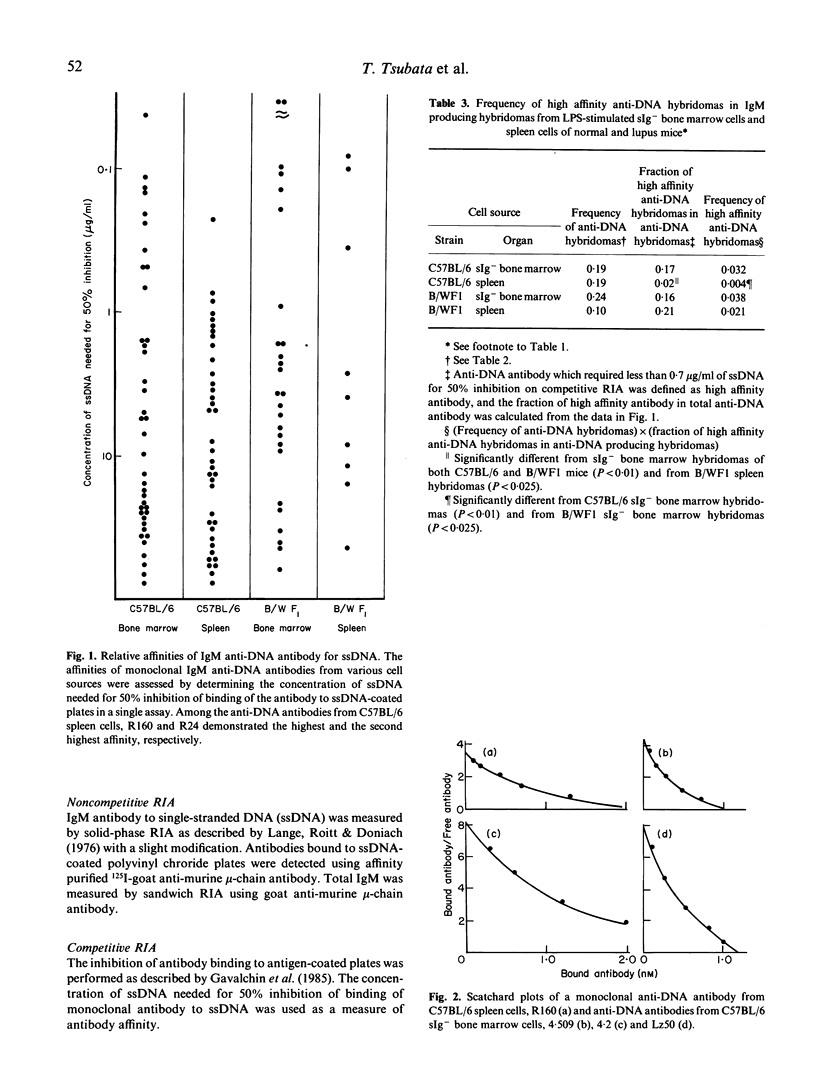
The precursor frequency for anti-DNA antibody producing cells and the affinity of antibodies secreted by these cells in both immature prereceptor B cell populations and mature B cell populations were compared between 8-week-old C57BL/6 female mice and 9-month-old B/WF1 female mice by producing a large collection of IgM secreting hybridomas from LPS-stimulated B cells. The data indicate that precursor cells for high affinity anti-DNA antibody are eliminated as they mature in C57BL/6 mice, while a sizable number of such clones are present in mature splenic B cells of aged B/WF1 mice. These results suggest that the emergence of precursors for high affinity anti-DNA producing cells in mature B cell population is an important factor in the pathogenesis of SLE.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cowdery J. S., Jacobi S. M., Pitts A. K., Tyler T. L. Defective B cell clonal regulation and autoantibody production in New Zealand black mice. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):760–764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dighiero G., Lymberi P., Holmberg D., Lundquist I., Coutinho A., Avrameas S. High frequency of natural autoantibodies in normal newborn mice. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):765–771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish F., Ziff M. The in vitro and in vivo induction of anti-double-stranded DNA antibodies in normal and autoimmune mice. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):409–414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froscher B. G., Klinman N. R. Strain-specific silencing of a predominant antidextran clonotype family. J Exp Med. 1985 Nov 1;162(5):1620–1633. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.5.1620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavalchin J., Nicklas J. A., Eastcott J. W., Madaio M. P., Stollar B. D., Schwartz R. S., Datta S. K. Lupus prone (SWR x NZB)F1 mice produce potentially nephritogenic autoantibodies inherited from the normal SWR parent. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):885–894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg D., Freitas A. A., Portnoï D., Jacquemart F., Avrameas S., Coutinho A. Antibody repertoires of normal BALB/c mice: B lymphocyte populations defined by state of activation. Immunol Rev. 1986 Oct;93:147–169. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1986.tb01506.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornick C. L., Karuch F. Antibody affinity. 3. The role of multivalance. Immunochemistry. 1972 Mar;9(3):325–340. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90096-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jyonouchi H., Kincade P. W., Landreth K. S., Lee G., Good R. A., Gershwin M. E. Age-dependent deficiency of B lymphocyte lineage precursors in NZB mice. J Exp Med. 1982 Jun 1;155(6):1665–1678. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.6.1665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinman D. M., Steinberg A. D. Proliferation of anti-DNA-producing NZB B cells in a non-autoimmune environment. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 1;137(1):69–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinman N. R., Schrater A. F., Katz D. H. Immature B cells as the target for in vivo tolerance induction. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):1970–1973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinman N. R., Stone M. R. Role of variable region gene expression and environmental selection in determining the antiphosphorylcholine B cell repertoire. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):1948–1961. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.1948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohno A., Yoshida H., Sekita K., Maruyama N., Ozaki S., Hirose S., Shirai T. Genetic regulation of the class conversion of dsDNA-specific antibodies in (NZB X NZW)F1 hybrid. Immunogenetics. 1983;18(5):513–524. doi: 10.1007/BF00364392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange A., Roitt I. M., Doniach D. A double antibody solid phase assay for DNA autoantibodies for clinical use. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Aug;25(2):191–198. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mach P. S., Kharouby M., Lutcher F., Olivier J. L., Bazely N., Dougados M., Amor B. The in vitro production and regulation of anti-double stranded DNA antibodies by peripheral blood mononuclear cells from normals and patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Aug;57(2):338–344. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa S., Takemori T., Rajewsky K. The expression of a set of antibody variable regions in lipopolysaccharide-reactive B cells at various stages of ontogeny and its control by anti-idiotypic antibody. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Apr;13(4):318–325. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papoian R., Pillarisetty R., Talal N. Immunological regulation of spontaneous antibodies to DNA and RNA. II. Sequential switch from IgM to IgG in NZB/NZW F1 mice. Immunology. 1977 Jan;32(1):75–79. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickard A. R., Havas H. F. The kinetics of antibody production and affinity in BALB-c mice immune and partially tolerant to the 2,4-dinitrophenyl determinant. J Immunol. 1972 Dec;109(6):1360–1370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisetsky D. S., Caster S. A. The B-cell repertoire for autoantibodies: frequency of precursor cells for anti-DNA antibodies. Cell Immunol. 1982 Sep 15;72(2):294–305. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90477-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley R. L., Klinman N. R. Differences in antibody repertoires for (4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl)acetyl (NP) in splenic vs immature bone marrow precursor cells. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3050–3055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siskind G. W., Benacerraf B. Cell selection by antigen in the immune response. Adv Immunol. 1969;10:1–50. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60414-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack J. H., Hang L., Barkley J., Fulton R. J., D'Hoostelaere L., Robinson A., Dixon F. J. Isotypes of spontaneous and mitogen-induced autoantibodies in SLE-prone mice. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1271–1275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward M. W., Hay F. C. Changes in immunoglobulin class and subclass of anti-DNA antibodies with increasing age in N/ZBW F1 hybrid mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Nov;26(2):363–370. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfield J. B., Faiferman I., Koffler D. Avidity of anti-DNA antibodies in serum and IgG glomerular eluates from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Association of high avidity antinative DNA antibody with glomerulonephritis. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jan;59(1):90–96. doi: 10.1172/JCI108626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida H., Kohno A., Ohta K., Hirose S., Maruyama N., Shirai T. Genetic studies of autoimmunity in New Zealand mice. III. Associations among anti-DNA antibodies, NTA, and renal disease in (NZB x NZW)F1 x NZW backcross mice. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):433–437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida M., Yoshida H., Muso E., Tamura T., Shimada T., Kawai C., Hamashima Y. Clonotypic comparison of IgG anti-DNA antibodies of healthy subjects and systemic lupus erythematosus patients: studies on heterogeneity and avidity. Immunol Lett. 1987 Jun;15(2):139–144. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(87)90045-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


