Abstract
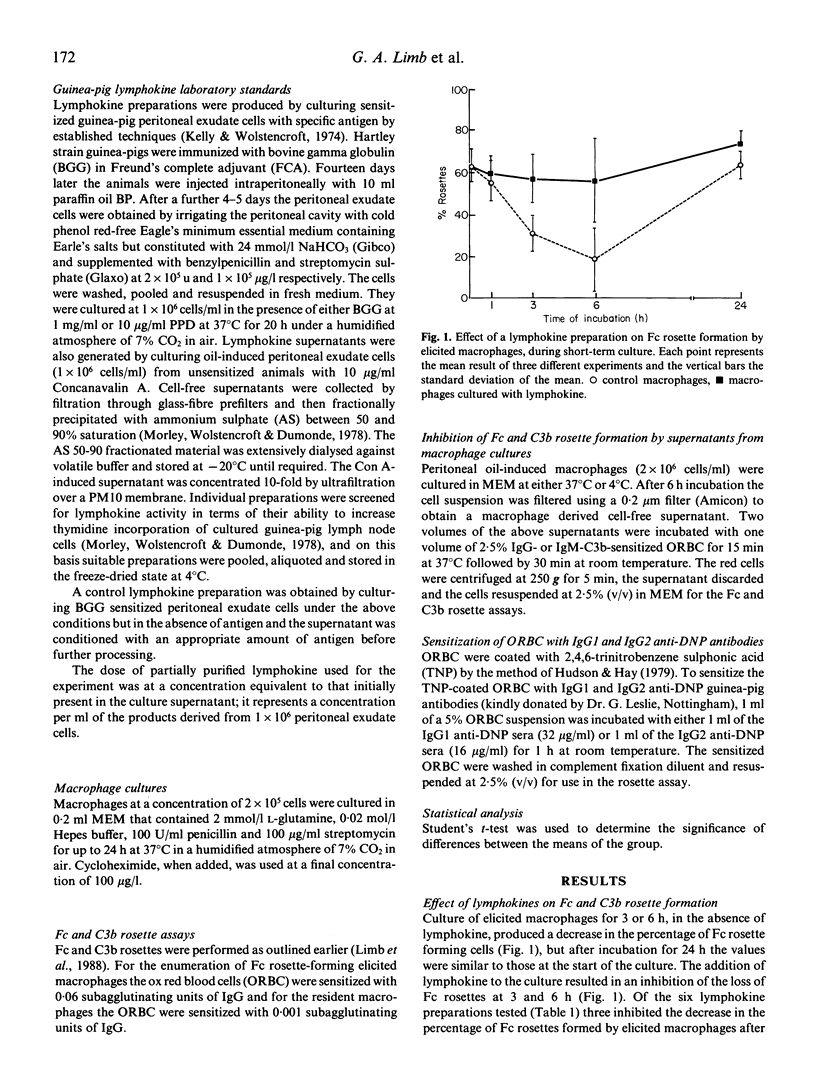
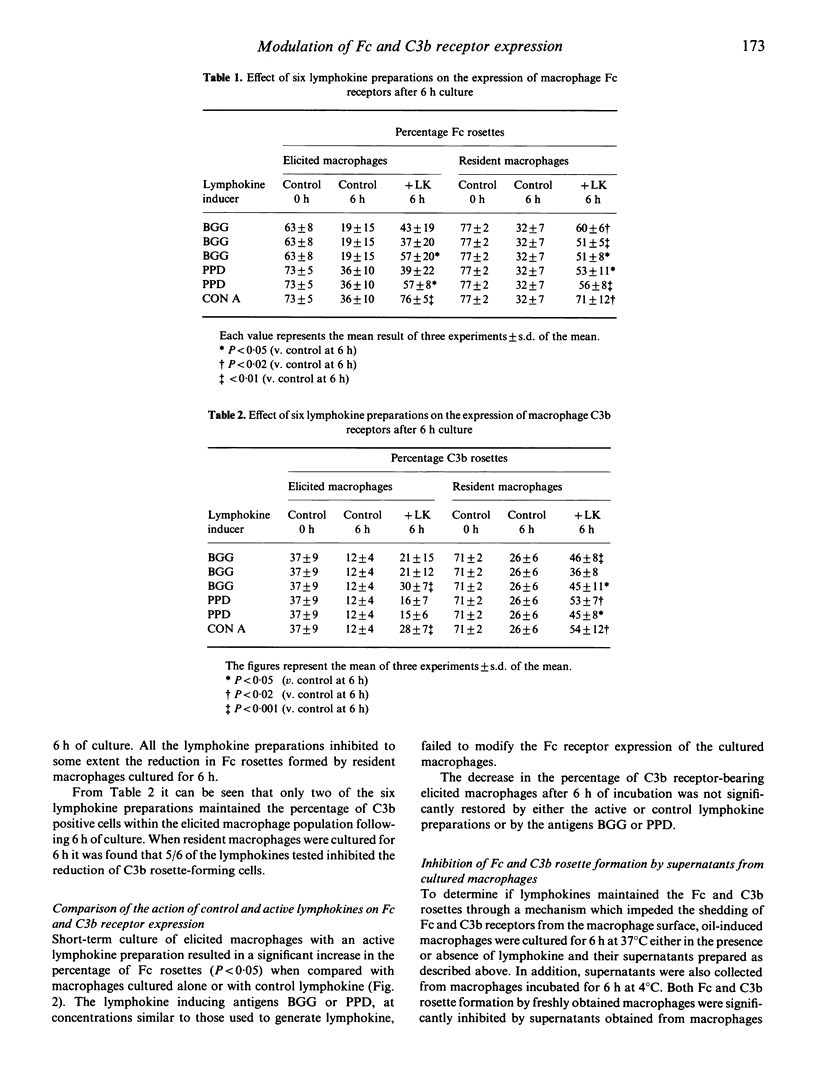
The decrease in Fc-receptor-positive cells that occurred during a 6 h incubation of resident and elicited guinea-pig macrophages was partly abrogated when lymphokines were present in the culture. When the same lymphokine preparations were tested on C3b receptor-expression they preferentially sustained the percentage of C3b rosettes formed by resident rather than elicited macrophages. This lymphokine-induced maintenance of Fc and C3b rosettes by cultured macrophages may have been due to an inhibition of receptor release or an increase in receptor synthesis. Supernatants from cultured macrophages contain shed Fc and C3b receptors which inhibit rosette formation by other macrophages. From the demonstration that culture supernatants from both lymphokine-treated and untreated macrophages significantly inhibited Fc and C3b rosette formation by freshly obtained macrophages it seems that the shedding of Fc and C3b receptors is not modified by lymphokines. The maintenance of Fc and C3b rosettes by lymphokines was inhibited by treatment of the macrophages with cycloheximide, suggesting that the lymphokine effect was due to an increase in synthesis de novo of the Fc and C3b receptors. The lymphokine-inducing antigens, BGG and PPD, and control lymphokine preparations were devoid of receptor modifying activity. The reduction in the percentage of Fc rosettes after 6 h culture appears to be due to a loss of Fc receptors for IgG1. Although lymphokines partly inhibited this effect they could not prevent the loss of these receptors following 24 h culture, unlike their action in augmenting the expression of Fc receptors for IgG2. These findings suggest that a selective enhancement of Fc receptor synthesis by lymphokines may modify the functional activities of macrophages.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arend W. P., Ammons J. T., Kotzin B. L. Lipopolysaccharide and interleukin 1 inhibit interferon-gamma-induced Fc receptor expression on human monocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):1873–1879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohnsack J. F., Kleinman H. K., Takahashi T., O'Shea J. J., Brown E. J. Connective tissue proteins and phagocytic cell function. Laminin enhances complement and Fc-mediated phagocytosis by cultured human macrophages. J Exp Med. 1985 May 1;161(5):912–923. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.5.912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman D. L., Culver K. E., Ryan J. L. Enhancement of macrophage immune and nonimmune receptor-mediated phagocytosis by a low molecular weight soluble factor from resident thymocytes. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):3121–3127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford R. M., Finbloom D. S., Ohara J., Paul W. E., Meltzer M. S. B cell stimulatory factor-1 (interleukin 4) activates macrophages for increased tumoricidal activity and expression of Ia antigens. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 1;139(1):135–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezekowitz R. A., Bampton M., Gordon S. Macrophage activation selectively enhances expression of Fc receptors for IgG2a. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):807–812. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fóris G., Hauck M., Dezsö B., Medgyesi G. A., Füst G. Effect of low-molecular-weight lymphokine components on the Fc and C3b receptor-mediated macrophage functions. Cell Immunol. 1983 Jun;78(2):276–284. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(83)90282-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey H. P., Purohit A. Characterization of a guinea-pig lymphokine, macrophage agglutination factor. Immunology. 1982 Jul;46(3):507–513. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresham H. D., Clement L. T., Lehmeyer J. E., Griffin F. M., Jr, Volanakis J. E. Stimulation of human neutrophil Fc receptor-mediated phagocytosis by a low molecular weight cytokine. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 1;137(3):868–875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyre P. M., Crabtree G. R., Bodwell J. E., Munck A. MLC-conditioned media stimulate an increase in Fc receptors on human macrophages. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):666–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyre P. M., Morganelli P. M., Miller R. Recombinant immune interferon increases immunoglobulin G Fc receptors on cultured human mononuclear phagocytes. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):393–397. doi: 10.1172/JCI110980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. H., Wolstencroft R. A. Germinal centre proliferation in response to mitogenic lymphokines. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Nov;18(3):321–336. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larrick J. W., Fischer D. G., Anderson S. J., Koren H. S. Characterization of a human macrophage-like cell line stimulated in vitro: a model of macrophage functions. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):6–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limb G. A., Brown K. A., Wolstencroft R. A., Dumonde D. C. Shedding and synthesis de novo of Fc and C3b receptors by cultured guinea-pig macrophages. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Feb;71(2):362–367. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Najjar V. A., Nishioka K. "Tuftsin": a natural phagocytosis stimulating peptide. Nature. 1970 Nov 14;228(5272):672–673. doi: 10.1038/228672a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pommier C. G., Inada S., Fries L. F., Takahashi T., Frank M. M., Brown E. J. Plasma fibronectin enhances phagocytosis of opsonized particles by human peripheral blood monocytes. J Exp Med. 1983 Jun 1;157(6):1844–1854. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.6.1844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama N., Tamoto K., Koyama J. Evidence for two distinct Fc receptors on guinea pig peritoneal macrophages. Mol Immunol. 1981 Nov;18(11):999–1005. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(81)90118-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G., Kobayashi M., Rosen M., Loudon R., Murphy M., Perussia B. Tumor necrosis factor and lymphotoxin induce differentiation of human myeloid cell lines in synergy with immune interferon. J Exp Med. 1986 Oct 1;164(4):1206–1225. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.4.1206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel S. N., Finbloom D. S., English K. E., Rosenstreich D. L., Langreth S. G. Interferon-induced enhancement of macrophage Fc receptor expression: beta-interferon treatment of C3H/HeJ macrophages results in increased numbers and density of Fc receptors. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1210–1214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel S. N., Rosenstreich D. L. Defective Fc receptor-mediated phagocytosis in C3H/HeJ macrophages. I. Correction by lymphokine-induced stimulation. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2842–2850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel S. N., Weedon L. L., Oppenheim J. J., Rosenstreich D. L. Defective Fc-mediated phagocytosis in C3H/HeJ macrophages. II. Correction by cAMP agonists. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):441–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancey K. B., O'Shea J., Chused T., Brown E., Takahashi T., Frank M. M., Lawley T. J. Human C5a modulates monocyte Fc and C3 receptor expression. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):465–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


