Abstract
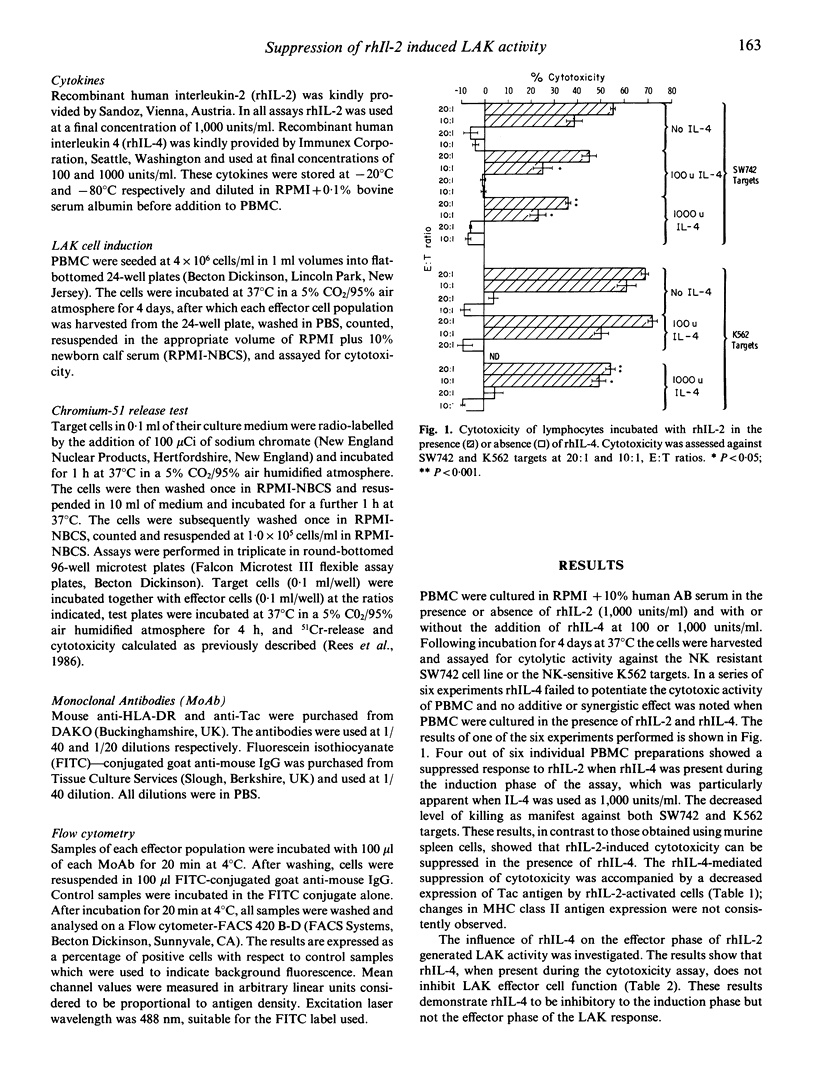
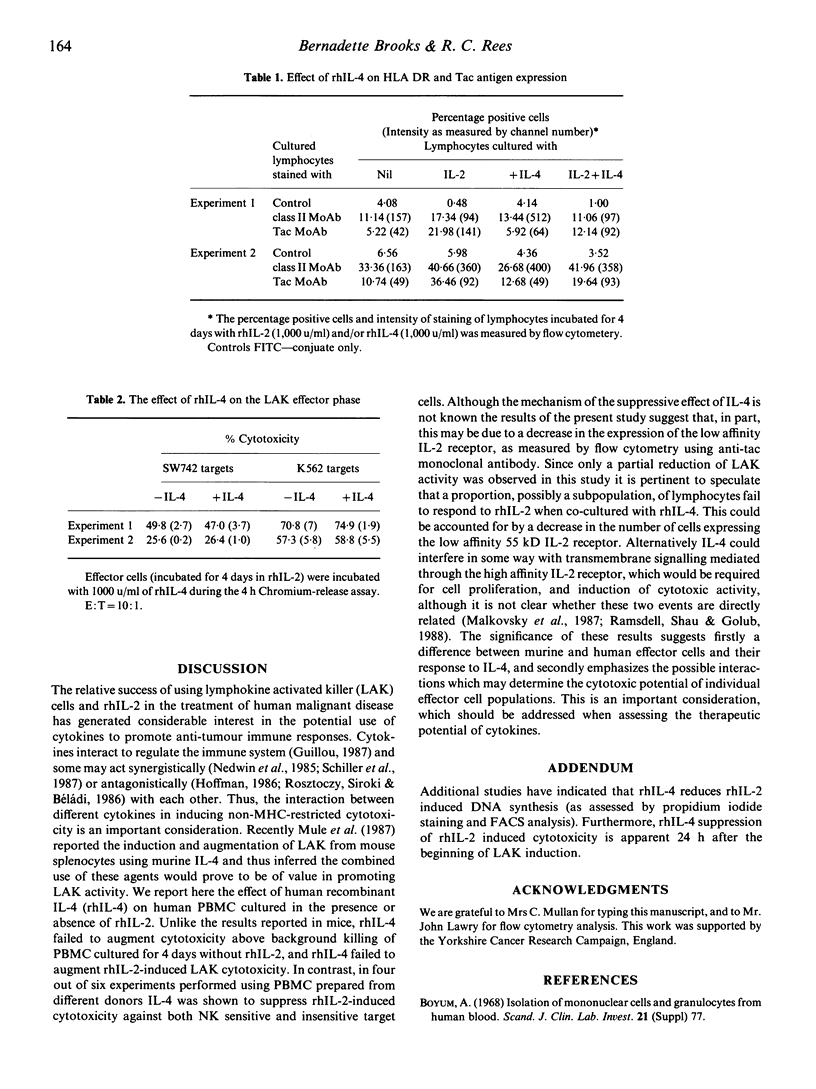
The effect of recombinant human interleukin 4 (rhIL-4) on the induction in vitro of human lymphokine activated killer cell (LAK) activity was investigated. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from normal healthy donors were incubated for 4 days with or without recombinant human interleukin-2 (rhIL-2) in the presence or absence of rhIL-4. LAK activity was measured against the NK-resistant colon adenocarcinoma cell line SW742, and NK mediated cytotoxicity was determined using NK sensitive K562 cells. Unlike previous reports using mouse effector cells, rhIL-4 neither induced LAK activity nor augmented the cytotoxic response induced by rhIL-2. In four out of six experiments there was a significant reduction of rhIL-2 induced LAK in the presence of rhIL-4, accompanied by a reduction of Tac antigen expression by rhIL-2 activated cells. Recombinant hIL-4 failed to influence the effector phase of the activated PBMC against SW742 or K562 targets.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Damle N. K., Doyle L. V., Bradley E. C. Interleukin 2-activated human killer cells are derived from phenotypically heterogeneous precursors. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 1;137(9):2814–2822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm E. A., Mazumder A., Zhang H. Z., Rosenberg S. A. Lymphokine-activated killer cell phenomenon. Lysis of natural killer-resistant fresh solid tumor cells by interleukin 2-activated autologous human peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1982 Jun 1;155(6):1823–1841. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.6.1823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillou P. J. Potential impact of immunobiotechnology on cancer therapy. Br J Surg. 1987 Aug;74(8):705–710. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800740820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman M. K. The effects of tumor necrosis factor on the production of interleukin-1 by macrophages. Lymphokine Res. 1986 Fall;5(4):255–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibovitz A., Stinson J. C., McCombs W. B., 3rd, McCoy C. E., Mazur K. C., Mabry N. D. Classification of human colorectal adenocarcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1976 Dec;36(12):4562–4569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozzio C. B., Lozzio B. B. Human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell-line with positive Philadelphia chromosome. Blood. 1975 Mar;45(3):321–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkovský M., Jíra M., Madar J., Malkovska V., Loveland B., Asherson G. L. Generation of lymphokine-activated killer cells does not require DNA synthesis. Immunology. 1987 Mar;60(3):471–473. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mingari M. C., Pende D., Cozzani R., Merli A., Poggi A., Ferrini S., Moretta L. Both the precursors and the effectors of human lymphokine-activated killer (LAK) cells may belong to T lymphocytes. Ric Clin Lab. 1986 Jul-Sep;16(3):437–441. doi: 10.1007/BF02886738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulé J. J., Smith C. A., Rosenberg S. A. Interleukin 4 (B cell stimulatory factor 1) can mediate the induction of lymphokine-activated killer cell activity directed against fresh tumor cells. J Exp Med. 1987 Sep 1;166(3):792–797. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.3.792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nedwin G. E., Svedersky L. P., Bringman T. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, Goeddel D. V. Effect of interleukin 2, interferon-gamma, and mitogens on the production of tumor necrosis factors alpha and beta. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2492–2497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortaldo J. R., Mason A., Overton R. Lymphokine-activated killer cells. Analysis of progenitors and effectors. J Exp Med. 1986 Oct 1;164(4):1193–1205. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.4.1193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsdell F. J., Shau H., Golub S. H. Role of proliferation in LAK cell development. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1988;26(2):139–144. doi: 10.1007/BF00205607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A. Immunotherapy of cancer using interleukin 2: current status and future prospects. Immunol Today. 1988 Feb;9(2):58–62. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91261-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Lotze M. T., Muul L. M., Leitman S., Chang A. E., Ettinghausen S. E., Matory Y. L., Skibber J. M., Shiloni E., Vetto J. T. Observations on the systemic administration of autologous lymphokine-activated killer cells and recombinant interleukin-2 to patients with metastatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 5;313(23):1485–1492. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512053132327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosztóczy I., Siroki O., Béládi I. Effects of interferons-alpha, -beta, and -gamma on human interleukin-2 production. J Interferon Res. 1986 Oct;6(5):581–589. doi: 10.1089/jir.1986.6.581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousset F., Malefijt R. W., Slierendregt B., Aubry J. P., Bonnefoy J. Y., Defrance T., Banchereau J., de Vries J. E. Regulation of Fc receptor for IgE (CD23) and class II MHC antigen expression on Burkitt's lymphoma cell lines by human IL-4 and IFN-gamma. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 15;140(8):2625–2632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller J. H., Bittner G., Storer B., Willson J. K. Synergistic antitumor effects of tumor necrosis factor and gamma-interferon on human colon carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1987 Jun 1;47(11):2809–2813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spits H., Yssel H., Takebe Y., Arai N., Yokota T., Lee F., Arai K., Banchereau J., de Vries J. E. Recombinant interleukin 4 promotes the growth of human T cells. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 15;139(4):1142–1147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilden A. B., Itoh K., Balch C. M. Human lymphokine-activated killer (LAK) cells: identification of two types of effector cells. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 15;138(4):1068–1073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota T., Otsuka T., Mosmann T., Banchereau J., DeFrance T., Blanchard D., De Vries J. E., Lee F., Arai K. Isolation and characterization of a human interleukin cDNA clone, homologous to mouse B-cell stimulatory factor 1, that expresses B-cell- and T-cell-stimulating activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5894–5898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



