Abstract
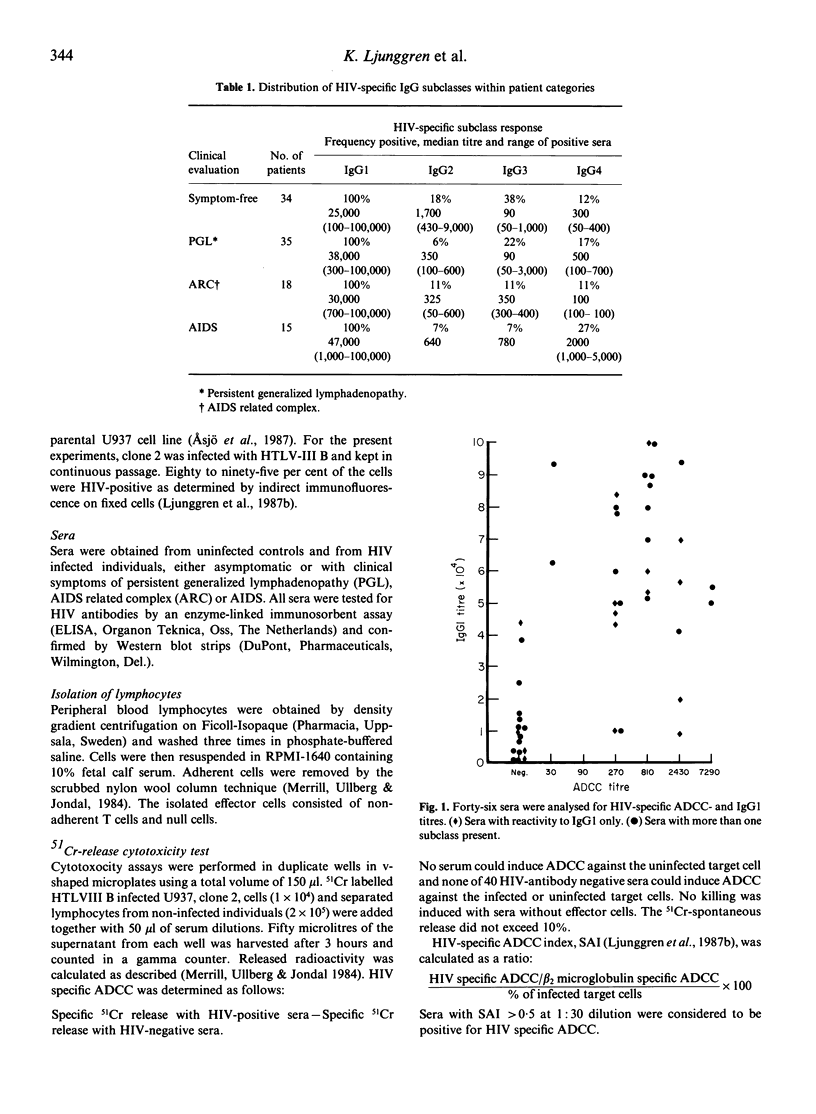
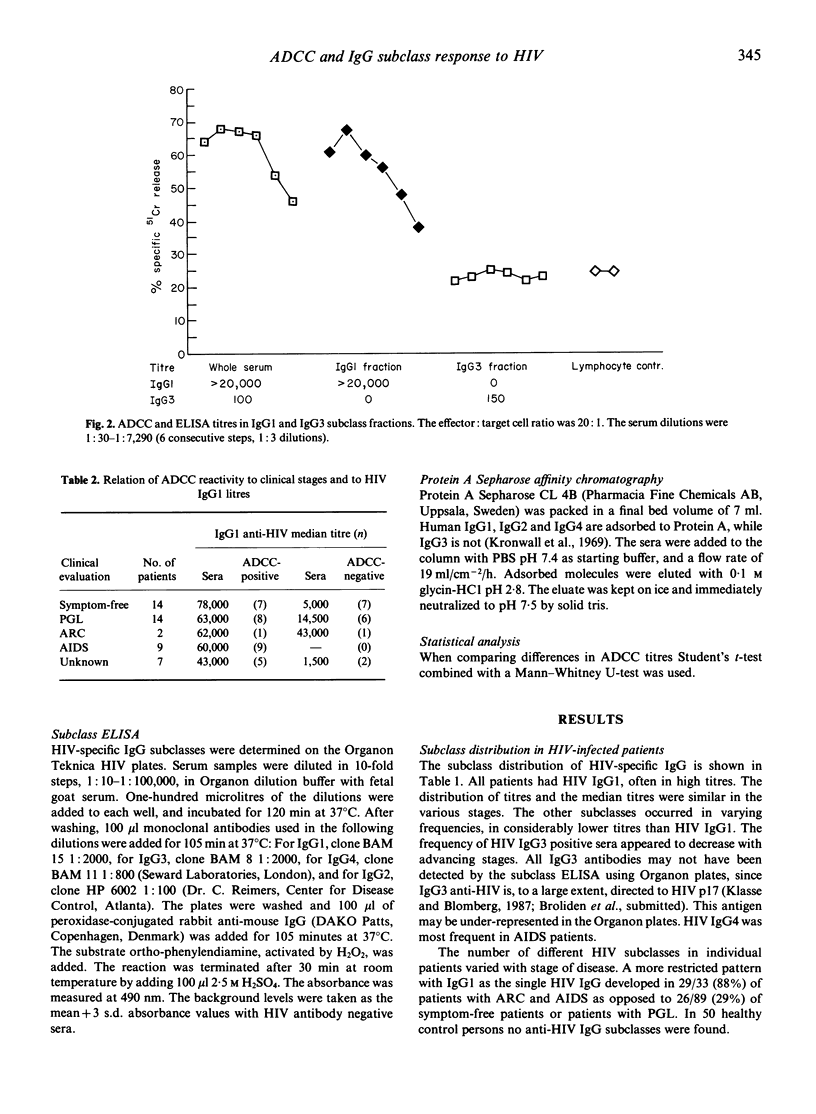
The anti-HIV IgG subclass response was analysed in sera from different clinical stages and related to virus specific antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). IgG1 was found to be the dominant subclass, present in all sera and with similar mean titres at different stages. The number of anti-HIV IgG3 positive sera, measured on whole viral lysate antigen plates, decreased during disease progression from 38% in symptom-free to 7% in AIDS patients. IgG2 and IgG4 subclasses were less prevalent although a slight increase of IgG4 frequency was found in AIDS patients. High IgG1 titres correlated with a positive ADCC reaction but there was no correlation between anti-HIV IgG1 and ADCC titres. Some sera which contained HIV IgG1 as the only subclass were able to mediate an ADCC reaction. In addition, when anti-HIV IgG3 was isolated, by protein A chromatography, no ADCC killing was induced by these antibodies. It is concluded that IgG1 is the major ADCC-active IgG subclass in HIV infected individuals. The lack of correlation between IgG1 and ADCC titres may be explained by a relatively small fraction of IgG1 antibodies mediating ADCC.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agius M. A., Geannopoulos C. J., Fairclough R. H., Richman D. P. Monoclonal anti-idiotopic antibodies against myasthenia-inducing anti-acetylcholine receptor monoclonal antibodies. Preponderance of nonparatope-directed antibodies affecting antigen binding. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 1;140(1):62–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammann A. J., Abrams D., Conant M., Chudwin D., Cowan M., Volberding P., Lewis B., Casavant C. Acquired immune dysfunction in homosexual men: immunologic profiles. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1983 Jun;27(3):315–325. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(83)90084-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asjö B., Ivhed I., Gidlund M., Fuerstenberg S., Fenyö E. M., Nilsson K., Wigzell H. Susceptibility to infection by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) correlates with T4 expression in a parental monocytoid cell line and its subclones. Virology. 1987 Apr;157(2):359–365. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90278-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aucouturier P., Couderc L. J., Gouet D., Danon F., Gombert J., Matheron S., Saimot A. G., Clauvel J. P., Preud'homme J. L. Serum immunoglobulin G subclass dysbalances in the lymphadenopathy syndrome and acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Jan;63(1):234–240. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chess Q., Daniels J., North E., Macris N. T. Serum immunoglobulin elevations in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS): IgG, IgA, IgM, and IgD. Diagn Immunol. 1984;2(3):148–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Sadr W., Stahl R., Sidhu G., Zolla-Pazner S. The acquired immune deficiency syndrome: laboratory findings, clinical features, and leading hypotheses. Diagn Immunol. 1984;2(2):73–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff W. L., Wagner G. G., Craig T. M., Long R. F. The role of specific immunoglobulins in antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity assays during Babesia bovis infection. Vet Parasitol. 1984 Mar;14(2):117–128. doi: 10.1016/0304-4017(84)90118-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klasse J., Blomberg J. Patterns of antibodies to human immunodeficiency virus proteins in different subclasses of IgG. J Infect Dis. 1987 Dec;156(6):1026–1030. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.6.1026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Williams R. C., Jr Differences in anti-protein A activity among IgG subgroups. J Immunol. 1969 Oct;103(4):828–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane H. C., Masur H., Edgar L. C., Whalen G., Rook A. H., Fauci A. S. Abnormalities of B-cell activation and immunoregulation in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1983 Aug 25;309(8):453–458. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198308253090803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linde G. A. Subclass distribution of rubella virus-specific immunoglobulin G. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jan;21(1):117–121. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.1.117-121.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljunggren K., Böttiger B., Biberfeld G., Karlson A., Fenyö E. M., Jondal M. Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity-inducing antibodies against human immunodeficiency virus. Presence at different clinical stages. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 1;139(7):2263–2267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill J. E., Ullberg M., Jondal M. Influence of IgG and IgM receptor triggering on human natural killer cell cytotoxicity measured on the level of the single effector cell. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Jul;11(7):536–541. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby E., Biberfeld G., Chiodi F., von Gegerfeldt A., Nauclér A., Parks E., Lerner R. Discrimination between antibodies to HIV and to related retroviruses using site-directed serology. Nature. 1987 Sep 17;329(6136):248–250. doi: 10.1038/329248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riesen W. F., Skvaril F., Braun D. G. Natural infection of man with group A streptococci. Levels; restriction in class, subclass, and type; and clonal appearance of polysaccharide-group-specific antibodies. Scand J Immunol. 1976;5(4):383–390. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1976.tb00292.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rook A. H., Lane H. C., Folks T., McCoy S., Alter H., Fauci A. S. Sera from HTLV-III/LAV antibody-positive individuals mediate antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity against HTLV-III/LAV-infected T cells. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 15;138(4):1064–1067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumaker V. N., Calcott M. A., Spiegelberg H. L., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Ultracentifuge studies of the binding of IgG of different subclasses to the Clq subunit of the first component of complement. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 16;15(23):5175–5181. doi: 10.1021/bi00668a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligmann M., Chess L., Fahey J. L., Fauci A. S., Lachmann P. J., L'Age-Stehr J., Ngu J., Pinching A. J., Rosen F. S., Spira T. J. AIDS--an immunologic reevaluation. N Engl J Med. 1984 Nov 15;311(20):1286–1292. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198411153112005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligmann M., Pinching A. J., Rosen F. S., Fahey J. L., Khaitov R. M., Klatzmann D., Koenig S., Luo N., Ngu J., Riethmüller G. Immunology of human immunodeficiency virus infection and the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. An update. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Aug;107(2):234–242. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-107-2-234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl R. E., Friedman-Kien A., Dubin R., Marmor M., Zolla-Pazner S. Immunologic abnormalities in homosexual men. Relationship to Kaposi's sarcoma. Am J Med. 1982 Aug;73(2):171–178. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90174-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starcich B. R., Hahn B. H., Shaw G. M., McNeely P. D., Modrow S., Wolf H., Parks E. S., Parks W. P., Josephs S. F., Gallo R. C. Identification and characterization of conserved and variable regions in the envelope gene of HTLV-III/LAV, the retrovirus of AIDS. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):637–648. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90778-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundqvist V. A., Linde A., Kurth R., Werner A., Helm E. B., Popovic M., Gallo R. C., Wahren B. Restricted IgG subclass responses to HTLV-III/LAV and to cytomegalovirus in patients with AIDS and lymphadenopathy syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1986 May;153(5):970–973. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.5.970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundqvist V. A., Linde A., Wahren B. Virus-specific immunoglobulin G subclasses in herpes simplex and varicella-zoster virus infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jul;20(1):94–98. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.1.94-98.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundström C., Nilsson K. Establishment and characterization of a human histiocytic lymphoma cell line (U-937). Int J Cancer. 1976 May 15;17(5):565–577. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urbaniak S. J., Greiss M. A. ADCC (K-cell) lysis of human erythrocytes sensitized with rhesus alloantibodies. III. Comparison of IgG anti-D agglutinating and lytic (ADCC) activity and the role of IgG subclasses. Br J Haematol. 1980 Nov;46(3):447–453. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1980.tb05992.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


