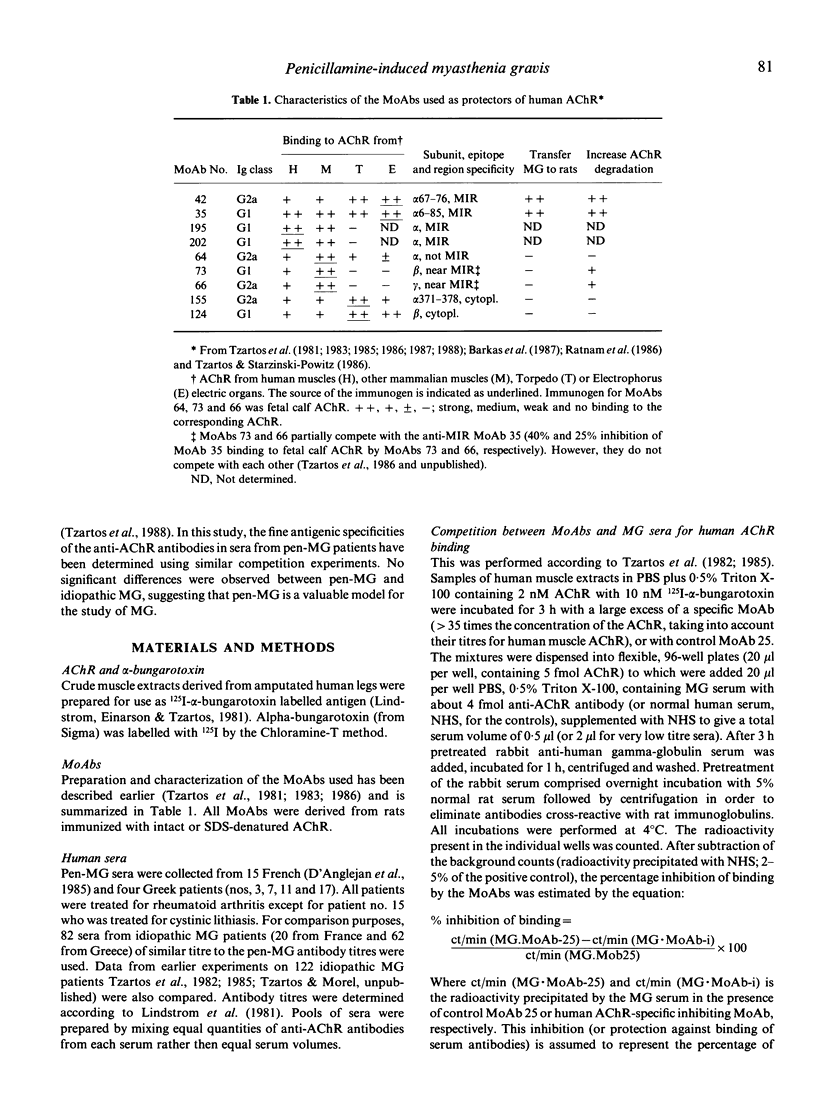
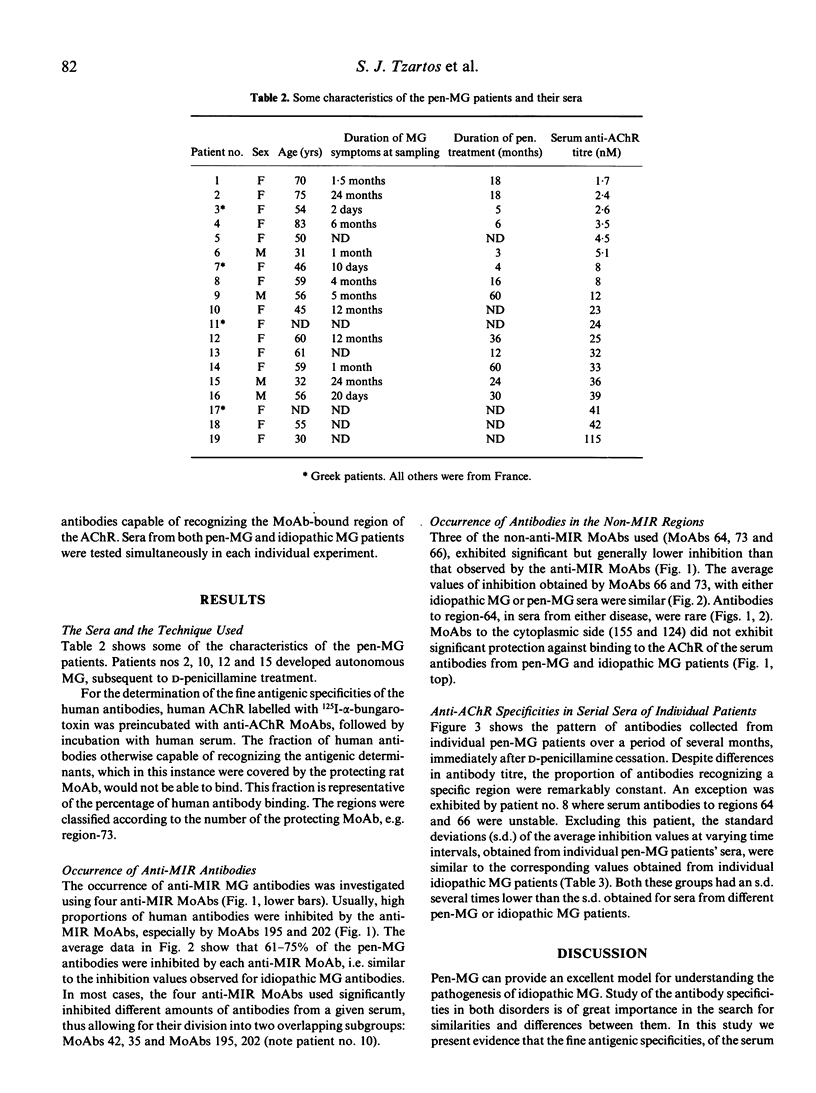
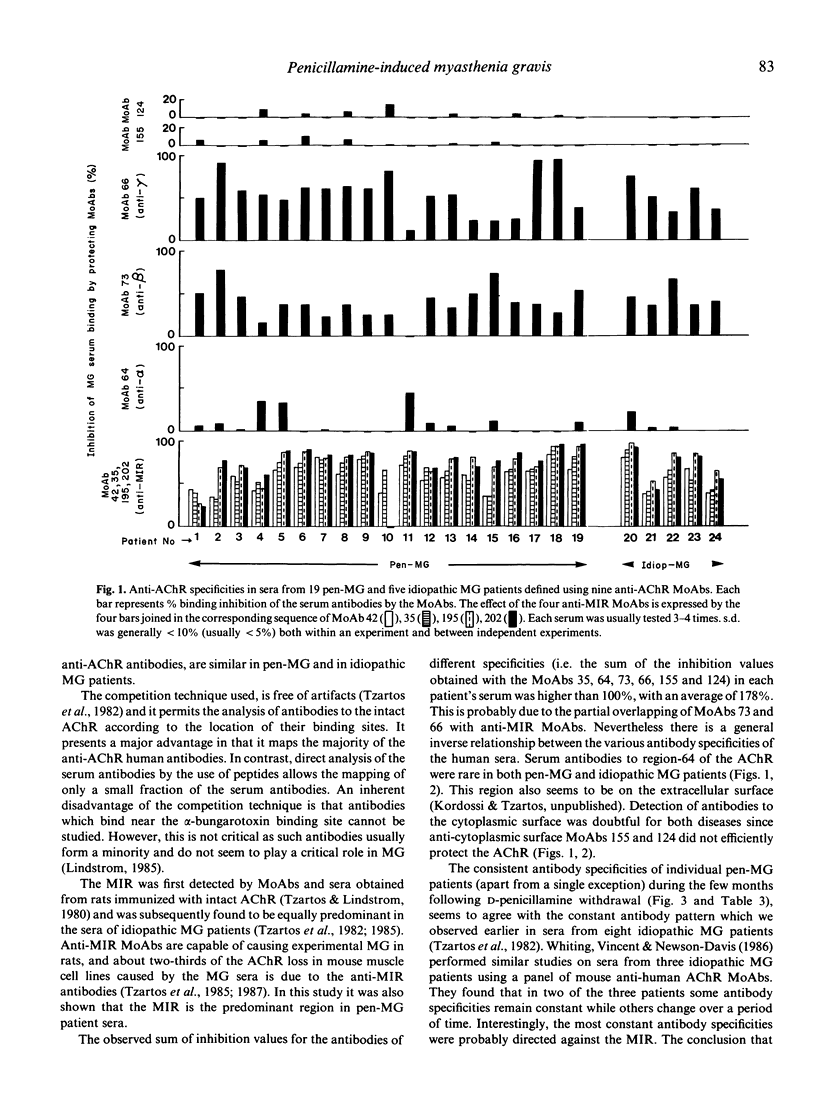
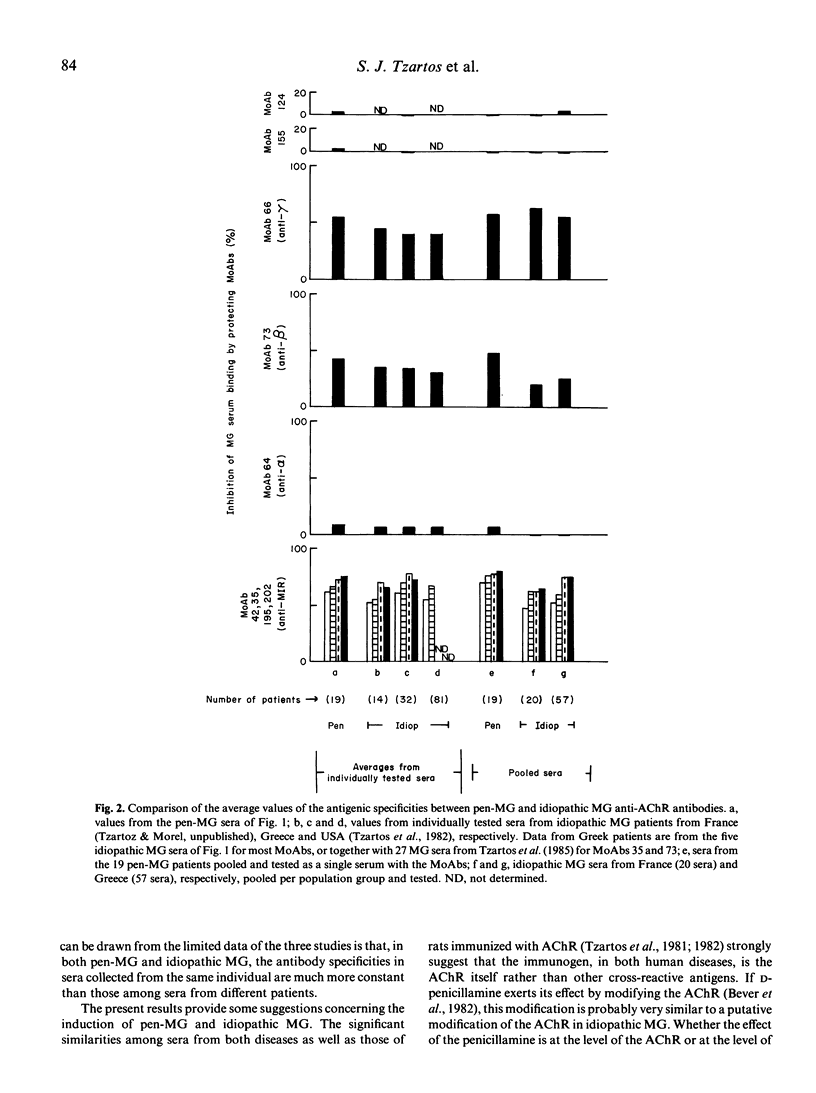
Abstract
A small fraction of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other diseases on D-penicillamine treatment may develop antibodies against the acetylcholine receptor (AChR) and symptoms of myasthenia gravis (MG). The mechanism leading to this phenomenon is not known. We have studied the fine antigenic specificities of the anti-AChR antibodies in 19 D-penicillamine-induced MG (pen-MG) patients and compared them with those of antibodies from 204 idiopathic MG patients (the data for 122 obtained from earlier experiments). Antigenic specificities of the circulating antibodies were determined by the capacity of monoclonal antibodies (MoAbs), against certain determinants on the AChR, to inhibit binding of the serum antibodies to the AChR. Monoclonal antibodies against alpha, beta and gamma subunits were used. The anti-AChR antibody patterns of pen-MG patients were very similar to those of idiopathic MG patients. Antibodies to the main immunogenic region, which is located on the extracellular surface of the alpha-subunit, were the predominant group. The variations of antibody specificities in serial sera collected from individual patients at different times were usually small, as were those of idiopathic MG. These results strongly suggest that the antibody repertoire in the sera of idiopathic and pen-MG patients is very similar.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albers J. W., Hodach R. J., Kimmel D. W., Treacy W. L. Penicillamine-associated myasthenia gravis. Neurology. 1980 Nov;30(11):1246–1249. doi: 10.1212/wnl.30.11.1246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkas T., Mauron A., Roth B., Alliod C., Tzartos S. J., Ballivet M. Mapping the main immunogenic region and toxin-binding site of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Science. 1987 Jan 2;235(4784):77–80. doi: 10.1126/science.2432658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bever C. T., Jr, Chang H. W., Penn A. S., Jaffe I. A., Bock E. Penicillamine-induced myasthenia gravis: effects of penicillamine on acetylcholine receptor. Neurology. 1982 Oct;32(10):1077–1082. doi: 10.1212/wnl.32.10.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucknall R. C. Myasthenia associated with D-penicillamine therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Proc R Soc Med. 1977;70 (Suppl 3):114–117. doi: 10.1177/00359157770700S335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burres S. A., Kanter M. E., Richman D. P., Arnason B. G. Studies on the pathophysiology of chronic D-penicillamine-induced myasthenia. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;377:640–651. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb33763.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drachman D. B., de Silva S., Ramsay D., Pestronk A. Humoral pathogenesis of myasthenia gravis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;505:90–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb51285.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuncl R. W., Pestronk A., Drachman D. B., Rechthand E. The pathophysiology of penicillamine-induced myasthenia gravis. Ann Neurol. 1986 Dec;20(6):740–744. doi: 10.1002/ana.410200617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Einarson B., Tzartos S. Production and assay of antibodies to acetylcholine receptors. Methods Enzymol. 1981;74(Pt 100):432–460. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)74031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J. Immunobiology of myasthenia gravis, experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis, and Lambert-Eaton syndrome. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:109–131. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.000545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnam M., Nguyen D. L., Rivier J., Sargent P. B., Lindstrom J. Transmembrane topography of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor: immunochemical tests contradict theoretical predictions based on hydrophobicity profiles. Biochemistry. 1986 May 6;25(9):2633–2643. doi: 10.1021/bi00357a052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell A. S., Lindstrom J. M. Penicillamine-induced myasthenia gravis associated with antibodies to acetylcholine receptor. Neurology. 1978 Aug;28(8):847–849. doi: 10.1212/wnl.28.8.847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent P. B., Hedges B. E., Tsavaler L., Clemmons L., Tzartos S., Lindstrom J. M. Structure and transmembrane nature of the acetylcholine receptor in amphibian skeletal muscle as revealed by cross-reacting monoclonal antibodies. J Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;98(2):609–618. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.2.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scadding G. K., Calder L., Newsom-Davis J. The in vitro effects of D-penicillamine upon anti-AChR production by thymic and peripheral blood lymphocytes from patients with myasthenia gravis. Muscle Nerve. 1983 Nov-Dec;6(9):656–660. doi: 10.1002/mus.880060906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S. J., Kokla A., Walgrave S. L., Conti-Tronconi B. M. Localization of the main immunogenic region of human muscle acetylcholine receptor to residues 67-76 of the alpha subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):2899–2903. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.2899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S. J., Lindstrom J. M. Monoclonal antibodies used to probe acetylcholine receptor structure: localization of the main immunogenic region and detection of similarities between subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):755–759. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S. J. Myasthenia gravis studied by monoclonal antibodies to the acetylcholine receptor. In Vivo. 1988 Jan-Feb;2(1):105–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S. J., Rand D. E., Einarson B. L., Lindstrom J. M. Mapping of surface structures of electrophorus acetylcholine receptor using monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8635–8645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S. J., Seybold M. E., Lindstrom J. M. Specificities of antibodies to acetylcholine receptors in sera from myasthenia gravis patients measured by monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):188–192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S. J., Sophianos D., Efthimiadis A. Role of the main immunogenic region of acetylcholine receptor in myasthenia gravis. An Fab monoclonal antibody protects against antigenic modulation by human sera. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2343–2349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S. J., Starzinski-Powitz A. Decrease in acetylcholine-receptor content of human myotube cultures mediated by monoclonal antibodies to alpha, beta and gamma subunits. FEBS Lett. 1986 Feb 3;196(1):91–95. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80220-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S., Hochschwender S., Vasquez P., Lindstrom J. Passive transfer of experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis by monoclonal antibodies to the main immunogenic region of the acetylcholine receptor. J Neuroimmunol. 1987 Jun;15(2):185–194. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(87)90092-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S., Langeberg L., Hochschwender S., Lindstrom J. Demonstration of a main immunogenic region on acetylcholine receptors from human muscle using monoclonal antibodies to human receptor. FEBS Lett. 1983 Jul 11;158(1):116–118. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80688-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S., Langeberg L., Hochschwender S., Swanson L. W., Lindstrom J. Characteristics of monoclonal antibodies to denatured Torpedo and to native calf acetylcholine receptors: species, subunit and region specificity. J Neuroimmunol. 1986 Jan;10(3):235–253. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(86)90105-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A., Newsom-Davis J. Acetylcholine receptor antibody characteristics in myasthenia gravis. II. Patients with penicillamine-induced myasthenia or idiopathic myasthenia of recent onset. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Aug;49(2):266–272. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiting P. J., Vincent A., Newsom-Davis J. Myasthenia gravis: monoclonal antihuman acetylcholine receptor antibodies used to analyze antibody specificities and responses to treatment. Neurology. 1986 May;36(5):612–617. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.5.612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- d'Anglejan J., Morel E., Feuillet-Fieux M. N., Raimond F., Vernet der Garabedian B., Jacob L., Bach J. F. Myasthénie induite par la D-pénicillamine. Etude des corrélations immuno-cliniques dans 23 cas. Presse Med. 1985 Dec 28;14(46):2336–2340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


