Abstract
When administered by various routes 48 h before a high systemic dose (10 degrees) of sheep red blood cells (SRBC), Cyclosporin A (CsA) prevented the suppression of delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH) reactions elicited 4 days later. Augmentation of DTH was observed over a wide range (5-200 mg/kg) and with circulating CsA levels ranging below 45 ng/ml at the time of immunization or antigen challenge. Splenic lymphocytes from vehicle- and CsA-treated mice exhibited good proliferative responses to mitogen in vitro, but only those from CsA-treated animals responded to antigen. Expression of DTH was associated with a progressive, 2-fold increase in the absolute numbers of splenic L3T4+ cells, whereas no significant alteration in the number of Lyt-2+ lymphocytes was recorded. B cell and macrophage numbers in the spleen were unaffected by CsA. In contrast to its potentiating effects on cell-mediated immunity, CsA caused profound (up to 100%) suppression of the concomitant production of splenic anti-SRBC IgM-secreting plasma cells. Circulating anti-SRBC antibody levels were also markedly reduced. These data show that CsA can permit induction of TDTH, whilst suppressing T-dependent humoral immunity and without significant change in absolute numbers of Lyt-2+ cells.
Full text
PDF

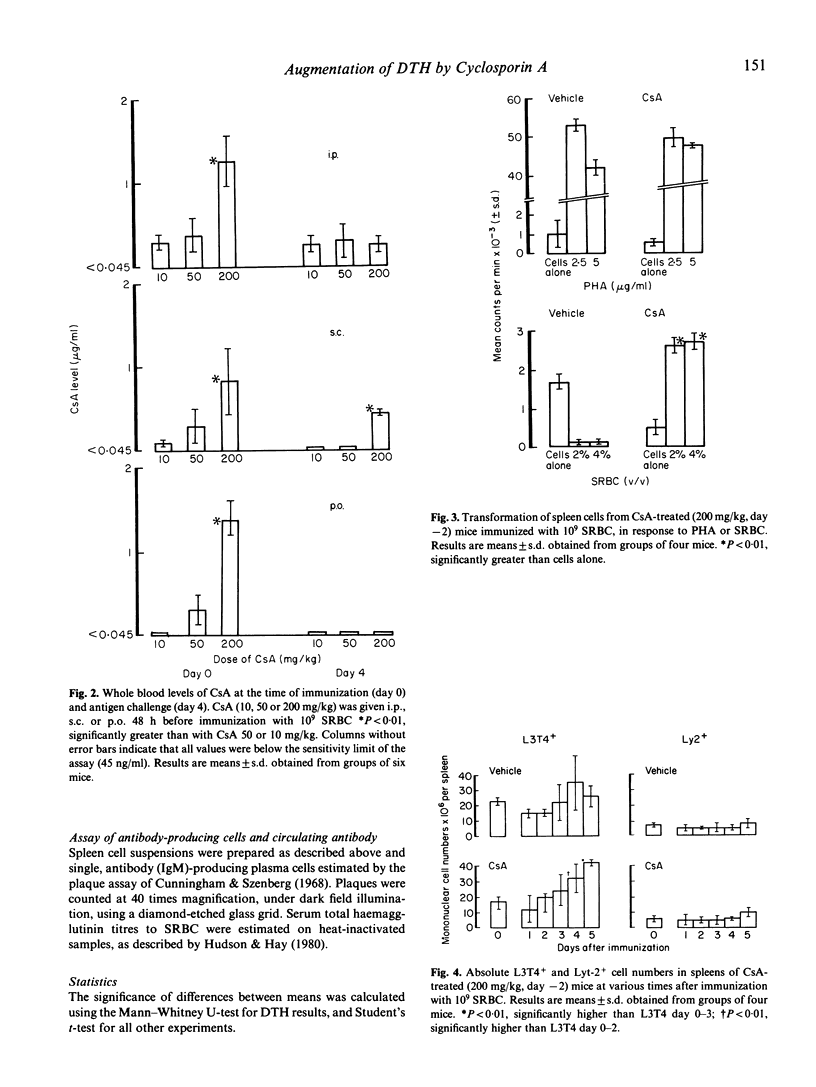



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldridge R. D., Thomson A. W. Paradoxical augmentation of tuberculin-like hypersensitivity, but not Jones-Mote or contact hypersensitivity, in cyclosporin A treated guinea pigs. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1986;79(3):225–230. doi: 10.1159/000233977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altmann D. M., Blyth W. A. The effects of cyclosporin A on the induction, expression and regulation of the immune response to herpes simplex virus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Jan;59(1):17–22. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Askenase P. W., Hayden B. J., Gershon R. K. Augmentation of delayed-type hypersensitivity by doses of cyclophosphamide which do not affect antibody responses. J Exp Med. 1975 Mar 1;141(3):697–702. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.3.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braida M., Knop J. Effect of cyclosporin A on the T-effector and T-suppressor cell response in contact sensitivity. Immunology. 1986 Dec;59(4):503–507. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor H., Shen F. W., Boyse E. A. Separation of helper T cells from suppressor T cells expressing different Ly components. II. Activation by antigen: after immunization, antigen-specific suppressor and helper activities are mediated by distinct T-cell subclasses. J Exp Med. 1976 Jun 1;143(6):1391–1340. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.6.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham A. J., Szenberg A. Further improvements in the plaque technique for detecting single antibody-forming cells. Immunology. 1968 Apr;14(4):599–600. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flood P. M., Louie D. C. Mechanisms of Ly2 suppressor cell activity. Activation of an Ly1 I-J+ cell is required to transduce the suppressive signal. J Exp Med. 1984 May 1;159(5):1413–1428. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.5.1413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill H. K., Liew F. Y. Regulation of delayed-type hypersensitivity. III. Effect of cyclophosphamide on the suppressor cells for delayed-type hypersensitivity to sheep erythrocytes in mice. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Mar;8(3):172–176. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaibara N., Hotokebuchi T., Takagishi K., Katsuki I. Paradoxical effects of cyclosporin A on collagen arthritis in rats. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):2007–2015. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerckhaert J. A., Van den Berg G. J., Willers J. M. Influence of cyclophosphamide on the delayed hypersensitivity of the mouse. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1974 Mar-Apr;125(3):415–426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagrange P. H., Mackaness G. B., Miller T. E. Influence of dose and route of antigen injection on the immunological induction of T cells. J Exp Med. 1974 Mar 1;139(3):528–542. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.3.528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew F. Y. Regulation of delayed-type hypersensitivity. I. T suppressor cells for delayed-type hypersensitivity to sheep erythrocytes in mice. Eur J Immunol. 1977 Oct;7(10):714–718. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830071013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew F. Y., Sia D. Y., Parish C. R., McKenzie I. F. Major histocompatibility gene complex (MHC)-coded determinants on antigen-specific suppressor factor for delayed-type hypersensitivity and surface phenotypes of cells producing the factor. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Apr;10(4):305–309. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh L. C., Morrice L. M., Udagawa Y., Thomson A. W. Influence of tumour carriage on the production of lymphokines affecting macrophage behaviour. Immunology. 1986 Mar;57(3):359–365. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milon G., Truffa-Bachi P., Shidani B., Marchal G. Cyclosporin A inhibits the delayed-type hypersensitivity effector function of T lymphocytes without affecting their clonal expansion. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1984 Nov-Dec;135D(3):237–245. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2625(84)81188-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker D., Drössler K., Turk J. L. Kinetics of the effect of a single dose of cyclosporin-A on antibody and cell mediated immune responses in the guinea pig. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1984;6(1):67–74. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(84)90037-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramshaw I. A., McKenzie I. F., Bretscher P. A., Parish C. R. Discrimination of suppressor T cells of humoral and cell-mediated immunity by anti-Ly and anti-Ia sera. Cell Immunol. 1977 Jun 15;31(2):364–369. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90038-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiltknecht E., Ada G. L. In vivo effects of cyclosporine on influenza A virus-infected mice. Cell Immunol. 1985 Mar;91(1):227–239. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90046-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shidani B., Motta I., Truffa-Bachi P. Cyclosporin A does not affect the in vitro induction of antigen-specific delayed-type hypersensitivity-mediating T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Feb;17(2):291–294. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimamura T., Habu S., Hashimoto K., Sasaki S. Feedback suppression of the immune response in vivo. III. Lyt-1+ B cells are suppressor-inducer cells. Cell Immunol. 1984 Jan;83(1):221–224. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90242-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A. W., Moon D. K., Inoue Y., Geczy C. L., Nelson D. S. Modification of delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions to ovalbumin in cyclosporin A-treated guinea-pigs. Immunology. 1983 Feb;48(2):301–308. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster L. M., Thomson A. W. Cyclosporin A prevents suppression of delayed-type hypersensitivity in mice immunized with high-dose sheep erythrocytes. Immunology. 1987 Mar;60(3):409–414. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wick G., Müller P. U., Schwarz S. Effect of cyclosporin A on spontaneous autoimmune thyroiditis of Obese strain (OS) chickens. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Oct;12(10):877–881. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830121014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


